Properties of the transition metals
... transitions can occur between them. These transitions require energy provided by light from the visible portion of the electromagnetic spectrum (this has the correct amount of energy). Hence the transition metal ions absorb part of the visible spectrum and we see only those parts of the spectrum whi ...
... transitions can occur between them. These transitions require energy provided by light from the visible portion of the electromagnetic spectrum (this has the correct amount of energy). Hence the transition metal ions absorb part of the visible spectrum and we see only those parts of the spectrum whi ...
F. ELECTRONIC SPECTRA OF COORDINATION COMPOUNDS
... pairs on opposite sides of the color wheel (Newton Wheel) shown in Figure. 1. ...
... pairs on opposite sides of the color wheel (Newton Wheel) shown in Figure. 1. ...
University of Groningen High energy spectroscopy on vanadium
... In a solid, the monopole term F 0 is largely screened due to polarization e ects [16]. The screening of the higher order multipole terms is much smaller [17], which means that transition metal ions in a solid still keep much of their atomic character. The multiplet structure is however di erent from ...
... In a solid, the monopole term F 0 is largely screened due to polarization e ects [16]. The screening of the higher order multipole terms is much smaller [17], which means that transition metal ions in a solid still keep much of their atomic character. The multiplet structure is however di erent from ...
1 5.03, Inorganic Chemistry Prof. Daniel G. Nocera Lecture 9 May 11
... by metal-metal σ bond formation In each case, the clusters assume an octahedral coordination as a result of burying 6 d electrons in what is formally t2g orbitals. The system loses the number of CO’s that is equivalent to the number of e–s in M-Lσ*. This permits maximum M-M bond formation and thus m ...
... by metal-metal σ bond formation In each case, the clusters assume an octahedral coordination as a result of burying 6 d electrons in what is formally t2g orbitals. The system loses the number of CO’s that is equivalent to the number of e–s in M-Lσ*. This permits maximum M-M bond formation and thus m ...
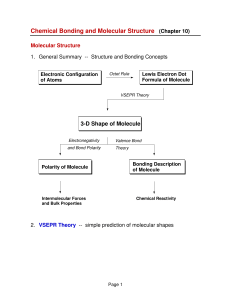
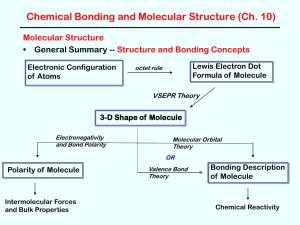
3-D Shape of Molecule
... 2. Molecular Orbitals for simple diatomic molecules (H2 and He2) in H2 the 1s atomic orbitals on the two H atoms are combined into: a bonding MO -- σ1s and an antibonding MO -- σ*1s MO energy level diagram for H2 (only the bonding MO is filled): ...
... 2. Molecular Orbitals for simple diatomic molecules (H2 and He2) in H2 the 1s atomic orbitals on the two H atoms are combined into: a bonding MO -- σ1s and an antibonding MO -- σ*1s MO energy level diagram for H2 (only the bonding MO is filled): ...
Chemistry 3211 – Coordination Chemistry II
... Although crystal field theory is useful in approximating energy levels in transition metal complexes, the fact that it ignores any possible covalent bonding interactions between the metal and its surrounding ligands is rubbish. We have already noted that the ligand field splitting parameters, Δ, are ...
... Although crystal field theory is useful in approximating energy levels in transition metal complexes, the fact that it ignores any possible covalent bonding interactions between the metal and its surrounding ligands is rubbish. We have already noted that the ligand field splitting parameters, Δ, are ...
Chapter1011
... • Write the MO diagram for HCl. Predict the bond order and sketch the bonding and antibonding MO’s. [note: H 1s energy = -13 eV, Cl 3s energy = -25 eV, Cl 3p energy = -14 ...
... • Write the MO diagram for HCl. Predict the bond order and sketch the bonding and antibonding MO’s. [note: H 1s energy = -13 eV, Cl 3s energy = -25 eV, Cl 3p energy = -14 ...
Chapter 5 – Bonding Models in Inorganic Chemistry: 2 The Covalent
... involved corrections, provide more accurate predictions. The best wave function to date has over 100 terms and is accurate to within 0.002%. It’s worth noting that, unlike the sum you’ve been shown here, not all of those one hundred terms have physically explainable meanings. Resonance occurs when m ...
... involved corrections, provide more accurate predictions. The best wave function to date has over 100 terms and is accurate to within 0.002%. It’s worth noting that, unlike the sum you’ve been shown here, not all of those one hundred terms have physically explainable meanings. Resonance occurs when m ...
Chemistry 2000 B Spring 2005 Answers to the Second Problem Set
... complex, so we must consider the splitting of the d orbitals. The electron configuration is [Ar]3d6. For oxygen donors, the high spin configuration is always found. This means the electron filling pattern will be: ...
... complex, so we must consider the splitting of the d orbitals. The electron configuration is [Ar]3d6. For oxygen donors, the high spin configuration is always found. This means the electron filling pattern will be: ...
2016 update to LO
... other also contain transition metals (the d block). The colors of transition metal compounds are highly variable. Aqueous solutions of nickel are green, of copper are blue, and of vanadium can range from yellow to blue to green to violet. What is the origin of these colors? A simple geometrical mode ...
