ATOMIC STRUCTURE
... staircase is a metal (includes the weird transition element rows outside and below the MPT), everything right of is non-metals. Few borderline cases are referred to as metalloids (semiconductors!!!!). All metals are shiny, conduct electricity and are malleable. Non-metals do not share a common prope ...
... staircase is a metal (includes the weird transition element rows outside and below the MPT), everything right of is non-metals. Few borderline cases are referred to as metalloids (semiconductors!!!!). All metals are shiny, conduct electricity and are malleable. Non-metals do not share a common prope ...
2.1 The Nature of Matter
... Chemical Compounds A chemical compound is a substance formed by the chemical combination of two or more elements in definite proportions. The physical and chemical properties of a compound are usually very different from those of the elements from which it is formed. Scientists use formulas to show ...
... Chemical Compounds A chemical compound is a substance formed by the chemical combination of two or more elements in definite proportions. The physical and chemical properties of a compound are usually very different from those of the elements from which it is formed. Scientists use formulas to show ...
The Atom
... Identifying isotopes You use the name of the element followed by the mass number of the isotope to identify the isotope: boron-10 and boron-11 are examples. The average atomic mass of an element is the average mass of the mixture of its isotopes. Find the average mass of Carbon on the periodic table ...
... Identifying isotopes You use the name of the element followed by the mass number of the isotope to identify the isotope: boron-10 and boron-11 are examples. The average atomic mass of an element is the average mass of the mixture of its isotopes. Find the average mass of Carbon on the periodic table ...
CHEM 1 0 1 - Near East University
... Atomic Number (Z): The number of protons in a particular atom. Mass Number (A): The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of a particular atom. Atomic symbols ...
... Atomic Number (Z): The number of protons in a particular atom. Mass Number (A): The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of a particular atom. Atomic symbols ...
AP Chemistry 2013 Semester 1 Final Exam Review Problems
... 12. An electron microscope employs a beam of electrons to obtain an image of an object. What energy must be imparted to each electron of the beam to obtain a wavelength of 10.0pm? Using the formula KE = ½mv2, calculate the energy in electron volts (eV) (1eV = 1.602 x 10-19J) 13. What is the differen ...
... 12. An electron microscope employs a beam of electrons to obtain an image of an object. What energy must be imparted to each electron of the beam to obtain a wavelength of 10.0pm? Using the formula KE = ½mv2, calculate the energy in electron volts (eV) (1eV = 1.602 x 10-19J) 13. What is the differen ...
Chapter 6 Review “The Periodic Table”
... that are characterized by the filling of p orbitals are classified as _____. As you move from left to right across the second period of the periodic table, ionization energy __. Atomic size generally decreases as you ____. ...
... that are characterized by the filling of p orbitals are classified as _____. As you move from left to right across the second period of the periodic table, ionization energy __. Atomic size generally decreases as you ____. ...
Democritus Proposes the Atom - Leon M. Goldstein High School for
... a. Atoms are the smallest piece of matter b. Atoms are always standing still c. Atoms join together to form different materials d. None of the above 3. We know that Democritus was right about atoms. So why did people ignore Democritus’s ideas for such a long time? ___________________________________ ...
... a. Atoms are the smallest piece of matter b. Atoms are always standing still c. Atoms join together to form different materials d. None of the above 3. We know that Democritus was right about atoms. So why did people ignore Democritus’s ideas for such a long time? ___________________________________ ...
Atomic Theory and Structure Test Review
... Know how to draw and label an atom: Make sure you have protons, neutrons, and electrons represented. As well as label the electron cloud area and nucleus. Don’t forget to add the charges to the particles when needed. ...
... Know how to draw and label an atom: Make sure you have protons, neutrons, and electrons represented. As well as label the electron cloud area and nucleus. Don’t forget to add the charges to the particles when needed. ...
Chapter 6 Powerpoint
... 1. Into what four classes can elements be sorted based on their electron configuration? 2. Why do the elements potassium and sodium have similar chemical properties? ...
... 1. Into what four classes can elements be sorted based on their electron configuration? 2. Why do the elements potassium and sodium have similar chemical properties? ...
Relationships in The PeriodicTable
... elements reflect differences in atomic structure. The metallic character of elements decreases across a period from metals through the metalloids and increases from top to bottom within a particular group of representative elements. 4. Atomic radius varies periodically with the arrangement of the el ...
... elements reflect differences in atomic structure. The metallic character of elements decreases across a period from metals through the metalloids and increases from top to bottom within a particular group of representative elements. 4. Atomic radius varies periodically with the arrangement of the el ...
Chemistry Notes with Blanks
... All nuclei contain positively charged particles called _________ (p+). Most contain particles that have no charge, called _________ (n0). Example: Carbon has 6 protons so its _________ number is 6 The space surrounding the nucleus contains extremely small, _________ charged particles called electron ...
... All nuclei contain positively charged particles called _________ (p+). Most contain particles that have no charge, called _________ (n0). Example: Carbon has 6 protons so its _________ number is 6 The space surrounding the nucleus contains extremely small, _________ charged particles called electron ...
