Chapter 28: Sources of Magnetic Field
... Now consider all of the points which are a distance R from the wire. They form a circle of circumference 2R. Now we evaluate the closed loop integral at this point. ...
... Now consider all of the points which are a distance R from the wire. They form a circle of circumference 2R. Now we evaluate the closed loop integral at this point. ...
Faraday Inquiry Problems File
... flow of electrons. Predict what you think will happen if a magnet approaches a wire loop. Will the movement of electrons producing the same magnetic field be encouraged or discouraged? Will the movement of electrons producing the opposite magnetic field be encouraged or discouraged? ...
... flow of electrons. Predict what you think will happen if a magnet approaches a wire loop. Will the movement of electrons producing the same magnetic field be encouraged or discouraged? Will the movement of electrons producing the opposite magnetic field be encouraged or discouraged? ...
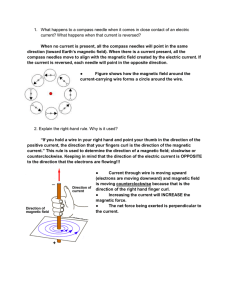
When no current is present, all the compass
... loop of wire adds to the strength of the magnetic field of any neighboring loops. Thus creating a stronger magnetic field, similar to a bar magnet. ● More loops and a stronger current will create a stronger magnetic field. ...
... loop of wire adds to the strength of the magnetic field of any neighboring loops. Thus creating a stronger magnetic field, similar to a bar magnet. ● More loops and a stronger current will create a stronger magnetic field. ...
Transformers and Generators - juan
... • A transformer can change electrical energy of a given voltage into electrical energy at a different voltage level. • It consists of two coils arranged in such a way that the magnetic field surrounding one coil cuts through the other coil. When an alternating voltage is applied to one coil, the var ...
... • A transformer can change electrical energy of a given voltage into electrical energy at a different voltage level. • It consists of two coils arranged in such a way that the magnetic field surrounding one coil cuts through the other coil. When an alternating voltage is applied to one coil, the var ...
Magnetic Fields
... 1. How do the magnetic field lines of two bar magnets compare to the electric field lines of an electronic dipole when the poles of the magnets facing each other are not alike? Make sure you are descriptive in your comparison. See Drawing #3. Incorporate a comparative sketch to support your statemen ...
... 1. How do the magnetic field lines of two bar magnets compare to the electric field lines of an electronic dipole when the poles of the magnets facing each other are not alike? Make sure you are descriptive in your comparison. See Drawing #3. Incorporate a comparative sketch to support your statemen ...
suggested contents (prof. Bury)
... - The flow of charge - Resistance and Ohm`s law - Resistors in series and paralel - Drude model of a metal - Conduction in semiconductors 6. Energy and current in Dc circuits - EMF and internal resistance of a battery - Electric energy and power - Kirchhoff`s rules - Rc circuits ...
... - The flow of charge - Resistance and Ohm`s law - Resistors in series and paralel - Drude model of a metal - Conduction in semiconductors 6. Energy and current in Dc circuits - EMF and internal resistance of a battery - Electric energy and power - Kirchhoff`s rules - Rc circuits ...
Do now! - MrSimonPorter
... 4. When a magnetic material is close to a magnet, it becomes a magnet itself. 5. Iron is a SOFT magnetic material;it is easily magnetised but easily loses its magnetism. 6. Steel is a HARD magnetic material; it is hard to magnetise but keeps its magnetism. 7. The magnetic field around a bar magnet i ...
... 4. When a magnetic material is close to a magnet, it becomes a magnet itself. 5. Iron is a SOFT magnetic material;it is easily magnetised but easily loses its magnetism. 6. Steel is a HARD magnetic material; it is hard to magnetise but keeps its magnetism. 7. The magnetic field around a bar magnet i ...
Magnetism - TeacherWeb
... The direction the north pole of a compass would point when placed at that location ...
... The direction the north pole of a compass would point when placed at that location ...
CHAPTER 3 QUIZ – ELECTROMAGNETISM
... An ELECTROMAGNET is a solenoid with iron in the middle of it. An instrument used to detect small currents is called a GALVANOMETER. OERSTED found that an electric current created a magnetic field. A long coil of wire with many loops is called a SOLENOID. ELECTROMAGNETISM is the relationship between ...
... An ELECTROMAGNET is a solenoid with iron in the middle of it. An instrument used to detect small currents is called a GALVANOMETER. OERSTED found that an electric current created a magnetic field. A long coil of wire with many loops is called a SOLENOID. ELECTROMAGNETISM is the relationship between ...
Q.5. What is a magnetic field?
... Q.24. Which device is used for converting electrical energy to mechanical energy? Q.25. What is Alnico? Q.26. When does the direction of induced current in an AC generator changes? Q.27. What is an electromagnet? Q.28. Which scientist suggested that the magnet must also exert an equal and opposite ...
... Q.24. Which device is used for converting electrical energy to mechanical energy? Q.25. What is Alnico? Q.26. When does the direction of induced current in an AC generator changes? Q.27. What is an electromagnet? Q.28. Which scientist suggested that the magnet must also exert an equal and opposite ...
lecture11
... 1. Electromagnetism in the laboratory and around us 2. Electromagnetism is simple. (If you know what it is!) •It is about: q - electric charges (magnetic charges do not exist) F - electromagnetic forces E - electric fields B - magnetic fields •The two most important questions: (1) How to find the fo ...
... 1. Electromagnetism in the laboratory and around us 2. Electromagnetism is simple. (If you know what it is!) •It is about: q - electric charges (magnetic charges do not exist) F - electromagnetic forces E - electric fields B - magnetic fields •The two most important questions: (1) How to find the fo ...