Earth`s Chemistry
... Chemical bonds = forces that hold atoms together to make compounds Ionic bonds = electrons are transferred from one atom to another Ion = an atom or group of atoms that carry an electrical charge ( positive or negative) ...
... Chemical bonds = forces that hold atoms together to make compounds Ionic bonds = electrons are transferred from one atom to another Ion = an atom or group of atoms that carry an electrical charge ( positive or negative) ...
Marking scheme
... The resistances larger / line (graph) higher (and horizontal) (Can score on Fig.1.2 a) The electrons collide more often / frequently (with vibrating atoms) ...
... The resistances larger / line (graph) higher (and horizontal) (Can score on Fig.1.2 a) The electrons collide more often / frequently (with vibrating atoms) ...
Chemistry 102B What`s in an atom? Before “Chemistry” Other Early
... Developed the “Law of conservation of Mass”. • Joseph Proust (early 1800s) – discovered that a given compound always contained the same proportions of certain elements by mass. “Law of Definite Proportions” • John Dalton (early 1800s) – noted that elements that combined to form more than one kind of ...
... Developed the “Law of conservation of Mass”. • Joseph Proust (early 1800s) – discovered that a given compound always contained the same proportions of certain elements by mass. “Law of Definite Proportions” • John Dalton (early 1800s) – noted that elements that combined to form more than one kind of ...
Document
... Rule of Octet or The Octet Rule Stable energy levels are full energy levels and allow atoms to not react. The first energy level is stable with 2 electrons and other levels with 8. This is known as the rule of Octet or Octet rule. ...
... Rule of Octet or The Octet Rule Stable energy levels are full energy levels and allow atoms to not react. The first energy level is stable with 2 electrons and other levels with 8. This is known as the rule of Octet or Octet rule. ...
Chemistry Review - pams-hoey
... Atomic Number and Mass • The number of protons in the nucleus determines the atomic number of the element • The mass number is the sum of the protons and neutrons and is used to distinguish one isotope ...
... Atomic Number and Mass • The number of protons in the nucleus determines the atomic number of the element • The mass number is the sum of the protons and neutrons and is used to distinguish one isotope ...
Revision topic 1-3
... superscripts must always total the number of electrons in the atom (or ion). ...
... superscripts must always total the number of electrons in the atom (or ion). ...
Electron
... • A subatomic particle of the nucleus of an atom without a charge that contributes to the mass of an atom. ...
... • A subatomic particle of the nucleus of an atom without a charge that contributes to the mass of an atom. ...
Chemistry I Honors
... ✦ Metals react with nonmetals ✦ Ions paired have lower energy (greater stability) than separated ions Covalent ✦ Electrons are shared by nuclei ✦ Pure covalent (nonpolar covalent) - electrons are shared evenly ✦ Polar covalent - electrons shared unequally ...
... ✦ Metals react with nonmetals ✦ Ions paired have lower energy (greater stability) than separated ions Covalent ✦ Electrons are shared by nuclei ✦ Pure covalent (nonpolar covalent) - electrons are shared evenly ✦ Polar covalent - electrons shared unequally ...
3. atomic structure
... In this class we will be performing an experiment called the “Flame Test”. We will be heating up metal powders in order to excite the electrons to jump from a lower energy level to a higher energy level. When an electron returns from a higher energy state to a lower energy state, it emits a specific ...
... In this class we will be performing an experiment called the “Flame Test”. We will be heating up metal powders in order to excite the electrons to jump from a lower energy level to a higher energy level. When an electron returns from a higher energy state to a lower energy state, it emits a specific ...
Semiconductivity
... electrons to fill the 3N levels of t2g band. For VO also, the t2g band is parly filled. As in the case of pure metals, a partly filled band leads to metallic conductivity. Consequently TiO & VO have metallic conductivity. On this basis one would expect MnO, CoO, NiO which also have partly filled ban ...
... electrons to fill the 3N levels of t2g band. For VO also, the t2g band is parly filled. As in the case of pure metals, a partly filled band leads to metallic conductivity. Consequently TiO & VO have metallic conductivity. On this basis one would expect MnO, CoO, NiO which also have partly filled ban ...
File - Mr. Holz`s Website
... b. Be able to answer the above question, and also be able to draw in the electrons for specific elements c. Why are the Elements in the first group SO reactive in water? Remember that video that showed Sodium, Lithium, Ceasium, etc. being dropped in water? Hint: It has something to do with the valen ...
... b. Be able to answer the above question, and also be able to draw in the electrons for specific elements c. Why are the Elements in the first group SO reactive in water? Remember that video that showed Sodium, Lithium, Ceasium, etc. being dropped in water? Hint: It has something to do with the valen ...
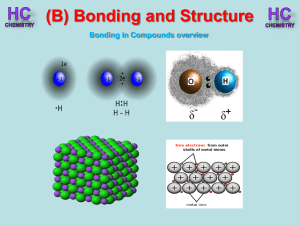
Lesson 1 - Bonding in compounds overview
... m.p.’s increase because the strength of the London dispersion forces increase with the increasing size of the molecule. So more Energy is needed to separate molecules. ...
... m.p.’s increase because the strength of the London dispersion forces increase with the increasing size of the molecule. So more Energy is needed to separate molecules. ...