... other also contain transition metals (the d block). The colors of transition metal compounds are highly variable. Aqueous solutions of nickel are green, of copper are blue, and of vanadium can range from yellow to blue to green to violet. What is the origin of these colors? A simple geometrical mode ...
Click www.ondix.com to visit our student-to
... They both lack the ability to form wide range of structural complexes show by the rest of the transitional elements (due to their limited oxidation state which can be relate to by their electronic configuration. See table in introduction) all the transitional elements have variable oxidation states, ...
... They both lack the ability to form wide range of structural complexes show by the rest of the transitional elements (due to their limited oxidation state which can be relate to by their electronic configuration. See table in introduction) all the transitional elements have variable oxidation states, ...
Coordination Chemistry II: Bonding
... where g is approximated to be 2 and n is the number of unpaired electrons. ...
... where g is approximated to be 2 and n is the number of unpaired electrons. ...
Exercises for Advanced Inorganic Chemistry, Part Coordination
... The complex [Ni(CN)4]2- is diamagnetic but [Ni(Cl)4]2- is paramagnetic with two unpaired electrons. Likewise, [Fe(CN)6]3- has only one unpaired electron but [Fe(H2O)6]3+ has five. Explain these observations using a) valence bond theory and b) simple crystal field theory. ...
... The complex [Ni(CN)4]2- is diamagnetic but [Ni(Cl)4]2- is paramagnetic with two unpaired electrons. Likewise, [Fe(CN)6]3- has only one unpaired electron but [Fe(H2O)6]3+ has five. Explain these observations using a) valence bond theory and b) simple crystal field theory. ...
model answers
... 5. The M-P distance in (η5-C5H5)Co(PEt3)2 is 221.8 pm and the P-C distance is 184.6 pm. The corresponding distances in [(η5-C5H5)Co(PEt3)2]+ are 223 pm and 182.9 pm. Account for the changes in these distances as the former complex is oxidised. The oxidised complex is less able to donate electron den ...
... 5. The M-P distance in (η5-C5H5)Co(PEt3)2 is 221.8 pm and the P-C distance is 184.6 pm. The corresponding distances in [(η5-C5H5)Co(PEt3)2]+ are 223 pm and 182.9 pm. Account for the changes in these distances as the former complex is oxidised. The oxidised complex is less able to donate electron den ...
I. Introduction. In this section we consider "simple" electrochemistry
... chelate complexes of bipyridine and phenanthroline do not follow the sequence perfectly due to the unique structural effects of the chelating ligand. The reason the trivalent complex can be favored is related to the large energy gain from the complex in the trivalent state (from -18Dq to -24Dq for t ...
... chelate complexes of bipyridine and phenanthroline do not follow the sequence perfectly due to the unique structural effects of the chelating ligand. The reason the trivalent complex can be favored is related to the large energy gain from the complex in the trivalent state (from -18Dq to -24Dq for t ...
L27
... Many transition metals have colored solutions and are also colored in the solid state. The transition metals have some of their d orbitals empty where a d-d transition can occur. The d-d transitions require excitation energy in the UV-Vis region. The direct interaction of the d electrons with ligand ...
... Many transition metals have colored solutions and are also colored in the solid state. The transition metals have some of their d orbitals empty where a d-d transition can occur. The d-d transitions require excitation energy in the UV-Vis region. The direct interaction of the d electrons with ligand ...
CHEM 415
... The properties of metal complexes can be understood from the energy splitting of the metal ion’s dorbitals in the lower symmetry that the ligands impose. This feature combined with the number of d electrons of the metal determines which orbitals are occupied and the possible spectroscopic transition ...
... The properties of metal complexes can be understood from the energy splitting of the metal ion’s dorbitals in the lower symmetry that the ligands impose. This feature combined with the number of d electrons of the metal determines which orbitals are occupied and the possible spectroscopic transition ...
Bioinorganic Chemistry
... The bound iron(III) ion at each binding site is surrounded by six donor atoms from various ligands. Thus, two oxygen atoms of a carbonate anion coordinate to the metal, and the following amino acid side chains from the protein primary structure also coordinate to the iron(III) ion with one potential ...
... The bound iron(III) ion at each binding site is surrounded by six donor atoms from various ligands. Thus, two oxygen atoms of a carbonate anion coordinate to the metal, and the following amino acid side chains from the protein primary structure also coordinate to the iron(III) ion with one potential ...
Jahn–Teller effect
-3D-balls.png?width=300)
The Jahn–Teller effect, sometimes also known as Jahn–Teller distortion, describes the geometrical distortion of molecules and ions that is associated with certain electron configurations. This electronic effect is named after Hermann Arthur Jahn and Edward Teller, who proved, using group theory, that orbital nonlinear spatially degenerate molecules cannot be stable. The Jahn–Teller theorem essentially states that any nonlinear molecule with a spatially degenerate electronic ground state will undergo a geometrical distortion that removes that degeneracy, because the distortion lowers the overall energy of the species. For a description of another type of geometrical distortion that occurs in crystals with substitutional impurities see article off-center ions.