History of the Periodic Table
... (e.g. Cl, Br, I; Ca, Ba, Sr; S, Se, Te) – first indication that elements were related to one another – atomic mass is related to chemical properties Karlsruhe Congress (big Chemistry Conference) 1860 Germany ...
... (e.g. Cl, Br, I; Ca, Ba, Sr; S, Se, Te) – first indication that elements were related to one another – atomic mass is related to chemical properties Karlsruhe Congress (big Chemistry Conference) 1860 Germany ...
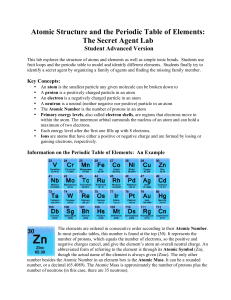
atomic number
... Valence Electrons (cont.) If there are not 8 electrons for the outer level, these empty spots are called vacancies and some electrons are thus unpaired The unpaired electrons in the outer layer are the valence electrons The valence electrons can pair with those from other atoms to “fill” the ...
... Valence Electrons (cont.) If there are not 8 electrons for the outer level, these empty spots are called vacancies and some electrons are thus unpaired The unpaired electrons in the outer layer are the valence electrons The valence electrons can pair with those from other atoms to “fill” the ...
The Periodic Table
... organize their collection. The result is the periodic table. The first scientist to present a comprehensive organized collection of the elements known at the time was Dimitri Mendeleev. What was amazing about his Periodic table is that it predicted elements unknown at that time. Even more he predict ...
... organize their collection. The result is the periodic table. The first scientist to present a comprehensive organized collection of the elements known at the time was Dimitri Mendeleev. What was amazing about his Periodic table is that it predicted elements unknown at that time. Even more he predict ...
unit-8-ppt-3-metalsnon-metalsie-and-size-of-atom
... 2. Elements become more metallic (or better metals) going down a family in the periodic table ...
... 2. Elements become more metallic (or better metals) going down a family in the periodic table ...
Topic 2 Part 1 Slides - Coral Gables Senior High
... Relative Atomic Mass (Ar): the average mass of an element, taking into account all the mass numbers of all the different types of isotopes that exist for the element and their respective percent abundances. This value if relative to (one atom of) 12-C. (The definition of RAM would be a 2 mark IB que ...
... Relative Atomic Mass (Ar): the average mass of an element, taking into account all the mass numbers of all the different types of isotopes that exist for the element and their respective percent abundances. This value if relative to (one atom of) 12-C. (The definition of RAM would be a 2 mark IB que ...
What makes a group of elements
... Because the chemical and physical properties repeated with the eight element, Newlands called this pattern the law of octaves. ...
... Because the chemical and physical properties repeated with the eight element, Newlands called this pattern the law of octaves. ...
Electronegativity
... Oxygen has more protons in its nucleus than carbon so it has a higher effective nuclear charge, which means that the electrons in the valence shell of oxygen are more attracted to the nucleus than the electrons in the valence shell of carbon. The greater attraction between the oxygen nucleus and its ...
... Oxygen has more protons in its nucleus than carbon so it has a higher effective nuclear charge, which means that the electrons in the valence shell of oxygen are more attracted to the nucleus than the electrons in the valence shell of carbon. The greater attraction between the oxygen nucleus and its ...
document
... • Each orbital and each shell can hold a specific number of electrons. •- The first shell can hold only two electrons. 2 electrons in an s orbital (1S2). •- The second shell can hold 8 electrons. 2 electrons in an s orbital and 6 electrons in 3 p orbitals. (2S2 2p6). •- The third shell can hold 18 e ...
... • Each orbital and each shell can hold a specific number of electrons. •- The first shell can hold only two electrons. 2 electrons in an s orbital (1S2). •- The second shell can hold 8 electrons. 2 electrons in an s orbital and 6 electrons in 3 p orbitals. (2S2 2p6). •- The third shell can hold 18 e ...
Chapter 03 Atomic Theory
... In fact, it is impossible to determine the exact location of an electron. The probable location of an electron is based on how much energy the electron has. The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle According to the modern atomic model, at atom has a small positively charged nucleus surrounded by a large ...
... In fact, it is impossible to determine the exact location of an electron. The probable location of an electron is based on how much energy the electron has. The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle According to the modern atomic model, at atom has a small positively charged nucleus surrounded by a large ...
synopsis - Mindfiesta
... order of their atomic weights, similarities appear in physical and chemical properties at regular intervals. The properties of the elements are a periodic function of their atomic weights. Arranged elements in horizontal rows and vertical columns of a table in order of their increasing atomic weight ...
... order of their atomic weights, similarities appear in physical and chemical properties at regular intervals. The properties of the elements are a periodic function of their atomic weights. Arranged elements in horizontal rows and vertical columns of a table in order of their increasing atomic weight ...
Periodic Trends C12-2-07
... 2. Computerchipium (Cc): This element is important for its use as a semiconductor in computers. 3. Lightium (L): This is the lightest of elements; aliens previously used it in their aircraft until their aircraft caught fire in a horrific accident. 4. Breathium(Br): When combined with Lightium (L), i ...
... 2. Computerchipium (Cc): This element is important for its use as a semiconductor in computers. 3. Lightium (L): This is the lightest of elements; aliens previously used it in their aircraft until their aircraft caught fire in a horrific accident. 4. Breathium(Br): When combined with Lightium (L), i ...
