Faraday`s Law of Induction
... negative of the rate of change of the magnetic flux through the area enclosed by the loop. This line integral is equal to the generated voltage or emf in the loop, so Faraday's law is the basis for electric generators. It also forms the basis for inductors and transformers. Application to voltage ge ...
... negative of the rate of change of the magnetic flux through the area enclosed by the loop. This line integral is equal to the generated voltage or emf in the loop, so Faraday's law is the basis for electric generators. It also forms the basis for inductors and transformers. Application to voltage ge ...
Word
... follow helical paths along the field lines either charged north or south. The light observed as auroras is due particles to ionization of atoms in the atmosphere when they collide with high speed charged particles. The free B electrons resulting from the collisions recombine with ionised atoms, losi ...
... follow helical paths along the field lines either charged north or south. The light observed as auroras is due particles to ionization of atoms in the atmosphere when they collide with high speed charged particles. The free B electrons resulting from the collisions recombine with ionised atoms, losi ...
Physics 203 Sample Exam 1
... [4] A magnetic field exerts a force on all the following EXCEPT (a) a current carrying wire (b) a moving electric charge (c) a stationary electric charge (d) a magnet [5] Which of the following will not drive an electric current in a conductive loop? (a) magnetic flux through the loop (b) a potentia ...
... [4] A magnetic field exerts a force on all the following EXCEPT (a) a current carrying wire (b) a moving electric charge (c) a stationary electric charge (d) a magnet [5] Which of the following will not drive an electric current in a conductive loop? (a) magnetic flux through the loop (b) a potentia ...
OCR G485 Definitions
... Isotopes - Two nuclides (a nucleus with a distinct number of protons and neutrons) with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Fundamental Particles - Particles which cannot be broken down into smaller components. Activity - The number of radioactive decays per unit time. Uni ...
... Isotopes - Two nuclides (a nucleus with a distinct number of protons and neutrons) with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Fundamental Particles - Particles which cannot be broken down into smaller components. Activity - The number of radioactive decays per unit time. Uni ...
Flux or flux linkage? - Institute of Physics
... use the concept of flux linkage to explain how transformers work ...
... use the concept of flux linkage to explain how transformers work ...
Electromagnetism - Lecture 3 Magnetic Fields
... Removing the integral over the area gives the differential form of Ampère’s Law: ∇ × B = µ0 J At any point in space the curl of the magnetic field is proportional to the local current density In electrostatics the equivalent statement for the electric field is: ∇ × E = −∇ × ∇V = 0 ...
... Removing the integral over the area gives the differential form of Ampère’s Law: ∇ × B = µ0 J At any point in space the curl of the magnetic field is proportional to the local current density In electrostatics the equivalent statement for the electric field is: ∇ × E = −∇ × ∇V = 0 ...
generators and transformers
... 120 degrees from each other. If you were to look at the three phases on a graph, they would look like this relative to ground: ...
... 120 degrees from each other. If you were to look at the three phases on a graph, they would look like this relative to ground: ...
Magnetism and Matter
... Magnetic field or magnetic flux density B will form at some point in space when an external free current loop is switched on or magnetic material is placed at that location. A charge, q moving with velocity, v generates a field, B in a perpendicular direction of its velocity vector. By Lorentz force ...
... Magnetic field or magnetic flux density B will form at some point in space when an external free current loop is switched on or magnetic material is placed at that location. A charge, q moving with velocity, v generates a field, B in a perpendicular direction of its velocity vector. By Lorentz force ...
induced magnetic field
... fields to produce voltage, and in a complete circuit, a current. Michael Faraday first discovered it in 1831, using some of the works of Hans Christian Oersted. He started by using different combinations of wires and magnetic strengths and currents, but it wasn't until he tried moving the wires ...
... fields to produce voltage, and in a complete circuit, a current. Michael Faraday first discovered it in 1831, using some of the works of Hans Christian Oersted. He started by using different combinations of wires and magnetic strengths and currents, but it wasn't until he tried moving the wires ...
