Final Exam Class Review - Mrs. Kittrell`s Science Classes
... • Make a given table that lists the information you are given. BE SURE to include the item you are to find! • USE the Reference sheet! Find the equation that fits what you have. • Put the item you need to find on one side of the equals sign. • Add the other numbers and punch in the ...
... • Make a given table that lists the information you are given. BE SURE to include the item you are to find! • USE the Reference sheet! Find the equation that fits what you have. • Put the item you need to find on one side of the equals sign. • Add the other numbers and punch in the ...
Atomic Physics - SFSU Physics & Astronomy
... • Higher states = “excited states” • Photon energy equals difference in state energies • Hydrogen atom example – Energy levels – Line spectra ...
... • Higher states = “excited states” • Photon energy equals difference in state energies • Hydrogen atom example – Energy levels – Line spectra ...
Semester Exam Review Guide
... 18. Which of the statement about the periodic table is true: a. elements are arranged by atomic number. b. metallic elements are placed on the right-hand side. c. elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons. d. both a and c. 19. __________ brought back the concept of the ato ...
... 18. Which of the statement about the periodic table is true: a. elements are arranged by atomic number. b. metallic elements are placed on the right-hand side. c. elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons. d. both a and c. 19. __________ brought back the concept of the ato ...
Jeopardy
... What property of metal best describes why an ice cube will melt faster in a metal pan than on a plastic cutting board---even if both items are at room temperature ...
... What property of metal best describes why an ice cube will melt faster in a metal pan than on a plastic cutting board---even if both items are at room temperature ...
here
... Intrinsic Semiconductors – No impurities and lattice defects in its crystal structure – If thermal or optical energy (E > Eg) break covalent bond free electron and hole – Electrons and holes are created in pairs, so no = po ≡ ni (at thermal equilibrium) o no = electron concentration at thermal e ...
... Intrinsic Semiconductors – No impurities and lattice defects in its crystal structure – If thermal or optical energy (E > Eg) break covalent bond free electron and hole – Electrons and holes are created in pairs, so no = po ≡ ni (at thermal equilibrium) o no = electron concentration at thermal e ...
Unit Five: Periodic Table Families
... Many paramagnetic: Attracted to magnetic fields Some ferromagnetic: Can make their own magnetic field More unpaired d electrons = harder, higher melting point, higher density Little variation to electronegativity and atomic size due to shielding Can lose both s and d electrons to form +1+/ ...
... Many paramagnetic: Attracted to magnetic fields Some ferromagnetic: Can make their own magnetic field More unpaired d electrons = harder, higher melting point, higher density Little variation to electronegativity and atomic size due to shielding Can lose both s and d electrons to form +1+/ ...
File
... • Since a pair of electrons is shared in a covalent bond, the electrons move throughout the entire molecular orbital. • In the above example, both hydrogen atoms gain the electron configuration of helium. • Covalent compounds are compounds with covalent bonds. • Covalent compounds form from atoms on ...
... • Since a pair of electrons is shared in a covalent bond, the electrons move throughout the entire molecular orbital. • In the above example, both hydrogen atoms gain the electron configuration of helium. • Covalent compounds are compounds with covalent bonds. • Covalent compounds form from atoms on ...
Chemistry Unit Study Guide Key
... laws says that no matter can be created or destroyed. Therefore, each side of the equation must be the same. ...
... laws says that no matter can be created or destroyed. Therefore, each side of the equation must be the same. ...
form revision a
... There are two types of compound. Covalent compounds form when non-metal atoms form covalent bonds by sharing their outer electrons. Covalent compounds exist as molecules. Ionic compounds form when metal atoms join to non-metal atoms by transferring electron(s) from the metal to the non-metal. The re ...
... There are two types of compound. Covalent compounds form when non-metal atoms form covalent bonds by sharing their outer electrons. Covalent compounds exist as molecules. Ionic compounds form when metal atoms join to non-metal atoms by transferring electron(s) from the metal to the non-metal. The re ...
