LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI
... Answer eight questions. estions. Each question carries five marks. 11. Crystal field theory treats square planar geometry as an extreme case of Jahn Teller distortion arising by the elongation of the axial ligands. Explain with the help of crystal field splitting energy ...
... Answer eight questions. estions. Each question carries five marks. 11. Crystal field theory treats square planar geometry as an extreme case of Jahn Teller distortion arising by the elongation of the axial ligands. Explain with the help of crystal field splitting energy ...
Chapter 16 – The Elements: The d
... If the t2g orbital is closer in energy to the π bonding orbital, the two orbitals will interact and the electron in the filled π orbitals will enter the lower energy molecular orbital therefore the electrons in the d-metal will have to occupy the higher energy molecular orbital which will decreases ...
... If the t2g orbital is closer in energy to the π bonding orbital, the two orbitals will interact and the electron in the filled π orbitals will enter the lower energy molecular orbital therefore the electrons in the d-metal will have to occupy the higher energy molecular orbital which will decreases ...
Slide 1
... In the case of octahedral complexes the tetragonal distortion reduces Oh symmetry of a complex to D4h producing either elongated or compressed tetragonal bipyramid and reduces degeneracy of eg and t2g orbitals. The most pronounced stabilization due to the tetragonal distortion is expected for the fo ...
... In the case of octahedral complexes the tetragonal distortion reduces Oh symmetry of a complex to D4h producing either elongated or compressed tetragonal bipyramid and reduces degeneracy of eg and t2g orbitals. The most pronounced stabilization due to the tetragonal distortion is expected for the fo ...
Chem 324 Fall 2009 Quiz #3 KEY NAME: KEY
... d8 Ni2+ can adopt either a square planar or tetrahedral geometry in 4-coordinate complexes whereas d8 Pt2+ adopts the square planar geometry without exception. Rationalize this observation using: [1 pt each] (a) an electronic argument The crystal field splitting favours a square planar arrangement o ...
... d8 Ni2+ can adopt either a square planar or tetrahedral geometry in 4-coordinate complexes whereas d8 Pt2+ adopts the square planar geometry without exception. Rationalize this observation using: [1 pt each] (a) an electronic argument The crystal field splitting favours a square planar arrangement o ...
Rules for filling and removal of d-electrons For filling the orbital order
... For filling the orbital order = 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p. 4s, 3d, 4p Helpful hint - d-orbital occupation and electronic configurations To be able to use Crystal Field Theory (CFT) successfully, it is essential that you can determine the electronic configuration of the central metal ion in any complex. Thi ...
... For filling the orbital order = 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p. 4s, 3d, 4p Helpful hint - d-orbital occupation and electronic configurations To be able to use Crystal Field Theory (CFT) successfully, it is essential that you can determine the electronic configuration of the central metal ion in any complex. Thi ...
$doc.title
... For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. ...
... For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. ...
Orbital Degeneracy versus Electronic Degeneracy
... Hermann Arthur Jahn English Scientist of German Origin ...
... Hermann Arthur Jahn English Scientist of German Origin ...
Transition Metals
... The 3d orbitals are not as important for bonding as are the 4s and 4p, but the details of what happens to the 3d orbitals determine the properties of transition metal complexes. ...
... The 3d orbitals are not as important for bonding as are the 4s and 4p, but the details of what happens to the 3d orbitals determine the properties of transition metal complexes. ...
Applications of CFT for Oh Complexes 1. High- and low
... CN- is a strong field ligand → low spin complex ...
... CN- is a strong field ligand → low spin complex ...
Homework 4.
... 3. Calculate the polarizability of an atom assuming a point charge nucleus in a spherical uniform distribution of electron charge with a radius R. 4. Calculate the increase in the singlet triplet splitting for a Hydrogen molecule in the Heitler London limit (U>>t)in free space relative to one lying ...
