2 - Castle High School
... • A box with a volume of 22.4 L contains 1.0 mol of nitrogen and 2.0 mol of hydrogen at 0C. Which of the following statements is true? • a. The total pressure in the box is 202.6 kPa. • b. The partial pressure of N2 and H2 are equal. • c. The total pressure is 101.3 kPa. • d. The partial pressure of ...
... • A box with a volume of 22.4 L contains 1.0 mol of nitrogen and 2.0 mol of hydrogen at 0C. Which of the following statements is true? • a. The total pressure in the box is 202.6 kPa. • b. The partial pressure of N2 and H2 are equal. • c. The total pressure is 101.3 kPa. • d. The partial pressure of ...
Final Exam Review Answers
... • An atom of an element with atomic number 48 and mass number 120 contains • a. 48 protons, 48 electrons, and 72 neutrons. • b. 72 protons, 48 electrons, and 48 neutrons. • c. 120 protons, 48 electrons, and 72 neutrons. • d. 72 protons, 72 electrons, and 48 neutrons. ...
... • An atom of an element with atomic number 48 and mass number 120 contains • a. 48 protons, 48 electrons, and 72 neutrons. • b. 72 protons, 48 electrons, and 48 neutrons. • c. 120 protons, 48 electrons, and 72 neutrons. • d. 72 protons, 72 electrons, and 48 neutrons. ...
Pulse and Continuous Wave Electron Spin Resonance Investigations of Atoms
... (Im-He) solids. The Im-He solids containing H, D or N atoms as impurities were created by sending a mixture gases consisting of 1-5% impurity molecules, and the remainder helium atoms, through a radio frequency discharge into a volume of superfluid 4 He at T =1.5 K. The kinetics of the tunnelling ex ...
... (Im-He) solids. The Im-He solids containing H, D or N atoms as impurities were created by sending a mixture gases consisting of 1-5% impurity molecules, and the remainder helium atoms, through a radio frequency discharge into a volume of superfluid 4 He at T =1.5 K. The kinetics of the tunnelling ex ...
Azimuthal and magnetic quantum numbers As angular momentum is
... Azimuthal and magnetic quantum numbers As angular momentum is a vector, one quantum number is related to its length, the other to its direction, in bound states the angular momentum is quantized as well. Spin and associated magnetic momentum of an electron ...
... Azimuthal and magnetic quantum numbers As angular momentum is a vector, one quantum number is related to its length, the other to its direction, in bound states the angular momentum is quantized as well. Spin and associated magnetic momentum of an electron ...
2nd nine weeks benchmark review homework
... d- atomic mass, protons When the physical composition of a substance changes, the chemical composition- ...
... d- atomic mass, protons When the physical composition of a substance changes, the chemical composition- ...
Untitled - Washington County Schools
... Atoms are the foundation of chemistry. They are the basis for everything in the Universe. As you know, matter is composed of atoms. Solids are made of densely packed atoms while gases have atoms that are spread out. We're going to cover basics like atomic structure and bonding between atoms. As you ...
... Atoms are the foundation of chemistry. They are the basis for everything in the Universe. As you know, matter is composed of atoms. Solids are made of densely packed atoms while gases have atoms that are spread out. We're going to cover basics like atomic structure and bonding between atoms. As you ...
Chem 1st Sem Rev Ch2
... 4. Chlorine, selenium, and bromine are located near each other on the period table. Which of these elements is a. the smallest atom? b. the atom with the highest ionization energy? 5. Which particle has the largest radius in each atom /ion pair? a. Na, Na+ b. S, S-2 6. Why don’t the noble gases appe ...
... 4. Chlorine, selenium, and bromine are located near each other on the period table. Which of these elements is a. the smallest atom? b. the atom with the highest ionization energy? 5. Which particle has the largest radius in each atom /ion pair? a. Na, Na+ b. S, S-2 6. Why don’t the noble gases appe ...
Reactions I Can..
