are conductors (metals). Insulators (rubber,
... determine the strength of an electromagnet. (The manipulated variable could be the number of coils of wire and the responding variable could be the number of paperclips the magnet can attract.) ...
... determine the strength of an electromagnet. (The manipulated variable could be the number of coils of wire and the responding variable could be the number of paperclips the magnet can attract.) ...
Electricity and Magnetism Study Guide - Mr. L`s Room
... (3) Induction—transfer of electrons without direct contact to one part of an object that is caused by the electric field of a second object (negative charge in a person’s fingertip produces an electric field that repels the electrons on the doorknob, so the doorknob becomes positively charged and ZA ...
... (3) Induction—transfer of electrons without direct contact to one part of an object that is caused by the electric field of a second object (negative charge in a person’s fingertip produces an electric field that repels the electrons on the doorknob, so the doorknob becomes positively charged and ZA ...
Non-KAM dynamical chaos in semiconductor superlattices Arkadii Krokhin, UNT
... I will present our new results concerning electron dynamics in semiconductor superlattices in the presence of non-parallel electric and magnetic field. In this geometry the electrons in the superlattice miniband turn out to form a non-KAM dynamical system that exhibits a non-traditional chaotic beha ...
... I will present our new results concerning electron dynamics in semiconductor superlattices in the presence of non-parallel electric and magnetic field. In this geometry the electrons in the superlattice miniband turn out to form a non-KAM dynamical system that exhibits a non-traditional chaotic beha ...
Cathode ray deflection tube
... A bar magnet can now be held at the side of the tube and you will see that the beam of electrons is deflected up or down depending which way round you hold the magnet. The same thing will happen of course if you use an electromagnet (see Figure 3). Magnetic field at right angles to the paper ...
... A bar magnet can now be held at the side of the tube and you will see that the beam of electrons is deflected up or down depending which way round you hold the magnet. The same thing will happen of course if you use an electromagnet (see Figure 3). Magnetic field at right angles to the paper ...
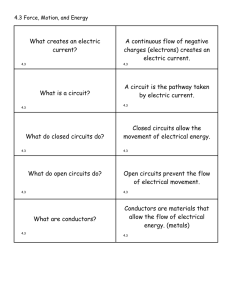
What creates an electric current
... Static electricity is created when certain materials are rubbed together. ...
... Static electricity is created when certain materials are rubbed together. ...
Electric current
An electric current is a flow of electric charge. In electric circuits this charge is often carried by moving electrons in a wire. It can also be carried by ions in an electrolyte, or by both ions and electrons such as in a plasma.The SI unit for measuring an electric current is the ampere, which is the flow of electric charge across a surface at the rate of one coulomb per second. Electric current is measured using a device called an ammeter.Electric currents cause Joule heating, which creates light in incandescent light bulbs. They also create magnetic fields, which are used in motors, inductors and generators.The particles that carry the charge in an electric current are called charge carriers. In metals, one or more electrons from each atom are loosely bound to the atom, and can move freely about within the metal. These conduction electrons are the charge carriers in metal conductors.