Chapter
... small molecules tend to react faster than large molecules gases tend to react faster than liquids, which react faster than solids powdered solids are more reactive than “blocks” more surface area for contact with other reactants certain types of chemicals are more reactive than others e.g. ...
... small molecules tend to react faster than large molecules gases tend to react faster than liquids, which react faster than solids powdered solids are more reactive than “blocks” more surface area for contact with other reactants certain types of chemicals are more reactive than others e.g. ...
Document
... small molecules tend to react faster than large molecules gases tend to react faster than liquids, which react faster than solids powdered solids are more reactive than “blocks” more surface area for contact with other reactants certain types of chemicals are more reactive than others e.g. ...
... small molecules tend to react faster than large molecules gases tend to react faster than liquids, which react faster than solids powdered solids are more reactive than “blocks” more surface area for contact with other reactants certain types of chemicals are more reactive than others e.g. ...
Chapter 14 (Kinetics) – Slides and Practice
... small molecules tend to react faster than large molecules gases tend to react faster than liquids, which react faster than solids powdered solids are more reactive than “blocks” more surface area for contact with other reactants certain types of chemicals are more reactive than others e.g. ...
... small molecules tend to react faster than large molecules gases tend to react faster than liquids, which react faster than solids powdered solids are more reactive than “blocks” more surface area for contact with other reactants certain types of chemicals are more reactive than others e.g. ...
National 5 - Deans Community High School
... Copy the graph showing reaction A and add the corresponding curves which could have been obtained for experiments B, C and D. (Label each curve clearly.) 18. The collision theory states that for two molecules to react, they must first collide with one another. Use the collision theory to explain the ...
... Copy the graph showing reaction A and add the corresponding curves which could have been obtained for experiments B, C and D. (Label each curve clearly.) 18. The collision theory states that for two molecules to react, they must first collide with one another. Use the collision theory to explain the ...
CHAPTER I
... An earlier notation used letters for the major electron shells: K, L, M, N, and so on, corresponding to n = 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on. That is, n is a measure of the orbital radial size or diameter. In atoms having more than one electron, two or more electrons may have the same n value. These electrons ...
... An earlier notation used letters for the major electron shells: K, L, M, N, and so on, corresponding to n = 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on. That is, n is a measure of the orbital radial size or diameter. In atoms having more than one electron, two or more electrons may have the same n value. These electrons ...
Powerpoint
... Bond enthalpy is usually applied for gaseous molecules because molecules are isolated in gaseous state. In solid and liquid states, molecules are held by each other by intermolecular forces. The importance of bond enthalpy relies on the fact that it can be calculated accurately and there are some ex ...
... Bond enthalpy is usually applied for gaseous molecules because molecules are isolated in gaseous state. In solid and liquid states, molecules are held by each other by intermolecular forces. The importance of bond enthalpy relies on the fact that it can be calculated accurately and there are some ex ...
CB document - mvhs
... energy is released when new bonds form than was required to break existing bonds, then the difference will result in an overall release of energy. If, on the other hand, more energy is required to break existing bonds than is released when new bonds form, the difference will result overall in energy ...
... energy is released when new bonds form than was required to break existing bonds, then the difference will result in an overall release of energy. If, on the other hand, more energy is required to break existing bonds than is released when new bonds form, the difference will result overall in energy ...
Chapter 15 Acids and Bases
... Arrhenius Acid-Base Reactions the H+ from the acid combines with the OH- from the base to make a molecule of H2O it is often helpful to think of H2O as H-OH the cation from the base combines with the anion from the acid to make a salt acid + base → salt + water HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) → NaCl(aq) + ...
... Arrhenius Acid-Base Reactions the H+ from the acid combines with the OH- from the base to make a molecule of H2O it is often helpful to think of H2O as H-OH the cation from the base combines with the anion from the acid to make a salt acid + base → salt + water HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) → NaCl(aq) + ...
Gases Properties of Gases Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases
... If we know the mass of gas in a sample of known volume, pressure and temperature, then we can calculate the relative molecular mass as we can calculate n. As n = ...
... If we know the mass of gas in a sample of known volume, pressure and temperature, then we can calculate the relative molecular mass as we can calculate n. As n = ...
The Free High School Science Texts
... textbooks you probably own or use. • We know people copy textbooks illegally but we would LOVE it if you copied our’s - go ahead copy to your hearts content, legally! • Publishers’ revenue is generated by controlling the market, we don’t want any money, go ahead, distribute our books far and wide - ...
... textbooks you probably own or use. • We know people copy textbooks illegally but we would LOVE it if you copied our’s - go ahead copy to your hearts content, legally! • Publishers’ revenue is generated by controlling the market, we don’t want any money, go ahead, distribute our books far and wide - ...
03-Chemical Rxns n Stoichiometry
... chemistry • Based on the Law of Conservation of Mass (Antoine Lavoisier, 1789) “We may lay it down as an incontestable axiom that, in all the operations of art and nature, nothing is created; an equal amount of matter exists both before and after the experiment. Upon this principle, the whole art of ...
... chemistry • Based on the Law of Conservation of Mass (Antoine Lavoisier, 1789) “We may lay it down as an incontestable axiom that, in all the operations of art and nature, nothing is created; an equal amount of matter exists both before and after the experiment. Upon this principle, the whole art of ...
