Crystal field theory states that d or f orbital degeneracy
... quadrants, with no electron density on the axes. These three orbitals form the t2g set. In most cases, the d orbitals are degenerate, but sometimes they can split, with the eg and t2g subsets having different energy. The CFT accounts for this. ...
... quadrants, with no electron density on the axes. These three orbitals form the t2g set. In most cases, the d orbitals are degenerate, but sometimes they can split, with the eg and t2g subsets having different energy. The CFT accounts for this. ...
t2g
... " If this were to occur, the ligands along z would be more strongly attracted to the central metal ion and their M-L bond lengths would be shortened relative to those in the xy plane. ! t2g6[(dx2-y2)1(dz2)2]: The single electron in the dx2-y2 orbital would less effectively shield ligands in the xy p ...
... " If this were to occur, the ligands along z would be more strongly attracted to the central metal ion and their M-L bond lengths would be shortened relative to those in the xy plane. ! t2g6[(dx2-y2)1(dz2)2]: The single electron in the dx2-y2 orbital would less effectively shield ligands in the xy p ...
Group 7 : Manganese Chemistry
... Jahn-Teller Theorem: For any nonlinear system in a degenerate state, a distortion will occur that will lift the degeneracy. ...
... Jahn-Teller Theorem: For any nonlinear system in a degenerate state, a distortion will occur that will lift the degeneracy. ...
Document
... Reading off the character table, we see that the group orbitals match the metal s orbital (A1g), the metal p orbitals (T1u), and the dz2 and dx2-y2 metal d orbitals (Eg). We expect bonding/antibonding combinations. The remaining three metal d orbitals are T2g and σ-nonbonding. ...
... Reading off the character table, we see that the group orbitals match the metal s orbital (A1g), the metal p orbitals (T1u), and the dz2 and dx2-y2 metal d orbitals (Eg). We expect bonding/antibonding combinations. The remaining three metal d orbitals are T2g and σ-nonbonding. ...
Chem 400 Chem 340 Inorg Review [AR].S17
... M.O. theory is one of the most important ideas in chemistry – it allows the analysis of bonding in molecules based on orbital interactions and is the basis for a clearer understanding of bonding and flow of electrons in all of chemistry. Provides a context for understanding the continuum of bonding ...
... M.O. theory is one of the most important ideas in chemistry – it allows the analysis of bonding in molecules based on orbital interactions and is the basis for a clearer understanding of bonding and flow of electrons in all of chemistry. Provides a context for understanding the continuum of bonding ...
File
... High Co-ordination seen at beginning of transition series Metal atoms have larger radii Fewer electrons making it easier to accept electrons in sigma donation ...
... High Co-ordination seen at beginning of transition series Metal atoms have larger radii Fewer electrons making it easier to accept electrons in sigma donation ...
Transition metal compounds have interesting magnetic properties.
... For an ion with a d4 electron configuration the number of unpaired electrons will depend on ". Which one will be high spin (more unpaired e!)? Low spin (fewer unpaired e!)? ...
... For an ion with a d4 electron configuration the number of unpaired electrons will depend on ". Which one will be high spin (more unpaired e!)? Low spin (fewer unpaired e!)? ...
CHE450G Final Exam CP-109 December 11, 2006 10:30
... metal orbitals (t2g set in Oh complexes); decrease Δo. (e.g. I-) π-acceptor (π-acids): ligands that do have empty π symmetry orbitals (p or π*) that can engage in π-bonding with transition metal orbitals (t2g set in Oh complexes) and no filled π symmetry orbitals that are close in energy to the meta ...
... metal orbitals (t2g set in Oh complexes); decrease Δo. (e.g. I-) π-acceptor (π-acids): ligands that do have empty π symmetry orbitals (p or π*) that can engage in π-bonding with transition metal orbitals (t2g set in Oh complexes) and no filled π symmetry orbitals that are close in energy to the meta ...
