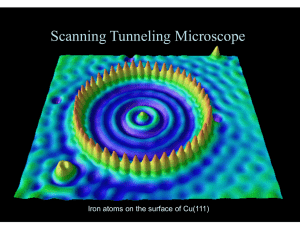
Atomic and Molecular Physics for Physicists Ben-Gurion University of the Negev
... In the hyperfine representation, the magnetic interaction is: V=-µ*B Here also you need a maximum or minimum of the magnetic field in order to have a trapping potential, but the Ernshaw theorem forbids this! In what conditions is the potential equal to: V = gF mF µB h |B| where µB = 1.4 MHz/G. Those ...
... In the hyperfine representation, the magnetic interaction is: V=-µ*B Here also you need a maximum or minimum of the magnetic field in order to have a trapping potential, but the Ernshaw theorem forbids this! In what conditions is the potential equal to: V = gF mF µB h |B| where µB = 1.4 MHz/G. Those ...
Magnetostatics – Magnetic Flux Density
... north and the south poles; as Figure shows, if you saw a magnet in half you get two magnets. Put another way, you cannot isolate a magnetic pole. From this characteristic of magnetic fields, it is easy to see that the net magnetic flux passing through a Gaussian surface (a closed surface as shown in ...
... north and the south poles; as Figure shows, if you saw a magnet in half you get two magnets. Put another way, you cannot isolate a magnetic pole. From this characteristic of magnetic fields, it is easy to see that the net magnetic flux passing through a Gaussian surface (a closed surface as shown in ...
Lecture 7 Extra
... Contains the force unit N for Newton and the unit A is the Ampere, the unit of electric current. With the magnetic permeability established, the electric permittivity takes the value given by the relationship ...
... Contains the force unit N for Newton and the unit A is the Ampere, the unit of electric current. With the magnetic permeability established, the electric permittivity takes the value given by the relationship ...
Magnetized_Phase_Diagram_Loewe
... scales. This means that the weak magnetic field approximation seems to be appropriate (eB <
... scales. This means that the weak magnetic field approximation seems to be appropriate (eB <
Maxwell`s Equations (4)
... whether induction can occur in the opposite sense; that is, can a changing electric flux induce a magnetic field? The answer is that it can; furthermore, the equation governing the induction of a magnetic field is almost symmetric with the above equation. We often call it Maxwell's law of induction ...
... whether induction can occur in the opposite sense; that is, can a changing electric flux induce a magnetic field? The answer is that it can; furthermore, the equation governing the induction of a magnetic field is almost symmetric with the above equation. We often call it Maxwell's law of induction ...
E & M
... (only current if closed wire or conductive) • Earth’s field can induce in moving things • There is also induced an electric force F= qE where E =V/d (d is length of wire) ...
... (only current if closed wire or conductive) • Earth’s field can induce in moving things • There is also induced an electric force F= qE where E =V/d (d is length of wire) ...
Chapter 17 - Northern Highlands
... Motors with electromagnets Just as with the magnet you flipped, the electromagnet must switch from north to south as each rotor magnet passes by to keep the rotor turning. The device that makes this happen is called a commutator. ...
... Motors with electromagnets Just as with the magnet you flipped, the electromagnet must switch from north to south as each rotor magnet passes by to keep the rotor turning. The device that makes this happen is called a commutator. ...
Maxwell`s equation
... point in space by currents J flowing along other curves in space. It has its experimental roots in Oersted’s great discovery that an electric current produces a magnetic field in the space around it. If another term is added to this equation, it follows that the magnetic field can be produced also i ...
... point in space by currents J flowing along other curves in space. It has its experimental roots in Oersted’s great discovery that an electric current produces a magnetic field in the space around it. If another term is added to this equation, it follows that the magnetic field can be produced also i ...
Lecture32
... . A cylindrical region of radius R = 3.0 cm contains a uniform magnetic field parallel to its axis. The field is 0 outside the cylinder. If the field is changing at the rate 0.60 T/s, the electric field induced at a point 2R from the cylinder axis is: ...
... . A cylindrical region of radius R = 3.0 cm contains a uniform magnetic field parallel to its axis. The field is 0 outside the cylinder. If the field is changing at the rate 0.60 T/s, the electric field induced at a point 2R from the cylinder axis is: ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 11. Prove the rectilinear propagation of light by Fresnel’s theory of half-period zones 12. Derive an expression for the loss of energy on sharing of charges between two capacitors. 13. Find the magnetic field at any point due to an infinitely long wire carrying current. 14. State and prove De Morga ...
... 11. Prove the rectilinear propagation of light by Fresnel’s theory of half-period zones 12. Derive an expression for the loss of energy on sharing of charges between two capacitors. 13. Find the magnetic field at any point due to an infinitely long wire carrying current. 14. State and prove De Morga ...
Chapter 15 Lesson 2 How are Electricity and Magnetism Related
... A free swinging magnet will point north with its north seeking pole-that end is marked with an N. Like electrical charges, opposite forces between magnetic poles attract, N-S, positive –negative Like poles repel: south repels south; north repels north Magnets keep their poles even when cut in two. A ...
... A free swinging magnet will point north with its north seeking pole-that end is marked with an N. Like electrical charges, opposite forces between magnetic poles attract, N-S, positive –negative Like poles repel: south repels south; north repels north Magnets keep their poles even when cut in two. A ...
Scanning SQUID microscope

A Scanning SQUID Microscope is a sensitive near-field imaging system for the measurement of weak magnetic fields by moving a Superconducting Quantum Interference Device (SQUID) across an area. The microscope can map out buried current-carrying wires by measuring the magnetic fields produced by the currents, or can be used to image fields produced by magnetic materials. By mapping out the current in an integrated circuit or a package, short circuits can be localized and chip designs can be verified to see that current is flowing where expected.






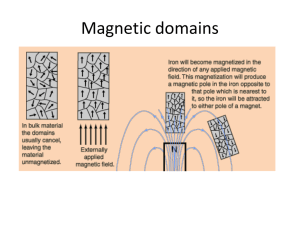
![2016 Farada review sheet[1][1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001271395_1-fc9c1a7e3076b57ba2cfadfbf9c2de3d-300x300.png)