TRANSITION METALS - Pennsylvania State University
... temp applications, e.g. in the reentry shield on the Apollo capsules. TiO2 is a white pigment in all white paints. V Vanadium steel (Fe/V alloy) is the toughest steel known. It is used in car springs. V2O5 is a catalyst used in sulfuric acid production. ...
... temp applications, e.g. in the reentry shield on the Apollo capsules. TiO2 is a white pigment in all white paints. V Vanadium steel (Fe/V alloy) is the toughest steel known. It is used in car springs. V2O5 is a catalyst used in sulfuric acid production. ...
Homework One - Calderglen High School
... Light of wavelength varying from 400 to 700 nm is passed through a solution containing [VO]2+ ions. Copy the axes shown below and draw the absorption spectrum that you would expect to obtain. (Page 14 of your Data Booklet may be helpful.) ...
... Light of wavelength varying from 400 to 700 nm is passed through a solution containing [VO]2+ ions. Copy the axes shown below and draw the absorption spectrum that you would expect to obtain. (Page 14 of your Data Booklet may be helpful.) ...
Document
... Ex. [Mn(CN)6]4 Strong-Field Ligands, such CN-, cause large crystal field splitting of the d-orbital energies, i.e., higher (D) (D) is larger than (Epairing) Thus, it takes less energy to pair up in the “t2g“ set than would be required to move up to the “eg” set The number of unpaired electr ...
... Ex. [Mn(CN)6]4 Strong-Field Ligands, such CN-, cause large crystal field splitting of the d-orbital energies, i.e., higher (D) (D) is larger than (Epairing) Thus, it takes less energy to pair up in the “t2g“ set than would be required to move up to the “eg” set The number of unpaired electr ...
Transition Metals and Complex Ion Chemistry - Ars
... metal ions because the electron pair is usually held in place by the positive charge. Coordination number - the total number of bonds Um metal forms with ligands. The most common coordination number is 6, although 4 is somewhat common also. Complex ions with coordination number of 2 through 8 are kn ...
... metal ions because the electron pair is usually held in place by the positive charge. Coordination number - the total number of bonds Um metal forms with ligands. The most common coordination number is 6, although 4 is somewhat common also. Complex ions with coordination number of 2 through 8 are kn ...
Lecture 17
... axial M-L bonds, and shortening of the in-plane bonds. Cu(II) is usually tetragonally distorted, while low-spin Ni(II) is ...
... axial M-L bonds, and shortening of the in-plane bonds. Cu(II) is usually tetragonally distorted, while low-spin Ni(II) is ...
HW-1-Ch1-Atomic-structure-W16
... 35. Penetration & Shielding of an Electron in multi-electron atom and how does it affect the filling order as given by “Building Up” principle? ...
... 35. Penetration & Shielding of an Electron in multi-electron atom and how does it affect the filling order as given by “Building Up” principle? ...
Chapter 2 - U of L Class Index
... These complexes are also hydrates. (Recall Chemistry 1000!) Thus, a co-ordination complex must contain a transition metal cation and several ligands. It may also have counter ion(s) (to balance charge) or extra water molecules. When naming a coordination complex or complex salt, look for these compo ...
... These complexes are also hydrates. (Recall Chemistry 1000!) Thus, a co-ordination complex must contain a transition metal cation and several ligands. It may also have counter ion(s) (to balance charge) or extra water molecules. When naming a coordination complex or complex salt, look for these compo ...
Document
... CH2 has two electrons in the 3a1 MO, favoured by a very small angle of 102.4o. Promotion of an e- from 3a1 to 1b1 results in both singlet and triplet states, where the molecule is still bent but with a larger angle. The triplet state of CH2, X3B1, lies lower in energy (by 37.75 kJ mol-1) than the si ...
... CH2 has two electrons in the 3a1 MO, favoured by a very small angle of 102.4o. Promotion of an e- from 3a1 to 1b1 results in both singlet and triplet states, where the molecule is still bent but with a larger angle. The triplet state of CH2, X3B1, lies lower in energy (by 37.75 kJ mol-1) than the si ...
PN junction Across - E
... A voltage applied to a circuit or device, esp a semiconductor device, in the direction that produces the larger current To treat a semiconductor with an additive used to improve its properties. The difference in energy between electron orbitals in which the electrons are not free to move (called val ...