Adv. Inorganic Chemistry
... This is an early theory of electronic structure of complexes especially for the properties of transition metal ions in ionic crystals. The model of an octahedral complex is used, with six ligands placed on the Cartesian axes centered on the metal ion. The ligands interact strongly with the central m ...
... This is an early theory of electronic structure of complexes especially for the properties of transition metal ions in ionic crystals. The model of an octahedral complex is used, with six ligands placed on the Cartesian axes centered on the metal ion. The ligands interact strongly with the central m ...
Use of the Jahn-Teller Theorem in Inorganic Chemistry
... The behavior of the xz - y z and z2 orbitals on a d-orbital model is shown by solid lines and may readily be derived using either the crystal field or the angular-overlapmodel'. The effect of s-d mixing is shown via a dashed line. With three electrons initially in the eBpair of orbitals (e.g., Cu",d ...
... The behavior of the xz - y z and z2 orbitals on a d-orbital model is shown by solid lines and may readily be derived using either the crystal field or the angular-overlapmodel'. The effect of s-d mixing is shown via a dashed line. With three electrons initially in the eBpair of orbitals (e.g., Cu",d ...
Relativistic effects on homonuclear triel clusters
... relative shift of the atomic orbital energies in comparison to the values obtained from non-relativistic calculations, thus stabilizing s- and p-states and destabilizing d- and f-states. The impact of this effect on the crystal chemistry and the properties of compounds containing heavy elements has ...
... relative shift of the atomic orbital energies in comparison to the values obtained from non-relativistic calculations, thus stabilizing s- and p-states and destabilizing d- and f-states. The impact of this effect on the crystal chemistry and the properties of compounds containing heavy elements has ...
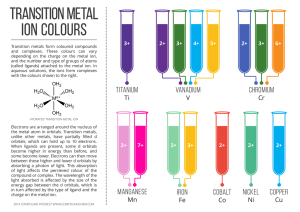
transition metal - Compound Interest
... When ligands are present, some d orbitals become higher in energy than before, and some become lower. Electrons can then move between these higher and lower d orbitals by absorbing a photon of light. This absorption of light affects the percieved colour of the compound or complex. The wavelength of ...
... When ligands are present, some d orbitals become higher in energy than before, and some become lower. Electrons can then move between these higher and lower d orbitals by absorbing a photon of light. This absorption of light affects the percieved colour of the compound or complex. The wavelength of ...
Homework 5 Insert space or answer ques
... Draw the splitting diagram for a square planar complex Be SURE to identify which d orbitals are located where!! 5.) What is the distinction between a weak field and a strong field ligand? What does it mean for electrons filling the d orbitals? Give an example of a weak field ligand. Give an exampl ...
... Draw the splitting diagram for a square planar complex Be SURE to identify which d orbitals are located where!! 5.) What is the distinction between a weak field and a strong field ligand? What does it mean for electrons filling the d orbitals? Give an example of a weak field ligand. Give an exampl ...
InorgCh11.2
... a. Special correlation diagrams useful for interpreting electronic spectra b. Lowest energy state plotted along horizontal axis c. Vertical distance above is correlated to energy of transition ...
... a. Special correlation diagrams useful for interpreting electronic spectra b. Lowest energy state plotted along horizontal axis c. Vertical distance above is correlated to energy of transition ...
Analogy Between Particle in a Box and Jahn–Teller Effect
... This e®ect was ¯rst predicted in 1937 by Hermann Arthur Jahn and Edward Teller, using group theory. The Jahn{ Teller theorem states that in a nonlinear molecule, if degenerate orbitals are asymmetrically occupied, a distortion will occur to remove the degeneracy. This theorem essentially states that ...
... This e®ect was ¯rst predicted in 1937 by Hermann Arthur Jahn and Edward Teller, using group theory. The Jahn{ Teller theorem states that in a nonlinear molecule, if degenerate orbitals are asymmetrically occupied, a distortion will occur to remove the degeneracy. This theorem essentially states that ...
Ligand Field Theory in the New Millenium: Is there Life after DFT?