Chapter 8 - TeacherWeb
... share one pair of valence electrons A double covalent bond occurs when two atoms share two pairs of valence electrons A triple covalent bond occurs when two atoms share three pairs of covalent bonds ...
... share one pair of valence electrons A double covalent bond occurs when two atoms share two pairs of valence electrons A triple covalent bond occurs when two atoms share three pairs of covalent bonds ...
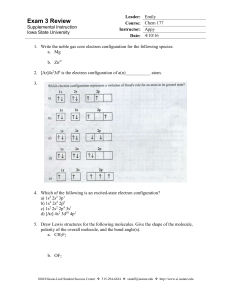
Exam 3 Review - Iowa State University
... 10. In terms of electronegativity, determine whether the following compounds contain nonpolar covalent, polar covalent, or ionic bonds. a. I—I b. NaI c. Cl—I d. H—I ...
... 10. In terms of electronegativity, determine whether the following compounds contain nonpolar covalent, polar covalent, or ionic bonds. a. I—I b. NaI c. Cl—I d. H—I ...
Chapter 4 REVIEW
... 28. Chlorine is a very reactive element that forms stable compounds with most other elements. For each of the following chlorine compounds, draw Lewis and structural diagrams, and then predict the polarity of the molecules: (a) NCl3 (c) PCl5 (b) SiCl4 (d) SCl6 ...
... 28. Chlorine is a very reactive element that forms stable compounds with most other elements. For each of the following chlorine compounds, draw Lewis and structural diagrams, and then predict the polarity of the molecules: (a) NCl3 (c) PCl5 (b) SiCl4 (d) SCl6 ...
Transition metal compounds have interesting magnetic properties.
... unpaired electrons will depend on ". Which one will be high spin (more unpaired e!)? Low spin (fewer unpaired e!)? ...
... unpaired electrons will depend on ". Which one will be high spin (more unpaired e!)? Low spin (fewer unpaired e!)? ...
Ch. 2 - Ltcconline.net
... 2. subatomic particles make up the atom. 3. Differences in elements 4. isotopes - different numbers of neutrons so mass changes E. Electron arrangement determines chemical properties of atom 1. electrons determine how an atom behaves 2. electrons vary in energy 3. electrons occur at certain energy l ...
... 2. subatomic particles make up the atom. 3. Differences in elements 4. isotopes - different numbers of neutrons so mass changes E. Electron arrangement determines chemical properties of atom 1. electrons determine how an atom behaves 2. electrons vary in energy 3. electrons occur at certain energy l ...
Course Syllabus - Honors Chemistry
... c. Salt crystals, such as NaCl, are repeating patterns of positive and negative ions held together by electrostatic attraction. d. Atoms and molecules in liquids move in a random pattern relative to one another because the intermolecular forces are too weak to hold the atoms or molecules in a solid ...
... c. Salt crystals, such as NaCl, are repeating patterns of positive and negative ions held together by electrostatic attraction. d. Atoms and molecules in liquids move in a random pattern relative to one another because the intermolecular forces are too weak to hold the atoms or molecules in a solid ...
AP Chapter 9 Molecular Shapes
... • Nonbonding pairs of electrons (unshared pairs) exert more repulsions than bonding pairs (shared pairs.) • Electron domains from multiple bonds exert slightly more repulsions than those from single bonds. ...
... • Nonbonding pairs of electrons (unshared pairs) exert more repulsions than bonding pairs (shared pairs.) • Electron domains from multiple bonds exert slightly more repulsions than those from single bonds. ...
Chapter 4 Notes - Atomic Theory
... Group 2 = alkaline earth metals (2+, reactive) Group 17 = the halogens (1-, very reactive) Group 18 = noble gases (0, unreactive) Periods are horizontal rows on the periodic table. ...
