Atomic Theory Practice Test
... Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 18. The electrons involved in the formation of a chemical bond are called a. dipoles. c. Lewis electrons. b. s electrons. d. valence electrons. ____ 19. In a chemical bond, the link between atoms result ...
... Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 18. The electrons involved in the formation of a chemical bond are called a. dipoles. c. Lewis electrons. b. s electrons. d. valence electrons. ____ 19. In a chemical bond, the link between atoms result ...
Unit1: Matter Review
... • Bohr’s model was readily accepted by scientists and they began drawing models of the atom using his theory. ...
... • Bohr’s model was readily accepted by scientists and they began drawing models of the atom using his theory. ...
Chapter 4 and 5 Powerpoint - School District of La Crosse
... an electron can have in the atom. Level 1= 2 e: level 2=8e: level 3= 18e: level 4=32: level 5=50 1. electrons gain energy to move to a higher level and give up energy when they drop back into a lower level( ground state) 1. No longer assumed the electron moved in definite orbitals( Heisenberg uncert ...
... an electron can have in the atom. Level 1= 2 e: level 2=8e: level 3= 18e: level 4=32: level 5=50 1. electrons gain energy to move to a higher level and give up energy when they drop back into a lower level( ground state) 1. No longer assumed the electron moved in definite orbitals( Heisenberg uncert ...
Unit 2 Lesson 1 - Mrs. Tainter`s Physical Science Class
... proton, found in nuclei of atoms along with protons the center of positive charge called protons – also contains protons (with no charge) the sum of the number of protons and the number of neutrons in a single atom. the number of protons in every atom of an element. atoms of the same element with di ...
... proton, found in nuclei of atoms along with protons the center of positive charge called protons – also contains protons (with no charge) the sum of the number of protons and the number of neutrons in a single atom. the number of protons in every atom of an element. atoms of the same element with di ...
Page|1 - askIITians
... Metallic character increases across a period. Chemical reactivity increases and then decreases across a period. Chemical reactivity increases across a period. ...
... Metallic character increases across a period. Chemical reactivity increases and then decreases across a period. Chemical reactivity increases across a period. ...
Unit 1 - Mount St. Mary Catholic High School
... ◦ thought the material world was made up of tiny indivisible particles called atomos ...
... ◦ thought the material world was made up of tiny indivisible particles called atomos ...
atoms - Cloudfront.net
... 2. Atoms of same element identical in size, mass, properties; atoms of diff elements diff. in size, mass, properties. 3. Atoms can’t be subdivided, created, destroyed. 4. Atoms of different elements combine in wholenumber ratios to form chemical compounds. 5. In chemical reactions, atoms are combine ...
... 2. Atoms of same element identical in size, mass, properties; atoms of diff elements diff. in size, mass, properties. 3. Atoms can’t be subdivided, created, destroyed. 4. Atoms of different elements combine in wholenumber ratios to form chemical compounds. 5. In chemical reactions, atoms are combine ...
Chapter 4 Atoms - LCMR School District
... Chlorine’s atomic number is 17 Average Atomic Mass – the average mass of an element, represents one mole of a that substance, Chlorine has a average atomic mass of 35.453 Mass Number – the average atomic mass rounded to a whole number; represents the number of neutrons and protons in the nucleus of ...
... Chlorine’s atomic number is 17 Average Atomic Mass – the average mass of an element, represents one mole of a that substance, Chlorine has a average atomic mass of 35.453 Mass Number – the average atomic mass rounded to a whole number; represents the number of neutrons and protons in the nucleus of ...
The Birth of Atomic Theory
... • The gold foil experiment showed the Plum Pudding model was incorrect. • Rutherford discovered the nucleus ...
... • The gold foil experiment showed the Plum Pudding model was incorrect. • Rutherford discovered the nucleus ...
Physical Science The Atoms Family Album
... Elliott is much smaller than Patty and Nelda and he is always angry because these bigger relatives will not let him in the Arcade. He has a frown on his face, eyes that are squinted with anger, and a very negative ...
... Elliott is much smaller than Patty and Nelda and he is always angry because these bigger relatives will not let him in the Arcade. He has a frown on his face, eyes that are squinted with anger, and a very negative ...
The Birth of Atomic Theory
... • The gold foil experiment showed the Plum Pudding model was incorrect. • Rutherford discovered the nucleus ...
... • The gold foil experiment showed the Plum Pudding model was incorrect. • Rutherford discovered the nucleus ...
希臘 - 中正大學化生系
... corresponds to their so-called valencies, as well as, to some extent, to their distinctive chemical properties; as is apparent among other series in that of Li, Be, B, C, N, O, and F. 4. The magnitude of the atomic weight determines the character of the element, just as the magnitude of the molecule ...