What You Need to Know to Pass the Chemistry
... 5. A balanced chemical equation represents conservation of atoms. 6. The coefficients in a balanced chemical equation can be used to determine mole ratios in the reaction. 7. The formula mass of a substance is the sum of the atomic masses of its atoms. The molar mass (gram formula mass) equals the m ...
... 5. A balanced chemical equation represents conservation of atoms. 6. The coefficients in a balanced chemical equation can be used to determine mole ratios in the reaction. 7. The formula mass of a substance is the sum of the atomic masses of its atoms. The molar mass (gram formula mass) equals the m ...
Periodic Trends
... Linus Pauling (shown in Figure 5) defined electronegativity as, “The power of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself.” Often electronegativity is set on a relative scale. Pauling’s scale assigns 4.0 to fluorine (the most electronegative element) and sets the other elements relative to ...
... Linus Pauling (shown in Figure 5) defined electronegativity as, “The power of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself.” Often electronegativity is set on a relative scale. Pauling’s scale assigns 4.0 to fluorine (the most electronegative element) and sets the other elements relative to ...
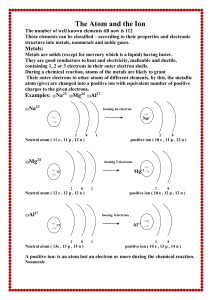
Intro To Atomic Theory
... • Atomic number: The number of protons in an atom OR charge on the nucleus • Neutral atoms: # electrons = # protons • Ion: If electrons are added or removed from a neutral atom, then it is called an ion ...
... • Atomic number: The number of protons in an atom OR charge on the nucleus • Neutral atoms: # electrons = # protons • Ion: If electrons are added or removed from a neutral atom, then it is called an ion ...
Chapter 4 Notes
... In 1909, Rutherford carried out experiments that revealed an arrangement far different from Thomson’s model of the atom. The experimenters set up a lead-shielded box containing radioactive polonium, which emitted a beam of positively charged subatomic particles through a small hole. The sheet of gol ...
... In 1909, Rutherford carried out experiments that revealed an arrangement far different from Thomson’s model of the atom. The experimenters set up a lead-shielded box containing radioactive polonium, which emitted a beam of positively charged subatomic particles through a small hole. The sheet of gol ...
Atomic Structure - WBR Teacher Moodle
... Model of the atom pictures the electrons moving around the nucleus in a region called an electron cloud. The electron cloud is a cloud of varying density surrounding the nucleus. The varying density shows where an electron is more or less likely to be. Atoms with electrons in higher energy levels ha ...
... Model of the atom pictures the electrons moving around the nucleus in a region called an electron cloud. The electron cloud is a cloud of varying density surrounding the nucleus. The varying density shows where an electron is more or less likely to be. Atoms with electrons in higher energy levels ha ...
Chapter 4
... 2. Which of these statements would Dalton have agreed with (use Dalton’s atomic theory)? a. Atoms are the smallest particles of matter b. The mass of an iron atom is different from the mass of ...
... 2. Which of these statements would Dalton have agreed with (use Dalton’s atomic theory)? a. Atoms are the smallest particles of matter b. The mass of an iron atom is different from the mass of ...
What is hydrogen peroxide?
... caused Rutherford to realize that Thomson's model was incorrect, and he proposed his own model. Rutherford's model included a nucleus in the atom. The positively charged proton is located in the very small space at the center of an atom. Most of the atom is empty space occupied by nearly massless el ...
... caused Rutherford to realize that Thomson's model was incorrect, and he proposed his own model. Rutherford's model included a nucleus in the atom. The positively charged proton is located in the very small space at the center of an atom. Most of the atom is empty space occupied by nearly massless el ...
Ch. 4.3 – Distinguishing Among Atoms
... A periodic table is an arrangement of elements in which the elements are separated into groups based on a set of repeating properties. A periodic table allows you to easily compare the properties of one element (or a group of elements) to another element (or group of elements). ...
... A periodic table is an arrangement of elements in which the elements are separated into groups based on a set of repeating properties. A periodic table allows you to easily compare the properties of one element (or a group of elements) to another element (or group of elements). ...
File
... Describe the atomic structure (nucleus / e- s) Write an abbreviated electron configuration State the number of valence electrons Identify at least 3 properties of phosphorous Compare P to N and S in at least 3 ways ...
... Describe the atomic structure (nucleus / e- s) Write an abbreviated electron configuration State the number of valence electrons Identify at least 3 properties of phosphorous Compare P to N and S in at least 3 ways ...
The Atom and the Ion
... liquid element which is bromine. They have no luster, not malleable or ductile (brittle), they are bad conductors to heat and electricity, except graphite which is good conductor to electricity. Most of nonmetals contain 5,6 or 7 electrons in their outer shells. Nonmetals atoms are likely to gain el ...
... liquid element which is bromine. They have no luster, not malleable or ductile (brittle), they are bad conductors to heat and electricity, except graphite which is good conductor to electricity. Most of nonmetals contain 5,6 or 7 electrons in their outer shells. Nonmetals atoms are likely to gain el ...
MENDELEEV AND THE ATOMIC TABLE Dmitri Ivanovich
... All versions of the periodic table only include chemical elements, not mixtures, compounds, or subatomic particles, and isotopes of a given element are represented in the same cell. Isotopes are atoms that have an excess or deficiency of Neutrons in the atomic nucleus, giving them in-between atomic ...
... All versions of the periodic table only include chemical elements, not mixtures, compounds, or subatomic particles, and isotopes of a given element are represented in the same cell. Isotopes are atoms that have an excess or deficiency of Neutrons in the atomic nucleus, giving them in-between atomic ...