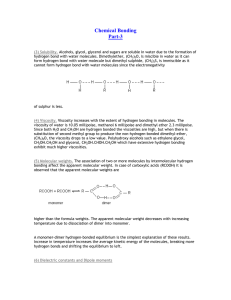
Honors Chemistry Midterm Review 2008
... Electrons jump to higher energy levels. When they drop back down to ground state they release bundles of energy “photons” in the form of light. Different amounts of energy = different wavelengths of light ROYGBIV Emission Spectra can be used to identify elements. ...
... Electrons jump to higher energy levels. When they drop back down to ground state they release bundles of energy “photons” in the form of light. Different amounts of energy = different wavelengths of light ROYGBIV Emission Spectra can be used to identify elements. ...
Medical Physics and Statistics
... equivalent to the (positive) energy to be invested for bond rupture. ...
... equivalent to the (positive) energy to be invested for bond rupture. ...
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes
... 13) If a pair of electrons is unequally shared between two atoms, a(n) ________ occurs. A) double covalent bond B) hydrogen bond C) polar covalent bond D) single covalent bond E) triple covalent bond ...
... 13) If a pair of electrons is unequally shared between two atoms, a(n) ________ occurs. A) double covalent bond B) hydrogen bond C) polar covalent bond D) single covalent bond E) triple covalent bond ...
File - docstover.org
... 2. Which element has a larger atomic radius A or C? _____________ 3. Which element has a larger atomic radius C or D? _____________ 4. Which element has a higher electronegativity? A or B? ____________ 5. Which element has a higher ionization energy? C or D? ___________ Elements in the same ______ ...
... 2. Which element has a larger atomic radius A or C? _____________ 3. Which element has a larger atomic radius C or D? _____________ 4. Which element has a higher electronegativity? A or B? ____________ 5. Which element has a higher ionization energy? C or D? ___________ Elements in the same ______ ...
Atoms, Elements, Compounds File
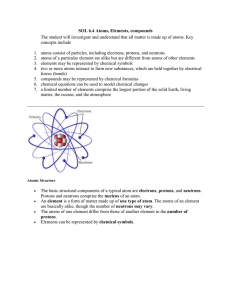
... SOL 6.4 Atoms, Elements, compounds The student will investigate and understand that all matter is made up of atoms. Key concepts include ...
... SOL 6.4 Atoms, Elements, compounds The student will investigate and understand that all matter is made up of atoms. Key concepts include ...
Physical bases of dental material science
... Ernest Rutherford (1909-11) : scattering of He-ions (α particles ) on a thin metal foil ...
... Ernest Rutherford (1909-11) : scattering of He-ions (α particles ) on a thin metal foil ...
Elements, Compounds, and Molecules
... . Sodium has one valence electron and transfers that electron to chlorine Na + Cl- the negative and positive electrical charges attract each other so the oppositely charged ions come together and form sodium chloride (salt). ...
... . Sodium has one valence electron and transfers that electron to chlorine Na + Cl- the negative and positive electrical charges attract each other so the oppositely charged ions come together and form sodium chloride (salt). ...
Matter is anything that occupies space and has mass. Examples
... 1. Metallic Bond 2. Covalent Bond 3. Ionic Bond ...
... 1. Metallic Bond 2. Covalent Bond 3. Ionic Bond ...
Hints for Names and Formulas (Ch. 4 in Zumdahl Chemistry)
... (8) most organic molecules are named according to systematic IUPAC nomenclature rules ● IUPAC stands for the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry committee (9) most covalent inorganic molecules are gases (sometimes liquids) at room temperature (R.T.) IONIC COMPOUNDS (1) ionic compounds ...
... (8) most organic molecules are named according to systematic IUPAC nomenclature rules ● IUPAC stands for the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry committee (9) most covalent inorganic molecules are gases (sometimes liquids) at room temperature (R.T.) IONIC COMPOUNDS (1) ionic compounds ...
Seeing Atoms and Electrons in Motion - The Munich
... Munich-Centre for Advanced Photonics (MAP) ...
... Munich-Centre for Advanced Photonics (MAP) ...
AP Chemistry
... Lattice unit cell Ionic solids Atomic solids (metallic, network, Group 18) Molecular solids Malleable Ductile Band model Alloys: substitutional, interstitial Diamonds vs graphite ...
... Lattice unit cell Ionic solids Atomic solids (metallic, network, Group 18) Molecular solids Malleable Ductile Band model Alloys: substitutional, interstitial Diamonds vs graphite ...
TEST on Atomic Structure
... _B__ 48) Which of the forces of molecular attraction is the weakest? (dispersion is just from the moving e-) a. dipole interaction b. dispersion c. hydrogen bond d. single covalent bond 49) Compare and Contrast Ionic and covalent bonds. 3 points ...
... _B__ 48) Which of the forces of molecular attraction is the weakest? (dispersion is just from the moving e-) a. dipole interaction b. dispersion c. hydrogen bond d. single covalent bond 49) Compare and Contrast Ionic and covalent bonds. 3 points ...
