Chapter 18
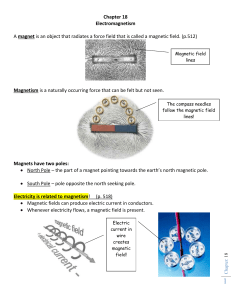
... Magnetism is a naturally occurring force that can be felt but not seen. The compass needles follow the magnetic field lines! ...
... Magnetism is a naturally occurring force that can be felt but not seen. The compass needles follow the magnetic field lines! ...
19.- Modeling Electromagnetic Fields in Induction Heating
... cylindrical symmetry. High frequency alternating current is made to flow through the inductor coils. Through the action of the associated fluctuating magnetic field, oscillating eddy currents are induced in the treated component without the need of electrical contact. The induced currents together w ...
... cylindrical symmetry. High frequency alternating current is made to flow through the inductor coils. Through the action of the associated fluctuating magnetic field, oscillating eddy currents are induced in the treated component without the need of electrical contact. The induced currents together w ...
Magnetic Induction
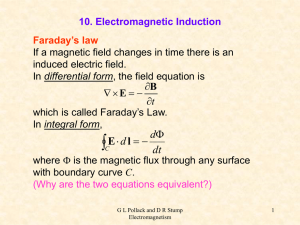
... An Intriguing Possibility... • If changing magnetic flux can create a current, can one also conclude that a changing magnetic field can produce an electric field? • Don’t we already have evidence that the converse - a changing electric field produces a magnetic field - occurs? ...
... An Intriguing Possibility... • If changing magnetic flux can create a current, can one also conclude that a changing magnetic field can produce an electric field? • Don’t we already have evidence that the converse - a changing electric field produces a magnetic field - occurs? ...
Lesson 1: Magnets have 2 poles. Like poles attract, unlike poles
... Magnets have 2 poles. Like poles attract, unlike poles repel. Magnets attract iron. Magnetic force is strongest around the poles of a magnet. Vocab: magnet Magnetism Magnetic pole Magnetic force Lesson 2: Magnetic fields spread out from one pole to the other. They are curves lines that never cross. ...
... Magnets have 2 poles. Like poles attract, unlike poles repel. Magnets attract iron. Magnetic force is strongest around the poles of a magnet. Vocab: magnet Magnetism Magnetic pole Magnetic force Lesson 2: Magnetic fields spread out from one pole to the other. They are curves lines that never cross. ...
Document
... A current I in a conducting loop creates a magnetic field. The flux through the loop is proportional to the current, = LI . The constant of proportionality L is the selfinductance, which depends on the geometry of the loop. If I changes in time there is an induced emf around the loop, which is by ...
... A current I in a conducting loop creates a magnetic field. The flux through the loop is proportional to the current, = LI . The constant of proportionality L is the selfinductance, which depends on the geometry of the loop. If I changes in time there is an induced emf around the loop, which is by ...
Slide 1
... MEG false color recording (left) of brain response to hearing pure tone, (center) superimposed on MRI cross-section of the brain. Right is the mapping of the MEG signal used to generate the false color recording. Gradiometer with two coils that cancel out distant spatially constant B fields. Note th ...
... MEG false color recording (left) of brain response to hearing pure tone, (center) superimposed on MRI cross-section of the brain. Right is the mapping of the MEG signal used to generate the false color recording. Gradiometer with two coils that cancel out distant spatially constant B fields. Note th ...
213 - jpsaos
... Eight pairs of electromagnets are shown below. The current in the left electromagnet is one amp and the current in the right one is two amps in each case. They are also separated by the same distance, and they have the same length and diameter. Carefully observe the orientation of the coil and direc ...
... Eight pairs of electromagnets are shown below. The current in the left electromagnet is one amp and the current in the right one is two amps in each case. They are also separated by the same distance, and they have the same length and diameter. Carefully observe the orientation of the coil and direc ...
Midterm Exam No. 02 (Spring 2015) PHYS 520B: Electromagnetic Theory
... PHYS 520B: Electromagnetic Theory Date: 2014 Mar 18 ...
... PHYS 520B: Electromagnetic Theory Date: 2014 Mar 18 ...
1. A bar magnet is broken in half. Each half is broken in half again
... B) a time-varying electric flux acts as a current for purposes of producing a magnetic field C) the speed of light could be determined from simple electrostatic and magnetostatic experiments (finding the values of µ0 and 5 0) D) the magnetic force on a moving charge particle is perpendicular to both ...
... B) a time-varying electric flux acts as a current for purposes of producing a magnetic field C) the speed of light could be determined from simple electrostatic and magnetostatic experiments (finding the values of µ0 and 5 0) D) the magnetic force on a moving charge particle is perpendicular to both ...
Scanning SQUID microscope

A Scanning SQUID Microscope is a sensitive near-field imaging system for the measurement of weak magnetic fields by moving a Superconducting Quantum Interference Device (SQUID) across an area. The microscope can map out buried current-carrying wires by measuring the magnetic fields produced by the currents, or can be used to image fields produced by magnetic materials. By mapping out the current in an integrated circuit or a package, short circuits can be localized and chip designs can be verified to see that current is flowing where expected.