File
... In Science 10 we learned that certain objects called magnets can exert a force on iron and other ferromagnetic materials such as cobalt, nickel, and gadolinium. Magnets are made of ________________ materials, usually iron, and have special properties at the atomic level, which allow them to be magne ...
... In Science 10 we learned that certain objects called magnets can exert a force on iron and other ferromagnetic materials such as cobalt, nickel, and gadolinium. Magnets are made of ________________ materials, usually iron, and have special properties at the atomic level, which allow them to be magne ...
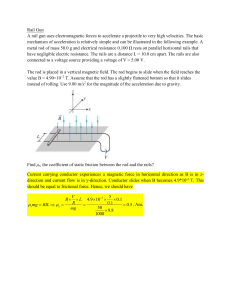
A rail gun uses electromagnetic forces to accelerate a projectile to
... mechanism of acceleration is relatively simple and can be illustrated in the following example. A metal rod of mass 50.0 g and electrical resistance 0.100 Ω rests on parallel horizontal rails that have negligible electric resistance. The rails are a distance L = 10.0 cm apart. The rails are also con ...
... mechanism of acceleration is relatively simple and can be illustrated in the following example. A metal rod of mass 50.0 g and electrical resistance 0.100 Ω rests on parallel horizontal rails that have negligible electric resistance. The rails are a distance L = 10.0 cm apart. The rails are also con ...
Part - Saraswathi Velu College of Engineering
... 7. What are the difference b/w line, elliptical and circular polarization? 8. Find the skin depth at a frequency of 2 MHz in aluminum whereσ = 38.2 μs/m and μr = 1. 9. What is Brewster angle? 10. What is the skin effect? 11. What is slepian vector? Part –B Unit-I 1. State and explain Coulomb’s law a ...
... 7. What are the difference b/w line, elliptical and circular polarization? 8. Find the skin depth at a frequency of 2 MHz in aluminum whereσ = 38.2 μs/m and μr = 1. 9. What is Brewster angle? 10. What is the skin effect? 11. What is slepian vector? Part –B Unit-I 1. State and explain Coulomb’s law a ...
magnetism - University of South Alabama
... y Can either attract or repel y Two kinds of poles: N = north(seeking); S = south(seeking) y All magnets are DIPOLES: always have both poles y POLES: Likes repel, opposites attract y Magnetic (force)field: y Direction to which a small magnetic dipole would align y Traced out by iron filings ...
... y Can either attract or repel y Two kinds of poles: N = north(seeking); S = south(seeking) y All magnets are DIPOLES: always have both poles y POLES: Likes repel, opposites attract y Magnetic (force)field: y Direction to which a small magnetic dipole would align y Traced out by iron filings ...
We’ll treat the charge and current in Maxwell’s Equations in Matter
... Start with the fundamental equations (1) ∇·E = ρ/ε0 (2) ∇·B = 0 (3) ∇ × E = −∂B/∂t (4) ∇ × B = μ0J + μ0ε0 ∂E/∂t where ρ(x,t) and J(x,t) satisfy the ...
... Start with the fundamental equations (1) ∇·E = ρ/ε0 (2) ∇·B = 0 (3) ∇ × E = −∂B/∂t (4) ∇ × B = μ0J + μ0ε0 ∂E/∂t where ρ(x,t) and J(x,t) satisfy the ...
Scanning SQUID microscope

A Scanning SQUID Microscope is a sensitive near-field imaging system for the measurement of weak magnetic fields by moving a Superconducting Quantum Interference Device (SQUID) across an area. The microscope can map out buried current-carrying wires by measuring the magnetic fields produced by the currents, or can be used to image fields produced by magnetic materials. By mapping out the current in an integrated circuit or a package, short circuits can be localized and chip designs can be verified to see that current is flowing where expected.