... 9. Describe the basic properties of alpha, beta, and gamma radiation. 10. Explain why some atomic nuclei are unstable 11. Predict the type of nuclear decay that will occur given the composition of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. 12. Balance a nuclear equation for both charge and mass. 13. Ident ...
... 9. Describe the basic properties of alpha, beta, and gamma radiation. 10. Explain why some atomic nuclei are unstable 11. Predict the type of nuclear decay that will occur given the composition of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. 12. Balance a nuclear equation for both charge and mass. 13. Ident ...
Atoms
... 6. Identify the phase (solid, liquid, gas) of each element on the Periodic Table. 7. Explain the basic periodic trends of radius and ionization energy 8. Explain the concept of Shielding 9. Explain how an ion can have a net charge 10. Determine the charge of an ion given the number of protons and el ...
... 6. Identify the phase (solid, liquid, gas) of each element on the Periodic Table. 7. Explain the basic periodic trends of radius and ionization energy 8. Explain the concept of Shielding 9. Explain how an ion can have a net charge 10. Determine the charge of an ion given the number of protons and el ...
Earth Materials
... outermost shell (valence) electrons • Elements will typically be reactive unless their valence shell is full • Atoms or groups of atoms with unequal numbers of protons and electrons, thus having a non-zero charge, are called ions. Positively charged ions are known as cations, and negative charges as ...
... outermost shell (valence) electrons • Elements will typically be reactive unless their valence shell is full • Atoms or groups of atoms with unequal numbers of protons and electrons, thus having a non-zero charge, are called ions. Positively charged ions are known as cations, and negative charges as ...
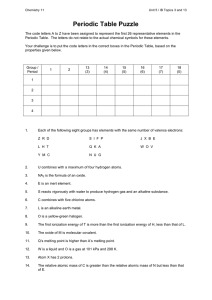
Periodic Table Puzzle
... The code letters A to Z have been assigned to represent the first 26 representative elements in the Periodic Table. The letters do not relate to the actual chemical symbols for these elements. Your challenge is to put the code letters in the correct boxes in the Periodic Table, based on the properti ...
... The code letters A to Z have been assigned to represent the first 26 representative elements in the Periodic Table. The letters do not relate to the actual chemical symbols for these elements. Your challenge is to put the code letters in the correct boxes in the Periodic Table, based on the properti ...
Midterm Review File
... 19. Answer the following questions about the periodic table. a. Explain why noble gases are inert and do not form ions. b. Identify the name of the group that contains the element fluorine _______________ c. Give the name of the element in the alkali group that has the greatest electron affinity ___ ...
... 19. Answer the following questions about the periodic table. a. Explain why noble gases are inert and do not form ions. b. Identify the name of the group that contains the element fluorine _______________ c. Give the name of the element in the alkali group that has the greatest electron affinity ___ ...
Ionic Bonding www.AssignmentPoint.com Ionic bonding is a type of
... because the cohesive forces that keep the lattice together are of a more collective nature. This is quite different in the case of covalent bonding, where we can often speak of a distinct bond localized between two particular atoms. However, even if ionic bonding is combined with some covalency, the ...
... because the cohesive forces that keep the lattice together are of a more collective nature. This is quite different in the case of covalent bonding, where we can often speak of a distinct bond localized between two particular atoms. However, even if ionic bonding is combined with some covalency, the ...
Chapter3 Solutions
... together by pure covalent bonds (O=O, N≡N, Cl−Cl). There is little attraction between the molecules because there are no dipoles, thus the molecules remain separate and the elements are gases. Another factor that contributes is the fact that the elements are relatively light, compared to iodine, for ...
... together by pure covalent bonds (O=O, N≡N, Cl−Cl). There is little attraction between the molecules because there are no dipoles, thus the molecules remain separate and the elements are gases. Another factor that contributes is the fact that the elements are relatively light, compared to iodine, for ...
2. Chemistry of Living Things Outline
... Negatively charged particles, called ______________ (-1) revolve around the nucleus at different distances from the nucleus. The electrons move in paths called shells or ____________________. Atoms have the ________ number of electrons and protons. Therefore, they are electrically ____________ (have ...