... 3. Calculate the polarizability of an atom assuming a point charge nucleus in a spherical uniform distribution of electron charge with a radius R. 4. Calculate the increase in the singlet triplet splitting for a Hydrogen molecule in the Heitler London limit (U>>t)in free space relative to one lying ...
crystal field theory, spectrochemical series, high spin
... if ∆o > pairing energy of electrons, electrons pair and low spin complexes sre formed if ∆o < pairing energy high spin complexes are formed Tetrahedral complexes: Four ligands approach from alternate corners of a cube while metal ion is at the center of the cube. Here t2 will interact more than e or ...
... if ∆o > pairing energy of electrons, electrons pair and low spin complexes sre formed if ∆o < pairing energy high spin complexes are formed Tetrahedral complexes: Four ligands approach from alternate corners of a cube while metal ion is at the center of the cube. Here t2 will interact more than e or ...
Document
... • UV / Vis frequencies are have photons with energies of the sort of values needed to promote electrons from their ground state energy level to a higher level. • A typical substance will require UV photons so does not absorb Visible light. • Most substances are colourless. ...
... • UV / Vis frequencies are have photons with energies of the sort of values needed to promote electrons from their ground state energy level to a higher level. • A typical substance will require UV photons so does not absorb Visible light. • Most substances are colourless. ...
Crystal field theory (II) Octahedral complexes and Jahn
... Octahedral complexes and: dx2‐y2 and dz2 orbitals lie along the x, y, z axis while dxy,dxz and dyz orbitals lie in between the axis. Six ligands are considered as approaching along the three axis. So they interact more with dx2‐y2 and dz2 (eg) than with dxy, dxz and dyz orbitals ...
... Octahedral complexes and: dx2‐y2 and dz2 orbitals lie along the x, y, z axis while dxy,dxz and dyz orbitals lie in between the axis. Six ligands are considered as approaching along the three axis. So they interact more with dx2‐y2 and dz2 (eg) than with dxy, dxz and dyz orbitals ...
Summary of Crystal Field Theory - uni
... Octahedral complexes: in an octahedral ligand field the d-orbitals split in two energy levels. Two of the orbitals, namely dz2 and dx2-y2 (eg-orbitals) point directly towards the ligands, and three orbitals, namely dxy dxz and dyz (t2g-orbitals) point between the ligands. The first ones have a great ...
... Octahedral complexes: in an octahedral ligand field the d-orbitals split in two energy levels. Two of the orbitals, namely dz2 and dx2-y2 (eg-orbitals) point directly towards the ligands, and three orbitals, namely dxy dxz and dyz (t2g-orbitals) point between the ligands. The first ones have a great ...
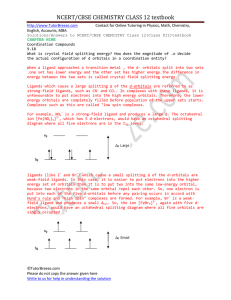
Solution 18. - TutorBreeze.com
... What is crystal field splitting energy? How does the magnitude of .o decide the actual configuration of d orbitals in a coordination entity? When a ligand approaches a transition metal , the d- orbitals split into two sets .one set has lower energy and the other set has higher energy.The difference ...
... What is crystal field splitting energy? How does the magnitude of .o decide the actual configuration of d orbitals in a coordination entity? When a ligand approaches a transition metal , the d- orbitals split into two sets .one set has lower energy and the other set has higher energy.The difference ...
Jahn–Teller effect
-3D-balls.png?width=300)
The Jahn–Teller effect, sometimes also known as Jahn–Teller distortion, describes the geometrical distortion of molecules and ions that is associated with certain electron configurations. This electronic effect is named after Hermann Arthur Jahn and Edward Teller, who proved, using group theory, that orbital nonlinear spatially degenerate molecules cannot be stable. The Jahn–Teller theorem essentially states that any nonlinear molecule with a spatially degenerate electronic ground state will undergo a geometrical distortion that removes that degeneracy, because the distortion lowers the overall energy of the species. For a description of another type of geometrical distortion that occurs in crystals with substitutional impurities see article off-center ions.
![Electronic spectrum of a 0.1 M aqueous solution of [Ti(H2O)6]3+](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/005719667_1-a6d66a78471c6778162e27e0ef555131-300x300.png)