Chapter 4 “Atomic Structure” Section 4.1 Defining the Atom
... one element are different from atoms of a different element. 3. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can be chemically combine to form compounds. 4. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged. However, atoms of an element never changes into atoms o ...
... one element are different from atoms of a different element. 3. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can be chemically combine to form compounds. 4. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged. However, atoms of an element never changes into atoms o ...
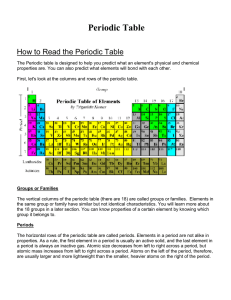
How to Read the Periodic Table
... Atomic Radius - Atomic radius is simply the radius of the atom, an indication of the atom's volume. Period - atomic radius decreases as you go from left to right across a period. Why? Stronger attractive forces in atoms (as you go from left to right) between the opposite charges in the nucleus and e ...
... Atomic Radius - Atomic radius is simply the radius of the atom, an indication of the atom's volume. Period - atomic radius decreases as you go from left to right across a period. Why? Stronger attractive forces in atoms (as you go from left to right) between the opposite charges in the nucleus and e ...
Unit 1- Matter and Energy 1
... Can be gained or lost from the outer most energy level. This is called the ______________ ______________ ________________ electrons are found in the valence shell. o These are responsible for most _____________ _____________ and in the formation of __________________. o Every atom wants __________ v ...
... Can be gained or lost from the outer most energy level. This is called the ______________ ______________ ________________ electrons are found in the valence shell. o These are responsible for most _____________ _____________ and in the formation of __________________. o Every atom wants __________ v ...
ATOM ATOMIC SYMBOL ATOMIC NUMBER
... Number of Protons = Atomic Number (Use the large colored marshmallows for protons) Number of Neutrons = Atomic Mass – Atomic Number (Use the large white marshmallows for neutrons) Number of Electrons = Number of Protons (Use the small colored marshmallows for electrons) ...
... Number of Protons = Atomic Number (Use the large colored marshmallows for protons) Number of Neutrons = Atomic Mass – Atomic Number (Use the large white marshmallows for neutrons) Number of Electrons = Number of Protons (Use the small colored marshmallows for electrons) ...
atoms - schultz915
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
THE MINISTRY OF HIGHER AND SECONDARY SPECIAL
... atomic weight and starting a new row or column when the characteristics of the elements began to repeat. The success of Mendeleev's table came from two decisions he made: The first was to leave gaps in the table when it seemed that the corresponding element had not yet been discovered. Mendeleev was ...
... atomic weight and starting a new row or column when the characteristics of the elements began to repeat. The success of Mendeleev's table came from two decisions he made: The first was to leave gaps in the table when it seemed that the corresponding element had not yet been discovered. Mendeleev was ...
Lesson 1 & 2 Periodic table trends and formation
... 2. What is the atomic mass of an element? The atomic mass is the mass of an atom of a particular element. It is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom of a particular element, averaged over all the isotopes of the element. (Note: students may not have studied isotopes yet ...
... 2. What is the atomic mass of an element? The atomic mass is the mass of an atom of a particular element. It is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom of a particular element, averaged over all the isotopes of the element. (Note: students may not have studied isotopes yet ...
Big Science from the Small World of Atom
... periodic table. On clicking a particular element in the alive periodic table, the atomic structure of the element, including the number of protons, neutrons and electrons, atomic mass, electron occupation in the different shells (energy levels) so that the number of core electrons and the valence el ...
... periodic table. On clicking a particular element in the alive periodic table, the atomic structure of the element, including the number of protons, neutrons and electrons, atomic mass, electron occupation in the different shells (energy levels) so that the number of core electrons and the valence el ...
Atoms and periodic properties
... single capitalized letter for their symbol • The rest, that have permanent names have two letters. – the first is capitalized and the second is lower case – the lower case letter is either the second letter in the name, or the letter of a strong consonant heard when the name of the element is spoken ...
... single capitalized letter for their symbol • The rest, that have permanent names have two letters. – the first is capitalized and the second is lower case – the lower case letter is either the second letter in the name, or the letter of a strong consonant heard when the name of the element is spoken ...