Particulate View of Matter
... Mendeleev – discoverer of the periodic law and thus the periodic table. He arranged the periodic table looking for trends or patterns (periodic). Has been changed over time . ...
... Mendeleev – discoverer of the periodic law and thus the periodic table. He arranged the periodic table looking for trends or patterns (periodic). Has been changed over time . ...
chemia simr01 en - Leszek Niedzicki
... accumulated in a small volume (not distributed on any neutrons); • In molecules in which hydrogen gives his electron away to atoms with strong affinity towards electrons (e.g. oxygen, nitrogen, fluorine) its electron (although formally shared) is ‘closer’ to the other atom; • Hydrogen is ‘looking’ f ...
... accumulated in a small volume (not distributed on any neutrons); • In molecules in which hydrogen gives his electron away to atoms with strong affinity towards electrons (e.g. oxygen, nitrogen, fluorine) its electron (although formally shared) is ‘closer’ to the other atom; • Hydrogen is ‘looking’ f ...
Chapter 3 - cloudfront.net
... 2) Atoms can be changed from one element into another – by __________ reaction 3) Atoms of the same element are not all exactly the same - ___________ ...
... 2) Atoms can be changed from one element into another – by __________ reaction 3) Atoms of the same element are not all exactly the same - ___________ ...
Ground state electron arrangement
... Write ground-state electron configurations for the following elements. a. Chlorine _________________________________________________ b. Silicon _________________________________________________ c. Carbon _________________________________________________ ...
... Write ground-state electron configurations for the following elements. a. Chlorine _________________________________________________ b. Silicon _________________________________________________ c. Carbon _________________________________________________ ...
Isotopes
... Gallium is a metallic element found in small lasers used in compact disc players. In a sample of gallium, there is: 60.2% of gallium 69 atoms 39.8% of gallium 71 atoms What is the atomic mass of gallium? ...
... Gallium is a metallic element found in small lasers used in compact disc players. In a sample of gallium, there is: 60.2% of gallium 69 atoms 39.8% of gallium 71 atoms What is the atomic mass of gallium? ...
Ch. 2. Atomic Structure and Periodic Table
... Atomic number: The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. Isotopes: Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. *Isotopes are identified by including the mass number with the element name. Ex: Carbon 14, Carbon 12 Average Atomic Mass: An estimate of the mass of an element’s a ...
... Atomic number: The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. Isotopes: Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. *Isotopes are identified by including the mass number with the element name. Ex: Carbon 14, Carbon 12 Average Atomic Mass: An estimate of the mass of an element’s a ...
Unit 2
... A. addition of energy levels. B. increase in the number of neutrons. C. formation of anew octet. D. increase in nuclear charge. 46. One-half the distance between the nuclei of identical atoms combined in an element is called the A. atomic diameter. B. electron cloud. C. atomic radius. D. atomic volu ...
... A. addition of energy levels. B. increase in the number of neutrons. C. formation of anew octet. D. increase in nuclear charge. 46. One-half the distance between the nuclei of identical atoms combined in an element is called the A. atomic diameter. B. electron cloud. C. atomic radius. D. atomic volu ...
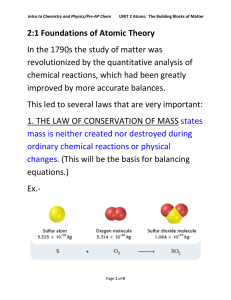
2:1 Foundations of Atomic Theory In the 1790s the study of matter
... ATOMIC NUMBER (Z) of an element is the number of protons of each atom of that element, so it identifies an element. The atomic number can be found above an element’s symbol on the periodic table. Elements are arranged in the Periodic Table in increasing atomic number. Ex.- Silver [Ag] has an atomic ...
... ATOMIC NUMBER (Z) of an element is the number of protons of each atom of that element, so it identifies an element. The atomic number can be found above an element’s symbol on the periodic table. Elements are arranged in the Periodic Table in increasing atomic number. Ex.- Silver [Ag] has an atomic ...
Unit 4 Powerpoint
... Below the main body of the periodic table Presence of e- in f orbitals “rare-earth elements” • Some more abundant than other elements ...
... Below the main body of the periodic table Presence of e- in f orbitals “rare-earth elements” • Some more abundant than other elements ...
Physical Science –McDougal-Littell Name
... 1. Who was John Dalton? 2. List two theories attributed to John Dalton. The Structure of an Atom, p.139 1. What key discovery about atomic particles led to the current concept of the model of the atom? 2. What charge might a particle have? 3. What is it that determines whether particles attract or r ...
... 1. Who was John Dalton? 2. List two theories attributed to John Dalton. The Structure of an Atom, p.139 1. What key discovery about atomic particles led to the current concept of the model of the atom? 2. What charge might a particle have? 3. What is it that determines whether particles attract or r ...
Atomic Structure - s3.amazonaws.com
... Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
... Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
Today in Science - Canton Local Schools
... England - used the results of his gold-foil experiment to state that all the mass of an atom was in a small positively-charged ball at the center of the atom. ...
... England - used the results of his gold-foil experiment to state that all the mass of an atom was in a small positively-charged ball at the center of the atom. ...