Electric Fields and Potential
... It is a vector quantity. It has both magnitude and direction. The direction of the field is always determined, by convention, with a small, positive test charge. Electric Field strength can be calculated using: E = F/q and E = kq/d ...
... It is a vector quantity. It has both magnitude and direction. The direction of the field is always determined, by convention, with a small, positive test charge. Electric Field strength can be calculated using: E = F/q and E = kq/d ...
Generators and Motors
... 16. When there is relative motion between the wire and a nearby magnet, we have created an _____________ current. 17. This connection between magnetism and electricity was used to develop ____________, ________________, and other electrical technology. What’s in a Generator? 18. Define AC – alternat ...
... 16. When there is relative motion between the wire and a nearby magnet, we have created an _____________ current. 17. This connection between magnetism and electricity was used to develop ____________, ________________, and other electrical technology. What’s in a Generator? 18. Define AC – alternat ...
Electric Current and Ohm`s Law
... • Resistance is the opposition to the flow of charges in a material • The SI unit of resistance is the ohm • A material’s thickness, length and temperature affect its resistance • Resistance is more in a longer wire • As temperature increases the resistance increases since the electrons collide more ...
... • Resistance is the opposition to the flow of charges in a material • The SI unit of resistance is the ohm • A material’s thickness, length and temperature affect its resistance • Resistance is more in a longer wire • As temperature increases the resistance increases since the electrons collide more ...
Electric Field – Notes and Examples
... An electric field is an area of influence around a charged object It is given as the amount of electrical force exerted on a positive test charge placed at a given point in the field ...
... An electric field is an area of influence around a charged object It is given as the amount of electrical force exerted on a positive test charge placed at a given point in the field ...
Electricity - WordPress.com
... electric field : an especially simple type of electromagnetic field produced by an electric charge even when it is not moving . The electric field produces a force on other charges in its vicinity. Moving charges additionally produce a magnetic field. electric potential: the capacity of an electric ...
... electric field : an especially simple type of electromagnetic field produced by an electric charge even when it is not moving . The electric field produces a force on other charges in its vicinity. Moving charges additionally produce a magnetic field. electric potential: the capacity of an electric ...
III. Producing Electric Current
... A. Electromagnetic Induction Electromagnetic Induction producing a current by moving a wire through a ...
... A. Electromagnetic Induction Electromagnetic Induction producing a current by moving a wire through a ...
Electromagnetism Cloze - Science
... A device that uses a coil of spinning wires in a magnetic field to make electricity is called a _________________. A _________________ power plant, for example, uses the energy of flowing water to generate electricity. As water flows from a high place to a low place, it pushes on _________________ b ...
... A device that uses a coil of spinning wires in a magnetic field to make electricity is called a _________________. A _________________ power plant, for example, uses the energy of flowing water to generate electricity. As water flows from a high place to a low place, it pushes on _________________ b ...
Class Notes 3/28/16 - Physics Internal Website
... Clicker question In the conducting wire, electrons are moving in the direction from A to B. The electric field in the wire A) points in the A-to-B direction. B) points in the B-to-A direction. C) is zero, since electric field inside a conductor is zero. D) not enough information to tell. ...
... Clicker question In the conducting wire, electrons are moving in the direction from A to B. The electric field in the wire A) points in the A-to-B direction. B) points in the B-to-A direction. C) is zero, since electric field inside a conductor is zero. D) not enough information to tell. ...
Study Guide - Chapter 33-1
... Displacement current is measured in amps (A), just like real current. However, displacement current is not actual current, it is just a changing electric field. We only think of it as current because it produces the same sort of magnetic field. For example, the magnetic field at a distance < from a ...
... Displacement current is measured in amps (A), just like real current. However, displacement current is not actual current, it is just a changing electric field. We only think of it as current because it produces the same sort of magnetic field. For example, the magnetic field at a distance < from a ...
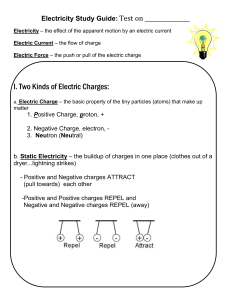
Electric Charge
... (same + and same -) then nothing happens electrically **this means both objects are neutral or have a neutral charge b. If an object has more If an object has more ...
... (same + and same -) then nothing happens electrically **this means both objects are neutral or have a neutral charge b. If an object has more If an object has more ...
Effects of Electric Current * Learning Outcomes
... Effects of Electric Current – Learning Outcomes Explain the heating, chemical, and magnetic effects. State Joule’s Law. Demonstrate each effect. ...
... Effects of Electric Current – Learning Outcomes Explain the heating, chemical, and magnetic effects. State Joule’s Law. Demonstrate each effect. ...
Electric current
An electric current is a flow of electric charge. In electric circuits this charge is often carried by moving electrons in a wire. It can also be carried by ions in an electrolyte, or by both ions and electrons such as in a plasma.The SI unit for measuring an electric current is the ampere, which is the flow of electric charge across a surface at the rate of one coulomb per second. Electric current is measured using a device called an ammeter.Electric currents cause Joule heating, which creates light in incandescent light bulbs. They also create magnetic fields, which are used in motors, inductors and generators.The particles that carry the charge in an electric current are called charge carriers. In metals, one or more electrons from each atom are loosely bound to the atom, and can move freely about within the metal. These conduction electrons are the charge carriers in metal conductors.