... Group 2 = alkaline earth metals (2+, reactive) Group 17 = the halogens (1-, very reactive) Group 18 = noble gases (0, unreactive) Periods are horizontal rows on the periodic table. ...
EOC Review - Dorman Freshman Campus
... Physical change: Change in a substance’s size, shape, or state of matter Chemical change: A change of one substance into a different substance Do you still have the same substance or is it a new substance? ...
... Physical change: Change in a substance’s size, shape, or state of matter Chemical change: A change of one substance into a different substance Do you still have the same substance or is it a new substance? ...
Advanced Chemistry Midterm
... 36. What are parts of the electromagnetic spectrum in order from lowest frequency/lowest energy to highest frequency/highest energy? ...
... 36. What are parts of the electromagnetic spectrum in order from lowest frequency/lowest energy to highest frequency/highest energy? ...
Microsoft Word
... whenever possible, valence electrons in covalent compounds distribute so that each main-group element is surrounded by 8 electrons (except hydrogen which wants 2 electrons around it). ...
... whenever possible, valence electrons in covalent compounds distribute so that each main-group element is surrounded by 8 electrons (except hydrogen which wants 2 electrons around it). ...
document
... Part A: Match the letter of the correct definition to the Vocabulary term. 1. Octet Rule E A. A reaction in which one substance breaks down into its parts. 2. Ion C B. A bond that is formed by sharing electrons. 3. Charge D C. A charged atom. D. The number of electrons an 4. Covalent Bond B element ...
... Part A: Match the letter of the correct definition to the Vocabulary term. 1. Octet Rule E A. A reaction in which one substance breaks down into its parts. 2. Ion C B. A bond that is formed by sharing electrons. 3. Charge D C. A charged atom. D. The number of electrons an 4. Covalent Bond B element ...
Ch. 8 Sections 8.1-8.3 Powerpoint
... •In ionic bonding the participating atoms are so different that one or more electrons are transferred to form oppositely charged ions, when then attract each other. •In covalent bonding (also called nonpolar covalent bonding) two identical atoms share electrons equally. •There are intermediate case ...
... •In ionic bonding the participating atoms are so different that one or more electrons are transferred to form oppositely charged ions, when then attract each other. •In covalent bonding (also called nonpolar covalent bonding) two identical atoms share electrons equally. •There are intermediate case ...
ionization energies
... the initial periodic table belonged to undiscovered elements • For example, in 1869, the element following Zn on the periodic table was As. Yet, he knew to put As in group 15 rather than 13 because As behaved like P, and he knew that two undiscovered elements (Ga and Ge) would fill the gaps. ...
... the initial periodic table belonged to undiscovered elements • For example, in 1869, the element following Zn on the periodic table was As. Yet, he knew to put As in group 15 rather than 13 because As behaved like P, and he knew that two undiscovered elements (Ga and Ge) would fill the gaps. ...
Study Guide 1st Semester
... 32. Where are the alkali metal elements found? How do their electron configurations end? What are some typical behaviors of alkali metals? 33. Where are the alkaline earth metals found? How do their electron configurations end? What are some typical behaviors of alkaline earth metals? 34. What is a ...
... 32. Where are the alkali metal elements found? How do their electron configurations end? What are some typical behaviors of alkali metals? 33. Where are the alkaline earth metals found? How do their electron configurations end? What are some typical behaviors of alkaline earth metals? 34. What is a ...
nature of Matter
... When electrons are transferred from one atom to another, an ionic bond is formed. An atom that loses electrons has a + charge. An atom that gains an electron has a – charge. These + & - charged atoms are known as ions. These oppositely charged ions have a strong attraction thus forming the ionic bon ...
... When electrons are transferred from one atom to another, an ionic bond is formed. An atom that loses electrons has a + charge. An atom that gains an electron has a – charge. These + & - charged atoms are known as ions. These oppositely charged ions have a strong attraction thus forming the ionic bon ...