Unit 1B1 - Uddingston Grammar School
... Atoms P and Q have the same number of protons Atoms Q and R have the same number of electrons Atoms P and S have the same number of neutrons Atoms R and S are isotopes of each other Atoms S and T have different chemical properties. ...
... Atoms P and Q have the same number of protons Atoms Q and R have the same number of electrons Atoms P and S have the same number of neutrons Atoms R and S are isotopes of each other Atoms S and T have different chemical properties. ...
PIB and HH - Unit 4 - Chemical Names and Formulas
... bonds is an ionic compound. Nearly all ionic compounds are crystalline solids at room temperature. They have high melting points. The total positive charge cancels out the total negative charge, yielding a neutral compound. When melted or in solution, ionic compounds can conduct electricity, because ...
... bonds is an ionic compound. Nearly all ionic compounds are crystalline solids at room temperature. They have high melting points. The total positive charge cancels out the total negative charge, yielding a neutral compound. When melted or in solution, ionic compounds can conduct electricity, because ...
Precursors to Modern Physics
... atom is affected by large orbital quantum numbers? The state of an electron in an atom is completely defined by its quantum numbers. The energy of the electron is also a function of Z, the total positive charge of the nucleus. For the electrons with the same quantum numbers, what is the trend of the ...
... atom is affected by large orbital quantum numbers? The state of an electron in an atom is completely defined by its quantum numbers. The energy of the electron is also a function of Z, the total positive charge of the nucleus. For the electrons with the same quantum numbers, what is the trend of the ...
Matter Unit
... mass which is unique to that element. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed in ordinary chemical reactions. However, these changes CAN occur in nuclear reactions! All matter is composed of atoms Atoms of any one element differ in properties from atoms of another element ...
... mass which is unique to that element. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed in ordinary chemical reactions. However, these changes CAN occur in nuclear reactions! All matter is composed of atoms Atoms of any one element differ in properties from atoms of another element ...
Chemistry ~ Fall Final Review
... Measurement: significant figures, sci. notation, guess digits, density Properties of Matter: atoms/molecules, elements & compounds, chemical/physical changes History of the atom: models & scientists Wave calculations: properties of waves, energy, frequency, wavelength Electron configuration: orbital ...
... Measurement: significant figures, sci. notation, guess digits, density Properties of Matter: atoms/molecules, elements & compounds, chemical/physical changes History of the atom: models & scientists Wave calculations: properties of waves, energy, frequency, wavelength Electron configuration: orbital ...
File
... composition that is uniform throughout, all the way down to the molecular level. • Hydrocarbon-any molecule consisting of only hydrogen and carbon atoms, typically fossil fuels and other compounds derived from them. • Ion- a charged atom, it has either gained or lost an electron. • Isotope-any varie ...
... composition that is uniform throughout, all the way down to the molecular level. • Hydrocarbon-any molecule consisting of only hydrogen and carbon atoms, typically fossil fuels and other compounds derived from them. • Ion- a charged atom, it has either gained or lost an electron. • Isotope-any varie ...
Chemical Change
... Heavy positively charged particles found in the nucleus Neutral particles that have about the same mass as protons and also found in nucleus ...
... Heavy positively charged particles found in the nucleus Neutral particles that have about the same mass as protons and also found in nucleus ...
Chemical bond
A chemical bond is an attraction between atoms that allows the formation of chemical substances that contain two or more atoms. The bond is caused by the electrostatic force of attraction between opposite charges, either between electrons and nuclei, or as the result of a dipole attraction. The strength of chemical bonds varies considerably; there are ""strong bonds"" such as covalent or ionic bonds and ""weak bonds"" such as Dipole-dipole interaction, the London dispersion force and hydrogen bonding.Since opposite charges attract via a simple electromagnetic force, the negatively charged electrons that are orbiting the nucleus and the positively charged protons in the nucleus attract each other. An electron positioned between two nuclei will be attracted to both of them, and the nuclei will be attracted toward electrons in this position. This attraction constitutes the chemical bond. Due to the matter wave nature of electrons and their smaller mass, they must occupy a much larger amount of volume compared with the nuclei, and this volume occupied by the electrons keeps the atomic nuclei relatively far apart, as compared with the size of the nuclei themselves. This phenomenon limits the distance between nuclei and atoms in a bond.In general, strong chemical bonding is associated with the sharing or transfer of electrons between the participating atoms. The atoms in molecules, crystals, metals and diatomic gases—indeed most of the physical environment around us—are held together by chemical bonds, which dictate the structure and the bulk properties of matter.All bonds can be explained by quantum theory, but, in practice, simplification rules allow chemists to predict the strength, directionality, and polarity of bonds. The octet rule and VSEPR theory are two examples. More sophisticated theories are valence bond theory which includes orbital hybridization and resonance, and the linear combination of atomic orbitals molecular orbital method which includes ligand field theory. Electrostatics are used to describe bond polarities and the effects they have on chemical substances.