... A voltage applied to a circuit or device, esp a semiconductor device, in the direction that produces the larger current To treat a semiconductor with an additive used to improve its properties. The difference in energy between electron orbitals in which the electrons are not free to move (called val ...
Name
... A weak field ligand can be thought of as a species that does not have enough strength to separate the d orbitals much from one another. It creates a small value, which means that electrons will fill in all the d orbitals, even the higher energy d orbitals before the electrons pair up. 6.) Draw orb ...
... A weak field ligand can be thought of as a species that does not have enough strength to separate the d orbitals much from one another. It creates a small value, which means that electrons will fill in all the d orbitals, even the higher energy d orbitals before the electrons pair up. 6.) Draw orb ...
Document
... axial M-L bonds, and shortening of the in-plane bonds. Cu(II) is usually tetragonally distorted, while low-spin Ni(II) is ...
... axial M-L bonds, and shortening of the in-plane bonds. Cu(II) is usually tetragonally distorted, while low-spin Ni(II) is ...
Chem312 Au03 Problem Set 4
... This paper reports unusual two-coordinate nickel complexes. The nickel can only bind two ligands because the ligands are so huge (also called bulky or sterically large or sterically encumbered). Figures 1 and 3 show the large size of the ligands. They are the results of Xray diffraction experiments ...
... This paper reports unusual two-coordinate nickel complexes. The nickel can only bind two ligands because the ligands are so huge (also called bulky or sterically large or sterically encumbered). Figures 1 and 3 show the large size of the ligands. They are the results of Xray diffraction experiments ...
Chapter 22 - U of L Class Index
... These complexes are also hydrates. (Recall Chemistry 1000!) Thus, a co-ordination complex must contain a transition metal cation and several ligands. It may also have counter ion(s) (to balance charge) or extra water molecules. When naming a coordination complex or complex salt, look for these compo ...
... These complexes are also hydrates. (Recall Chemistry 1000!) Thus, a co-ordination complex must contain a transition metal cation and several ligands. It may also have counter ion(s) (to balance charge) or extra water molecules. When naming a coordination complex or complex salt, look for these compo ...
Chemical Bonding and Electronic Structure of Buckminsterfullerene
... Since C60 has 12,500 resonance structures involving its 60 r-electrons we may profitably consider the r-electrons to be particles delocalized over a sphere. The solution of SchrOdinger's equation for a particle on a sphere is well known. Since a particle on a sphere is restricted to move in two dire ...
... Since C60 has 12,500 resonance structures involving its 60 r-electrons we may profitably consider the r-electrons to be particles delocalized over a sphere. The solution of SchrOdinger's equation for a particle on a sphere is well known. Since a particle on a sphere is restricted to move in two dire ...
InorgCh15.1
... a) Mn(CO)5 CH3 [Fe(CO)5]+ [Cr(CO)5]b) Coordination number should be the same 2) Gain or loss of electrons from two isolobal fragments yields isolobal fragments a) CH3 [Fe(CO)5]+ [Cr(CO)5]- (7e- or 17e- species) b) CH3+ [Fe(CO)5]2+ [Cr(CO)5]o (6e- or 16e- species) c) CH3- ...
... a) Mn(CO)5 CH3 [Fe(CO)5]+ [Cr(CO)5]b) Coordination number should be the same 2) Gain or loss of electrons from two isolobal fragments yields isolobal fragments a) CH3 [Fe(CO)5]+ [Cr(CO)5]- (7e- or 17e- species) b) CH3+ [Fe(CO)5]2+ [Cr(CO)5]o (6e- or 16e- species) c) CH3- ...
department of chemistry ch 102 (inorganic): tutorial no. 5
... 1. The following complexes have the indicated effective magnetic moments. Describe the structure and bonding of the complexes on the basis of the meff values. K2NiF6 0.0; Ni(NH3)2Cl2 3.3; Ni(PEt3)2Cl2 0.0; Ni(Ph3AsO)2Cl2 3.95. ...
... 1. The following complexes have the indicated effective magnetic moments. Describe the structure and bonding of the complexes on the basis of the meff values. K2NiF6 0.0; Ni(NH3)2Cl2 3.3; Ni(PEt3)2Cl2 0.0; Ni(Ph3AsO)2Cl2 3.95. ...
