* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Left Hand Rule - World of Teaching
Magnetic nanoparticles wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Insulator (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Faraday paradox wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Induction motor wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electrical injury wikipedia , lookup
Scanning SQUID microscope wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
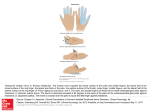
The Left Hand Rule( for motors) shows what happens when charged particles (such as electrons in a current) enter a magnetic field • • • • • • • • This rule is also called Fleming's Left Hand Rule, after English electronics pioneer John Ambrose Fleming First finger represents the direction of the Field. The Second finger represents the direction of the Current [conventional current, positive(+) to negative(-). The Thumb represents the direction of the Thrust or resultant Motion. FBI - moving from thumb to second finger. The thumb is the force F The first finger is the magnetic field B The second finger is the of current I The Right Hand Rule simply shows how a current-carrying wire generates a magnetic field • point your thumb in the direction of the current and let your fingers assume a curved position, the magnetic field circling around the wires flows in the direction in which your four fingers point. • Fleming's right hand rule (for generators). The appropriatelyhanded rule can be recalled by remembering that the letter "g" is in "right" and "generator" Fleming's left hand rule (for electric motors) shows the direction of the . thrust on a conductor carrying a current in a magnetic field • An electric motor is a motor that uses electrical energy to produce mechanical energy, usually through the interaction of magnetic fields and currentcarrying conductors. • Electric motors are used in most, modern machines. Obvious uses would be in rotating machines such as fans, turbines, drills, the wheels on electric cars, locomotives and conveyor belts. • The reverse process, producing electrical energy from mechanical energy, is accomplished by a generator or dynamo • A generator forces electric charges to move through an external electrical circuit, but it does not create electricity or charge, which is already present in the wire of its windings. It is analogous to a water pump, which creates a flow of water but does not create the water inside. This powerpoint was kindly donated to www.worldofteaching.com http://www.worldofteaching.com Is home to well over a thousand powerpoints submitted by teachers. This a free site. Please visit and I hope it will help in your teaching