The Structure of the Atom
... The ancient Greek philosopher Democritus coined what word for a tiny piece of matter that cannot be divided? a) Element b) Electron c) Atom d) Molecule Dalton’s theory (~1800; based on behavior of gasses) included all but one of the following points. Which is not from Dalton? a) All elements are com ...
... The ancient Greek philosopher Democritus coined what word for a tiny piece of matter that cannot be divided? a) Element b) Electron c) Atom d) Molecule Dalton’s theory (~1800; based on behavior of gasses) included all but one of the following points. Which is not from Dalton? a) All elements are com ...
Ionization Energy
... On the periodic table, elements are arranged least to greatest by atomic number, which is the number of protons in the nucleus. The periodic table is also arranged in groups which are vertical columns of elements, and periods, which are the horizontal rows of elements. Each element has ionization en ...
... On the periodic table, elements are arranged least to greatest by atomic number, which is the number of protons in the nucleus. The periodic table is also arranged in groups which are vertical columns of elements, and periods, which are the horizontal rows of elements. Each element has ionization en ...
- Lexington JHS
... Described the electrons moving around the nucleus in fixed orbits. Each orbit has a set amount of energy. We use this model for a basic understanding of the atom’s structure. However, more recent research has shown that electrons move around the nucleus in waves rather than elliptical orbits. Electr ...
... Described the electrons moving around the nucleus in fixed orbits. Each orbit has a set amount of energy. We use this model for a basic understanding of the atom’s structure. However, more recent research has shown that electrons move around the nucleus in waves rather than elliptical orbits. Electr ...
Document
... Described the electrons moving around the nucleus in fixed orbits. Each orbit has a set amount of energy. We use this model for a basic understanding of the atom’s structure. However, more recent research has shown that electrons move around the nucleus in waves rather than elliptical orbits. Electr ...
... Described the electrons moving around the nucleus in fixed orbits. Each orbit has a set amount of energy. We use this model for a basic understanding of the atom’s structure. However, more recent research has shown that electrons move around the nucleus in waves rather than elliptical orbits. Electr ...
lecture 7
... give the H2 molecule. As the atoms approach one another, their 1s orbitals begin to overlap. Each electron can then occupy the space around both atoms. In other words, the two electrons can be shared by the atoms. The electrons are attracted simultaneously by the positive charges of the two hydrogen ...
... give the H2 molecule. As the atoms approach one another, their 1s orbitals begin to overlap. Each electron can then occupy the space around both atoms. In other words, the two electrons can be shared by the atoms. The electrons are attracted simultaneously by the positive charges of the two hydrogen ...
Introduction to Chemistry for Coach Keith`s Biology
... * Gases do not have a definite volume or definite shape, but they take the volume & shape of their container * Chemical Changes in matter are essential to all life processes * Biologists study chemistry because all living things are made of the same kinds of matter that make up nonliving things ...
... * Gases do not have a definite volume or definite shape, but they take the volume & shape of their container * Chemical Changes in matter are essential to all life processes * Biologists study chemistry because all living things are made of the same kinds of matter that make up nonliving things ...
Review for Chemistry Unit Test #2 (Chapters 4, 11, and 12) Chapter
... What is an isotope? What is an ion? What holds atoms together? ...
... What is an isotope? What is an ion? What holds atoms together? ...
Name
... 27. _____________________ is the particles or energy emitted from an atomic nucleus when it is unstable due to stronger ________________ repulsive forces than ______________ attractive forces. ...
... 27. _____________________ is the particles or energy emitted from an atomic nucleus when it is unstable due to stronger ________________ repulsive forces than ______________ attractive forces. ...
sub
... Deuterium. Deuterium is not radioactive. Water made from deuterium is called heavy water because the extra neutron makes it heavier. It is used in nuclear reactors. The third isotope of hydrogen is known as Tritium. It has one proton and two neutrons in its nucleus. It IS radioactive. It is formed i ...
... Deuterium. Deuterium is not radioactive. Water made from deuterium is called heavy water because the extra neutron makes it heavier. It is used in nuclear reactors. The third isotope of hydrogen is known as Tritium. It has one proton and two neutrons in its nucleus. It IS radioactive. It is formed i ...