เนื้อหาของรายวิชา 2304104 GEN PHYS II
... Coulomb’s law Electric field Gauss’ law The electric potential Electric field and electric potential due to continuous charge distribution and dipole Calculating the field from the potential Capacitance and Dielectric Electric current and electromotive force Conductivity of materia ...
... Coulomb’s law Electric field Gauss’ law The electric potential Electric field and electric potential due to continuous charge distribution and dipole Calculating the field from the potential Capacitance and Dielectric Electric current and electromotive force Conductivity of materia ...
N - PembyPhysics
... thin isolated laminations or sheets. The laminations minimize eddy currents in the iron. Eddy currents are circulatory currents induced in the metal by the changing magnetic field. These currents produce an undesirable by-product—heat in the iron. Energy loss in a transformer can be reduced by using ...
... thin isolated laminations or sheets. The laminations minimize eddy currents in the iron. Eddy currents are circulatory currents induced in the metal by the changing magnetic field. These currents produce an undesirable by-product—heat in the iron. Energy loss in a transformer can be reduced by using ...
modello di descrizione delle singole attivita`formative
... conductors; electric potential and potential energy; capacitors; energy density of the electric field; D field. Electric current: electromotive force; Ohm, Joule, Kirchhoff’s laws. Magnetism: magnets and magnetic dipoles; Lorenz force; Ampère’s equivalence principle; 1st and 2nd Laplace formula; Amp ...
... conductors; electric potential and potential energy; capacitors; energy density of the electric field; D field. Electric current: electromotive force; Ohm, Joule, Kirchhoff’s laws. Magnetism: magnets and magnetic dipoles; Lorenz force; Ampère’s equivalence principle; 1st and 2nd Laplace formula; Amp ...
Notes: Magnetism
... Force of attraction or repulsion between various substances, especially those made of iron, nickel and cobalt; it is due to the motion of electric charges" Magnetic Field What is it? ...
... Force of attraction or repulsion between various substances, especially those made of iron, nickel and cobalt; it is due to the motion of electric charges" Magnetic Field What is it? ...
Course Syllabus
... Electric current in gaseous media. Plasma. Thermoelectric emission and thermoelectric phenomena. Magnetic interaction of currents. Ampere force. Magnetic field and its characteristics. Lorentz force. Magnetic field of current-carrying cunductor. Biot-Savart law and its application. Magnetic moment o ...
... Electric current in gaseous media. Plasma. Thermoelectric emission and thermoelectric phenomena. Magnetic interaction of currents. Ampere force. Magnetic field and its characteristics. Lorentz force. Magnetic field of current-carrying cunductor. Biot-Savart law and its application. Magnetic moment o ...
Magnets and Electromagnets
... Magnetic Forces Magnetic Poles: Points on a magnet that have opposite magnetic properties. (north and south) Poles are always in pairs Magnetic forces: force of attraction or repulsion ...
... Magnetic Forces Magnetic Poles: Points on a magnet that have opposite magnetic properties. (north and south) Poles are always in pairs Magnetic forces: force of attraction or repulsion ...
PPT - Mr.E Science
... At the atomic level, there are protons (+ charge) & neutrons (neutral charge) in the nucleus, and electrons (- charge) spinning in orbits around the nucleus. The moving electron acts as a mini electrical charge and therefore has a magnetic field associated w/ it. In ferrous materials clusters of ato ...
... At the atomic level, there are protons (+ charge) & neutrons (neutral charge) in the nucleus, and electrons (- charge) spinning in orbits around the nucleus. The moving electron acts as a mini electrical charge and therefore has a magnetic field associated w/ it. In ferrous materials clusters of ato ...
what is a manget17213
... they hung these stones from a string, one end of the stone pointed north. These stones were called lodestones, or "leading stones". They could be used to lead people in the direction they wanted to go. The lodestones are a type of rock called magnetite. Magnetite is naturally magnetic. When a rock i ...
... they hung these stones from a string, one end of the stone pointed north. These stones were called lodestones, or "leading stones". They could be used to lead people in the direction they wanted to go. The lodestones are a type of rock called magnetite. Magnetite is naturally magnetic. When a rock i ...
1818 ACC Chemistry
... Where q is the charge, v is the speed of the charge, B is the magnetic flux density, and is the angle between the direction of the charge and the direction of the magnetic field. ...
... Where q is the charge, v is the speed of the charge, B is the magnetic flux density, and is the angle between the direction of the charge and the direction of the magnetic field. ...
Magnetic Field Lines
... current-carrying wire so that the field encircles the wire. Right-Hand Grip Rule: Imagine that you grab the wire with your right hand so that your thumb points in the direction of the current (I), your fingers will then point in the direction of the magnetic field lines (B) induced by the current. N ...
... current-carrying wire so that the field encircles the wire. Right-Hand Grip Rule: Imagine that you grab the wire with your right hand so that your thumb points in the direction of the current (I), your fingers will then point in the direction of the magnetic field lines (B) induced by the current. N ...
Practice Sheet #24
... Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank. ...
... Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank. ...
Magnetism
... • Used to find the direction of the FORCE acting on a current carrying wire in a magnetic field • Using the right hand – Point your thumb in the direction of the conventional current and your index finger in the direction of magnetic field. The force will be in a direction OUT of your palm. ...
... • Used to find the direction of the FORCE acting on a current carrying wire in a magnetic field • Using the right hand – Point your thumb in the direction of the conventional current and your index finger in the direction of magnetic field. The force will be in a direction OUT of your palm. ...
Electromagnetics I Course Syllabus, spring 2008
... Office Hours: T-Th: 4-5 pm; Mon-Wed: 12:30-1:30 pm Designation: Required core course for electrical engineering/ communication major. University Bulletin Description: Static electric and magnetic fields, solutions to static field problems, Maxwell’s equations, electromagnetic waves, boundary conditi ...
... Office Hours: T-Th: 4-5 pm; Mon-Wed: 12:30-1:30 pm Designation: Required core course for electrical engineering/ communication major. University Bulletin Description: Static electric and magnetic fields, solutions to static field problems, Maxwell’s equations, electromagnetic waves, boundary conditi ...
Even if the forces acting on a body are balanced in
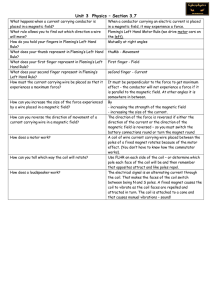
... When a conductor carrying an electric current is placed in a magnetic field, it may experience a force. Fleming’s Left Hand Motor Rule (we drive motor cars on the left). Mutually at right angles thuMb - Movement First finger - Field seCond finger - Current It must be perpendicular to the force to ge ...
... When a conductor carrying an electric current is placed in a magnetic field, it may experience a force. Fleming’s Left Hand Motor Rule (we drive motor cars on the left). Mutually at right angles thuMb - Movement First finger - Field seCond finger - Current It must be perpendicular to the force to ge ...