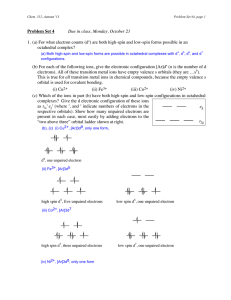
[Zn(NH3)4]SO4 [Cr(NH3)5Cl]Cl2 [Co(en)2Br2]2SO4
... A weak field ligand can be thought of as a species that does not have enough strength to separate the d orbitals much from one another. It creates a small ∆ value, which means that electrons will fill in all the d orbitals, even the higher energy d orbitals before the electrons pair up. 6.) Draw orb ...
... A weak field ligand can be thought of as a species that does not have enough strength to separate the d orbitals much from one another. It creates a small ∆ value, which means that electrons will fill in all the d orbitals, even the higher energy d orbitals before the electrons pair up. 6.) Draw orb ...
Get Day 16 - Mattson Creighton
... octahedral field of ligands present. Hint: The three d-orbitals 3 – 5 all behave the same; they are energetically degenerate. The other two are also energetically degenerate among the two of them. While this isn’t obvious by looking at the diversely different structures of each, they do have the sa ...
... octahedral field of ligands present. Hint: The three d-orbitals 3 – 5 all behave the same; they are energetically degenerate. The other two are also energetically degenerate among the two of them. While this isn’t obvious by looking at the diversely different structures of each, they do have the sa ...
for quiz on 13 Mar
... 20.1 **CORRECTION to this answer… something even I forgot: when you’re filling the orbitals with electrons, 4s fills before 3d. However, when you’re removing electrons (forming cations), the d orbitals will remain filled while you first remove s electrons (for instance, you first remove the 2 electr ...
... 20.1 **CORRECTION to this answer… something even I forgot: when you’re filling the orbitals with electrons, 4s fills before 3d. However, when you’re removing electrons (forming cations), the d orbitals will remain filled while you first remove s electrons (for instance, you first remove the 2 electr ...
Covalent and Metallic Bonding
... Electron Pair Repulsion Theory This is a useful model for predicting the structures of covalent molecules. It is especially useful for molecules constructed of first-row atoms (e.g., N, C, O and F). • In a molecule, each atom contributes the electrons in its outer shell (n-quantum number) as “valen ...
... Electron Pair Repulsion Theory This is a useful model for predicting the structures of covalent molecules. It is especially useful for molecules constructed of first-row atoms (e.g., N, C, O and F). • In a molecule, each atom contributes the electrons in its outer shell (n-quantum number) as “valen ...
Ligand Field Theory www.AssignmentPoint.com Ligand field theory
... are anti-bonding π* orbitals. These orbitals are close in energy to the dxy, dxz and dyz orbitals, with which they combine to form bonding orbitals (i.e. orbitals of lower energy than the aforementioned set of d-orbitals). The corresponding anti-bonding orbitals are higher in energy than the anti-bo ...
... are anti-bonding π* orbitals. These orbitals are close in energy to the dxy, dxz and dyz orbitals, with which they combine to form bonding orbitals (i.e. orbitals of lower energy than the aforementioned set of d-orbitals). The corresponding anti-bonding orbitals are higher in energy than the anti-bo ...
+1 0
... described by a new set of quantum numbers. ML = total orbital angular momentum =Σml MS = total spin angular momentum = Σms ...
... described by a new set of quantum numbers. ML = total orbital angular momentum =Σml MS = total spin angular momentum = Σms ...
Jahn–Teller effect
-3D-balls.png?width=300)
The Jahn–Teller effect, sometimes also known as Jahn–Teller distortion, describes the geometrical distortion of molecules and ions that is associated with certain electron configurations. This electronic effect is named after Hermann Arthur Jahn and Edward Teller, who proved, using group theory, that orbital nonlinear spatially degenerate molecules cannot be stable. The Jahn–Teller theorem essentially states that any nonlinear molecule with a spatially degenerate electronic ground state will undergo a geometrical distortion that removes that degeneracy, because the distortion lowers the overall energy of the species. For a description of another type of geometrical distortion that occurs in crystals with substitutional impurities see article off-center ions.
















![[Zn(NH3)4]SO4 [Cr(NH3)5Cl]Cl2 [Co(en)2Br2]2SO4](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000163042_1-5a721100d3f3517024b8f44b530a31a4-300x300.png)