... corresponds to their so-called valencies, as well as, to some extent, to their distinctive chemical properties; as is apparent among other series in that of Li, Be, B, C, N, O, and F. 4. The magnitude of the atomic weight determines the character of the element, just as the magnitude of the molecule ...
Atoms and Elements
... spaces closest to the ground floor, then spread farther up as the spots get filled. ...
... spaces closest to the ground floor, then spread farther up as the spots get filled. ...
Chapter 3 – Atoms - Waukee Community School District Blogs
... 1. Law of Conservation of Mass = States that mass is neither created nor destroyed during ordinary chemical reactions or physical changes 2. Law of Definite Proportions = A chemical compound contains ...
... 1. Law of Conservation of Mass = States that mass is neither created nor destroyed during ordinary chemical reactions or physical changes 2. Law of Definite Proportions = A chemical compound contains ...
ATOMIC TIMELINE - Dublin Schools
... electrons) • He designed the “Plum Pudding Model” or “Blueberry Muffin Model”. Positively charged atom with negatively charged electrons scattered within. ...
... electrons) • He designed the “Plum Pudding Model” or “Blueberry Muffin Model”. Positively charged atom with negatively charged electrons scattered within. ...
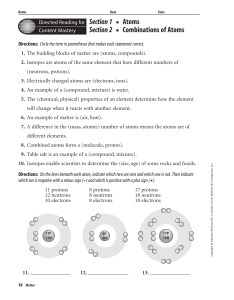
Chapter 18 Resource: Matter
... Directions: Circle the term in parentheses that makes each statement correct. 1. The building blocks of matter are (atoms, compounds). 2. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of (neutrons, protons). 3. Electrically charged atoms are (electrons, ions). 4. An example of a ...
... Directions: Circle the term in parentheses that makes each statement correct. 1. The building blocks of matter are (atoms, compounds). 2. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of (neutrons, protons). 3. Electrically charged atoms are (electrons, ions). 4. An example of a ...
unit iii - atomic theory 1
... (therefore, different amounts of neutrons), these different forms are called isotopes of that element - when dealing with samples of an element containing two or more different isotopes, the mass number must be indicated with the element’s name: - another way to represent different isotopes is to pu ...
... (therefore, different amounts of neutrons), these different forms are called isotopes of that element - when dealing with samples of an element containing two or more different isotopes, the mass number must be indicated with the element’s name: - another way to represent different isotopes is to pu ...
ionization energy
... charge in the nucleus will have the largest ionization energy. • For the isoelectronic series S2-, Cl-, and Ar, Ar has the largest ionization energy because it has the most protons in its nucleus. ...
... charge in the nucleus will have the largest ionization energy. • For the isoelectronic series S2-, Cl-, and Ar, Ar has the largest ionization energy because it has the most protons in its nucleus. ...
4-1 Atomic Structure
... Less than 100 years after Dalton published his atomic theory, scientists determined that atoms consisted of still smaller particles and could be broken down even further. a. Atoms are made of protons, neutrons, and electrons i. Protons have a positive charge (+)and are located in the nucleus ii. Neu ...
... Less than 100 years after Dalton published his atomic theory, scientists determined that atoms consisted of still smaller particles and could be broken down even further. a. Atoms are made of protons, neutrons, and electrons i. Protons have a positive charge (+)and are located in the nucleus ii. Neu ...
Chapter 8 PPT - Richsingiser.com
... charge in the nucleus will have the largest ionization energy. • For the isoelectronic series S2-, Cl-, and Ar, Ar has the largest ionization energy because it has the most protons in its nucleus. ...
... charge in the nucleus will have the largest ionization energy. • For the isoelectronic series S2-, Cl-, and Ar, Ar has the largest ionization energy because it has the most protons in its nucleus. ...
Periodic Trends Note Packet Key
... atomic weight, their chemical and physical properties repeated at regular intervals. ...
... atomic weight, their chemical and physical properties repeated at regular intervals. ...
Notes on Atomic Structure atoms
... same proportions (by mass and by number) of its elements This means a given compound always has the same composition, regardless of where it came from. ...
... same proportions (by mass and by number) of its elements This means a given compound always has the same composition, regardless of where it came from. ...
Unit 5 Review
... 32. Define fission. __Splitting an atom’s nucleus into 2 smaller daughter nuclei._____________________ 33. What is an ion and how is it formed? _A ion is an atom with a charge, formed by gaining or losing electrons. 34. In isotope notation, which number always stays the same? ___atomic number (botto ...
... 32. Define fission. __Splitting an atom’s nucleus into 2 smaller daughter nuclei._____________________ 33. What is an ion and how is it formed? _A ion is an atom with a charge, formed by gaining or losing electrons. 34. In isotope notation, which number always stays the same? ___atomic number (botto ...