4 - College of Arts and Sciences
... Identify the GROUP of elements that corresponds to each of the following generalized electron configurations ...
... Identify the GROUP of elements that corresponds to each of the following generalized electron configurations ...
Shiny, Happy Pretest - Alex LeMay – Science
... 18. First to get an stream of electrons to pass through a vacuum tube, establishing the existence of cathode rays. _____________________ 19. Is credited with discovering the electron, calculating the electron’s mass to charge ratio, and creating the plum pudding or blueberry muffin model of the atom ...
... 18. First to get an stream of electrons to pass through a vacuum tube, establishing the existence of cathode rays. _____________________ 19. Is credited with discovering the electron, calculating the electron’s mass to charge ratio, and creating the plum pudding or blueberry muffin model of the atom ...
What is matter made of?
... substances around us: your table, your body, a pencil, water, air or all solids liquids & gasses. Anything that has mass and volume (takes up space) Made up of different kinds of atoms ...
... substances around us: your table, your body, a pencil, water, air or all solids liquids & gasses. Anything that has mass and volume (takes up space) Made up of different kinds of atoms ...
Document
... (E) none of the above 47. Lanthanide or rare earth elements have atoms or ions with partially filled: (A) s subshells (B) p subshells (C) d subshells (D) f subshells (E) g subshells 48. Which of the following liquids would make a good solvent for iodine, I2? (A) HCl (B) H2O (C) CH3OH (D) NH3 (E) CS ...
... (E) none of the above 47. Lanthanide or rare earth elements have atoms or ions with partially filled: (A) s subshells (B) p subshells (C) d subshells (D) f subshells (E) g subshells 48. Which of the following liquids would make a good solvent for iodine, I2? (A) HCl (B) H2O (C) CH3OH (D) NH3 (E) CS ...
Chapter Outline • Review of Atomic Structure Electrons, protons
... for instance the hardest it is to melt the solid, or to evaporate its atoms. ...
... for instance the hardest it is to melt the solid, or to evaporate its atoms. ...
Preliminary Course Atomic Structure 1 + 2
... Molecules are discrete entities with discrete properties Atoms form molecules in a very predictable way, based on their elements ...
... Molecules are discrete entities with discrete properties Atoms form molecules in a very predictable way, based on their elements ...
Electrical conduction - University of Toronto Physics
... Superconductors are those materials which are neither conductors nor insulators. They are totally dependent on the temperature. As the temperature changes their properties also change. In metals and certain other materials, a transition to the superconducting state occurs at low (sub-cryogenic) temp ...
... Superconductors are those materials which are neither conductors nor insulators. They are totally dependent on the temperature. As the temperature changes their properties also change. In metals and certain other materials, a transition to the superconducting state occurs at low (sub-cryogenic) temp ...
Chemistry Part 1
... combined chemically Compound—two or more different atoms combined chemically ...
... combined chemically Compound—two or more different atoms combined chemically ...
Metals & Metallurgy
... Because the bands are so close, it is easy to promote electrons to a higher energy level. With M.O.'s, half of the orbitals are bonding and half are antibonding. Thus, with halffilled d subshells, the bonding M.O.'s are filled. After that, the electrons begin to fill antibonding orbitals which weake ...
... Because the bands are so close, it is easy to promote electrons to a higher energy level. With M.O.'s, half of the orbitals are bonding and half are antibonding. Thus, with halffilled d subshells, the bonding M.O.'s are filled. After that, the electrons begin to fill antibonding orbitals which weake ...
chapter 6 sec 2 resonance structure
... H is 2.1 and O is 3.5. 3.5 – 2.1 = 1.4 so the bond between H and O is a polar covalent bond. By definition a neutral group of atoms held together by covalent bonds is a molecule. So, the H2O particle is a molecule H2O is a molecule which makes H2O a molecular compound and a molecular formula. But H2 ...
... H is 2.1 and O is 3.5. 3.5 – 2.1 = 1.4 so the bond between H and O is a polar covalent bond. By definition a neutral group of atoms held together by covalent bonds is a molecule. So, the H2O particle is a molecule H2O is a molecule which makes H2O a molecular compound and a molecular formula. But H2 ...
Electron Arrangement
... The non-metal takes these electrons to form a negative ion. The electrostatic force of attraction holds these oppositely charged ions together very tightly. This is why ionic compounds tend to have high melting and boiling points. The structure is a large lattice. Metallic Bonding Found in metal ele ...
... The non-metal takes these electrons to form a negative ion. The electrostatic force of attraction holds these oppositely charged ions together very tightly. This is why ionic compounds tend to have high melting and boiling points. The structure is a large lattice. Metallic Bonding Found in metal ele ...
Chemistry Notes with Blanks
... Table salt (NaCl) is a compound composed of the _________ sodium and chlorine. A _________ bond holds the two hydrogen atoms together. A molecule is a group of atoms held together by covalent bonds. It has no_________charge. _________ electrons in the 1st shell, _________in the 2nd, and ____ ...
... Table salt (NaCl) is a compound composed of the _________ sodium and chlorine. A _________ bond holds the two hydrogen atoms together. A molecule is a group of atoms held together by covalent bonds. It has no_________charge. _________ electrons in the 1st shell, _________in the 2nd, and ____ ...