... Both F- and CN- can form π bonds. Averaged configuration DFT calculations on hypothetical CoL4 species yields ‘d’ orbital energies which can be fitted to standard AOM expressions to determine eπ to eσ ratio. Co-F: ~0.3 Co-CN: ~0.1 (CN π donor!) ...
... Both F- and CN- can form π bonds. Averaged configuration DFT calculations on hypothetical CoL4 species yields ‘d’ orbital energies which can be fitted to standard AOM expressions to determine eπ to eσ ratio. Co-F: ~0.3 Co-CN: ~0.1 (CN π donor!) ...
Molecular orbital approach to bonding in octahedral complexes, ML 6
... Td complexes are less “d-d” than are t2g → eg transitions in Oh complexes. They are therefore more allowed and have larger absorbtivity values (e) ...
... Td complexes are less “d-d” than are t2g → eg transitions in Oh complexes. They are therefore more allowed and have larger absorbtivity values (e) ...
Inorganic Chemistry: Study Guide – Exam 4 – Fall... Study Guide – Suggested Topics A periodic table will be given.
... Be able to predict of a complex is high/low spin, corresponding electron configuration (e.g t2gxegy or ext2y) Derivation of distorted octahedral, square planar, orbital energy levels Jahn-Teller distortions, reasons behind and which e- configurations tend to exhibit. Given splitting of orbit ...
... Be able to predict of a complex is high/low spin, corresponding electron configuration (e.g t2gxegy or ext2y) Derivation of distorted octahedral, square planar, orbital energy levels Jahn-Teller distortions, reasons behind and which e- configurations tend to exhibit. Given splitting of orbit ...
Magnetic Susceptibility Synthesis of Mn(acac)3
... of Unpaired Electrons • Related to the oxidation state of the metal. • Helpful in assigning geometry. • Information provided about metal-metal bonding. • Information provided about the bonding between the metal and its ligands. ...
... of Unpaired Electrons • Related to the oxidation state of the metal. • Helpful in assigning geometry. • Information provided about metal-metal bonding. • Information provided about the bonding between the metal and its ligands. ...
AP Notes Chapter 11
... Crystal Field Theory All the d orbitals are equal in energy they are said to be degenerate Atomic bond theory and molecular orbital theory cannot explain many complexes and their behavior or bonding The electrostatic field or ligand field exists when the atom or ion is approached by a legand. Elect ...
... Crystal Field Theory All the d orbitals are equal in energy they are said to be degenerate Atomic bond theory and molecular orbital theory cannot explain many complexes and their behavior or bonding The electrostatic field or ligand field exists when the atom or ion is approached by a legand. Elect ...
Electronic Structures and Chemical Bonding of Minerals and
... If atoms have similar electronegativities, they adopt closed-shell configurations by sharing electrons with each other; the atoms are held together by covalent bonds. The chemical bond between two different elements is intermediate between the ionic and covalent extremes. The %ionic character is det ...
... If atoms have similar electronegativities, they adopt closed-shell configurations by sharing electrons with each other; the atoms are held together by covalent bonds. The chemical bond between two different elements is intermediate between the ionic and covalent extremes. The %ionic character is det ...
Jahn–Teller effect
-3D-balls.png?width=300)
The Jahn–Teller effect, sometimes also known as Jahn–Teller distortion, describes the geometrical distortion of molecules and ions that is associated with certain electron configurations. This electronic effect is named after Hermann Arthur Jahn and Edward Teller, who proved, using group theory, that orbital nonlinear spatially degenerate molecules cannot be stable. The Jahn–Teller theorem essentially states that any nonlinear molecule with a spatially degenerate electronic ground state will undergo a geometrical distortion that removes that degeneracy, because the distortion lowers the overall energy of the species. For a description of another type of geometrical distortion that occurs in crystals with substitutional impurities see article off-center ions.





![Chem 400 Chem 340 Inorg Review [AR].S17](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000220292_1-82084c4723d43bb722b21295b237196f-300x300.png)