1 Mole
... Sometimes polyatomic ions break apart in a chemical reaction and sometimes they do not e.x. sulfate appears on both sides of the reaction so SO4 can be treated like one atom: Mg(s) + CuSO4(aq) MgSO4(aq) + Cu(s) e.x. carbonate breaks apart so atoms must be balanced individually: CaCO3(aq) + HCl ...
... Sometimes polyatomic ions break apart in a chemical reaction and sometimes they do not e.x. sulfate appears on both sides of the reaction so SO4 can be treated like one atom: Mg(s) + CuSO4(aq) MgSO4(aq) + Cu(s) e.x. carbonate breaks apart so atoms must be balanced individually: CaCO3(aq) + HCl ...
OCR Gateway Science
... (d) Explain why you would not use universal indicator for this titration. (e) Phenolphthalein indicator was used to find the end point of the titration. Why is this a suitable indicator and what is the colour change at the end point? The diagram shows the change in pH when an acid is added to an alk ...
... (d) Explain why you would not use universal indicator for this titration. (e) Phenolphthalein indicator was used to find the end point of the titration. Why is this a suitable indicator and what is the colour change at the end point? The diagram shows the change in pH when an acid is added to an alk ...
EquiSage
... Leaching arsenic-bearing copper concentrate Standard equilibrium: non-ideal solution Fe-Mn-Si-C Adding slag: An explanation on SlagA, SlagB, Slag? Standard case: Desulphurisation of steel adding CaSi Standard case: Pitzer aqueous with NaCl Heterogeneous equilibria and the phase rule Compound species ...
... Leaching arsenic-bearing copper concentrate Standard equilibrium: non-ideal solution Fe-Mn-Si-C Adding slag: An explanation on SlagA, SlagB, Slag? Standard case: Desulphurisation of steel adding CaSi Standard case: Pitzer aqueous with NaCl Heterogeneous equilibria and the phase rule Compound species ...
11.1 Enthalpy PowerPoint
... Yes, but indirectly. We can measure a change in temperature, we can then calculate the change in thermal energy (Q=mct). Then, using the law of conservation of energy we can infer the molar enthalpy. ...
... Yes, but indirectly. We can measure a change in temperature, we can then calculate the change in thermal energy (Q=mct). Then, using the law of conservation of energy we can infer the molar enthalpy. ...
CHOICE BASED CREDIT SYSTEM B. Sc. WITH CHEMISTRY
... Conformations with respect to ethane, butane and cyclohexane. Interconversion of Wedge Formula, Newmann, Sawhorse and Fischer representations. Concept of chirality (upto two carbon atoms). Configuration: Geometrical and Optical isomerism; Enantiomerism, Diastereomerism and Meso compounds). Threo and ...
... Conformations with respect to ethane, butane and cyclohexane. Interconversion of Wedge Formula, Newmann, Sawhorse and Fischer representations. Concept of chirality (upto two carbon atoms). Configuration: Geometrical and Optical isomerism; Enantiomerism, Diastereomerism and Meso compounds). Threo and ...
Stoichiometry - Bruder Chemistry
... Commercial brass is an alloy of Cu and Zn. It reacts with HCl by the following reaction Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) ZnCl2 (aq) + H2(g) Cu does not react. When 0.5065 g of brass is reacted with excess HCl, 0.0985 g of ZnCl2 are eventually isolated. What is the composition of the brass? ...
... Commercial brass is an alloy of Cu and Zn. It reacts with HCl by the following reaction Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) ZnCl2 (aq) + H2(g) Cu does not react. When 0.5065 g of brass is reacted with excess HCl, 0.0985 g of ZnCl2 are eventually isolated. What is the composition of the brass? ...
Chem. 1310 Fall 2005 Final Exam-white ... Name _________________________________ Section Number ___________________
... 1. On the Scantron card, you must bubble-in your GTid number. In the space provided, write your Name. Write the Color of your exam in the Subject section and bubble-in the letter for the Test Form (White=A, Green=B, Yellow=C). Write your section number in the Hour/Date section. See sample below. 2. ...
... 1. On the Scantron card, you must bubble-in your GTid number. In the space provided, write your Name. Write the Color of your exam in the Subject section and bubble-in the letter for the Test Form (White=A, Green=B, Yellow=C). Write your section number in the Hour/Date section. See sample below. 2. ...
12 U Chem Review
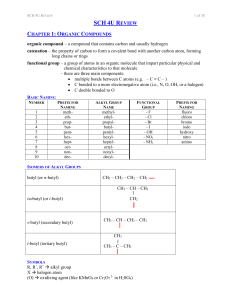
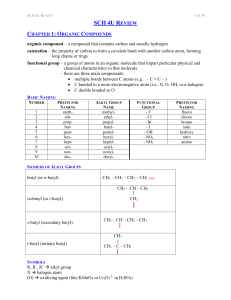
... catenation – the property of carbon to form a covalent bond with another carbon atom, forming long chains or rings functional group – a group of atoms in an organic molecule that impart particular physical and chemical characteristics to that molecule – there are three main components: multiple bo ...
... catenation – the property of carbon to form a covalent bond with another carbon atom, forming long chains or rings functional group – a group of atoms in an organic molecule that impart particular physical and chemical characteristics to that molecule – there are three main components: multiple bo ...