... Negatively charged particles, called ______________ (-1) revolve around the nucleus at different distances from the nucleus. The electrons move in paths called shells or ____________________. Atoms have the ________ number of electrons and protons. Therefore, they are electrically ____________ (have ...
Chemistry of Living Things Outline
... Negatively charged particles, called ______________ (-1) revolve around the nucleus at different distances from the nucleus. The electrons move in paths called shells or ____________________. Atoms have the ________ number of electrons and protons. Therefore, they are electrically ____________ ...
... Negatively charged particles, called ______________ (-1) revolve around the nucleus at different distances from the nucleus. The electrons move in paths called shells or ____________________. Atoms have the ________ number of electrons and protons. Therefore, they are electrically ____________ ...
Elements, basic principles, periodic table
... Chemical behavior controlled by electrons Elements in same columns (periodic behavior) behave similarly due to similar electron configura:ons. Outer most electrons most important in chemistry since more readily ...
... Chemical behavior controlled by electrons Elements in same columns (periodic behavior) behave similarly due to similar electron configura:ons. Outer most electrons most important in chemistry since more readily ...
Fundamentals of Chemistry
... • http://www.webelements.com/ • http://periodictable.com/ • http://www.uky.edu/Projects/Chemcomics/ ...
... • http://www.webelements.com/ • http://periodictable.com/ • http://www.uky.edu/Projects/Chemcomics/ ...
HOMEWORK 6-1 - losbanosusd.k12.ca.us
... 1. Nature favors chemical bonding because _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________. 2. When atoms are drawn together by attractive forces, their potential energy ______________________. 3. Potential energy is ...
... 1. Nature favors chemical bonding because _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________. 2. When atoms are drawn together by attractive forces, their potential energy ______________________. 3. Potential energy is ...
electrons - Portal UniMAP
... Molecular orbitals – delocalized over entire molecule. First Principle • The total number of molecular orbitals is always equal to the total number of atomic orbitals contributed by the atoms that have combined. ...
... Molecular orbitals – delocalized over entire molecule. First Principle • The total number of molecular orbitals is always equal to the total number of atomic orbitals contributed by the atoms that have combined. ...
Chemical bond
A chemical bond is an attraction between atoms that allows the formation of chemical substances that contain two or more atoms. The bond is caused by the electrostatic force of attraction between opposite charges, either between electrons and nuclei, or as the result of a dipole attraction. The strength of chemical bonds varies considerably; there are ""strong bonds"" such as covalent or ionic bonds and ""weak bonds"" such as Dipole-dipole interaction, the London dispersion force and hydrogen bonding.Since opposite charges attract via a simple electromagnetic force, the negatively charged electrons that are orbiting the nucleus and the positively charged protons in the nucleus attract each other. An electron positioned between two nuclei will be attracted to both of them, and the nuclei will be attracted toward electrons in this position. This attraction constitutes the chemical bond. Due to the matter wave nature of electrons and their smaller mass, they must occupy a much larger amount of volume compared with the nuclei, and this volume occupied by the electrons keeps the atomic nuclei relatively far apart, as compared with the size of the nuclei themselves. This phenomenon limits the distance between nuclei and atoms in a bond.In general, strong chemical bonding is associated with the sharing or transfer of electrons between the participating atoms. The atoms in molecules, crystals, metals and diatomic gases—indeed most of the physical environment around us—are held together by chemical bonds, which dictate the structure and the bulk properties of matter.All bonds can be explained by quantum theory, but, in practice, simplification rules allow chemists to predict the strength, directionality, and polarity of bonds. The octet rule and VSEPR theory are two examples. More sophisticated theories are valence bond theory which includes orbital hybridization and resonance, and the linear combination of atomic orbitals molecular orbital method which includes ligand field theory. Electrostatics are used to describe bond polarities and the effects they have on chemical substances.