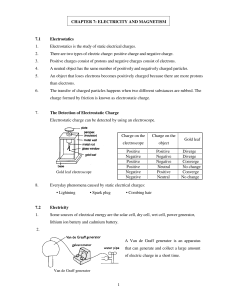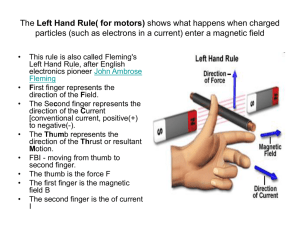
The Left Hand Rule - World of Teaching
... • An electric motor is a motor that uses electrical energy to produce mechanical energy, usually through the interaction of magnetic fields and currentcarrying conductors. • Electric motors are used in most, modern machines. Obvious uses would be in rotating machines such as fans, turbines, drills, ...
... • An electric motor is a motor that uses electrical energy to produce mechanical energy, usually through the interaction of magnetic fields and currentcarrying conductors. • Electric motors are used in most, modern machines. Obvious uses would be in rotating machines such as fans, turbines, drills, ...
Electricity - Petal School District
... build up of an electric charge on the surface of an object. The charge builds up but does not flow. Static electricity is potential energy. It does not move. It is stored. ...
... build up of an electric charge on the surface of an object. The charge builds up but does not flow. Static electricity is potential energy. It does not move. It is stored. ...
Vocabulary Terms
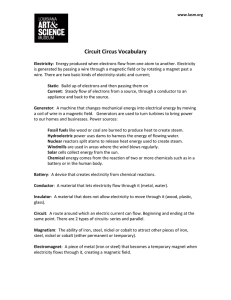
... Circuit Circus Vocabulary Electricity: Energy produced when electrons flow from one atom to another. Electricity is generated by passing a wire through a magnetic field or by rotating a magnet past a wire. There are two basic kinds of electricity-static and current; Static: Build up of electrons and ...
... Circuit Circus Vocabulary Electricity: Energy produced when electrons flow from one atom to another. Electricity is generated by passing a wire through a magnetic field or by rotating a magnet past a wire. There are two basic kinds of electricity-static and current; Static: Build up of electrons and ...
Engineering Electromagnetic
... In electrostatic fields, following principle are applicable to conductors: Within a Conductor, charge or change density(pv c/ m3) is zero and a surface charge density (ps c/m3) is present on the other surface of the conductor. ...
... In electrostatic fields, following principle are applicable to conductors: Within a Conductor, charge or change density(pv c/ m3) is zero and a surface charge density (ps c/m3) is present on the other surface of the conductor. ...
the electric force of a current: weber and the surface charge of
... moments? This is a significant piece of scholarship that penetrates into a rather common misconception, no force on a stationary charge outside a current carrying wire, to elucidate its cause of error and to present the correct and insightful picture of the phenomenon. No theory can survive without ...
... moments? This is a significant piece of scholarship that penetrates into a rather common misconception, no force on a stationary charge outside a current carrying wire, to elucidate its cause of error and to present the correct and insightful picture of the phenomenon. No theory can survive without ...
Electricity and Magnetism Review Name: Directions: Answer the
... 12. ___friction___ is the transfer of electrons by rubbing two objects together. 13. Alternating current is when electrons move back and forth as it flows. 14. A complete, closed path in which electrons only have one path to follow is called a ____series__ circuit. 15. ___conduction__ is the transfe ...
... 12. ___friction___ is the transfer of electrons by rubbing two objects together. 13. Alternating current is when electrons move back and forth as it flows. 14. A complete, closed path in which electrons only have one path to follow is called a ____series__ circuit. 15. ___conduction__ is the transfe ...
1 CHAPTER 7: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM 7.1
... Diverge Diverge Converge No change Converge No change ...
... Diverge Diverge Converge No change Converge No change ...
Physics 30 Concept Check 6 Concept: Calculate the electric
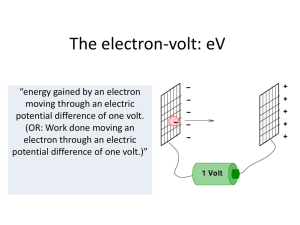
... If a particle is moved 3.0 cm perpendicular to two plates producing a uniform electric field of 10 000 N/C, what is the potential difference between the it’s starting position ...
... If a particle is moved 3.0 cm perpendicular to two plates producing a uniform electric field of 10 000 N/C, what is the potential difference between the it’s starting position ...
Electric current
An electric current is a flow of electric charge. In electric circuits this charge is often carried by moving electrons in a wire. It can also be carried by ions in an electrolyte, or by both ions and electrons such as in a plasma.The SI unit for measuring an electric current is the ampere, which is the flow of electric charge across a surface at the rate of one coulomb per second. Electric current is measured using a device called an ammeter.Electric currents cause Joule heating, which creates light in incandescent light bulbs. They also create magnetic fields, which are used in motors, inductors and generators.The particles that carry the charge in an electric current are called charge carriers. In metals, one or more electrons from each atom are loosely bound to the atom, and can move freely about within the metal. These conduction electrons are the charge carriers in metal conductors.