Biol 1406 notes Ch 2 8thed - Chemistry
... o Because carbon and hydrogen do not differ greatly in electronegativities, the bonds of CH4 are nonpolar. When two atoms that differ in electronegativity bond, they do not share the electron pair equally and they form a polar covalent bond. o The bonds between oxygen and hydrogen in water are polar ...
... o Because carbon and hydrogen do not differ greatly in electronegativities, the bonds of CH4 are nonpolar. When two atoms that differ in electronegativity bond, they do not share the electron pair equally and they form a polar covalent bond. o The bonds between oxygen and hydrogen in water are polar ...
Classification – 3 main groups
... Alkali Group 1 on periodic table & Alkaline Earth Metals group 2 Halogen group 17 or 7A Noble Gases group 18 or 8A Chapter 11 Lessons 1-3 Valence Electron outer shell electrons; related to group # Electron dot diagram representation that only shows valence electrons Chemical bond an attraction betwe ...
... Alkali Group 1 on periodic table & Alkaline Earth Metals group 2 Halogen group 17 or 7A Noble Gases group 18 or 8A Chapter 11 Lessons 1-3 Valence Electron outer shell electrons; related to group # Electron dot diagram representation that only shows valence electrons Chemical bond an attraction betwe ...
F324 summary - Macmillan Academy
... • Benzene, C6H6, consists of a sigma-bonded framework of carbon and hydrogen atoms. • Above and below the plane of atoms is a p-bond, which consists of a delocalised electron cloud. • The Kekule structure of benzene assumes that all the bonds are localised i.e. cannot move. However, evidence to supp ...
... • Benzene, C6H6, consists of a sigma-bonded framework of carbon and hydrogen atoms. • Above and below the plane of atoms is a p-bond, which consists of a delocalised electron cloud. • The Kekule structure of benzene assumes that all the bonds are localised i.e. cannot move. However, evidence to supp ...
EOC Review - Dorman Freshman Campus
... the pollution and other gases emitted from the environment which is surrounded by dust and dirt in clouds….the dust and dirt fall as rain bringing with it the pollution which is ...
... the pollution and other gases emitted from the environment which is surrounded by dust and dirt in clouds….the dust and dirt fall as rain bringing with it the pollution which is ...
Chapter 4 The Structure of Matter
... • 5. Formula unit is the smallest ratio of ions in ionic compounds • a. Na+1Cl-1 or Ca+2F2-1 • b. When melted or dissolved in H2O ionic compounds will conduct electricity because the ions are free to move. • c. As solids the ions are locked so tightly that they do not conduct electricity. ...
... • 5. Formula unit is the smallest ratio of ions in ionic compounds • a. Na+1Cl-1 or Ca+2F2-1 • b. When melted or dissolved in H2O ionic compounds will conduct electricity because the ions are free to move. • c. As solids the ions are locked so tightly that they do not conduct electricity. ...
effective nuclear charge
... ◦ shrinkage in size due to having more protons than electrons ◦ outer electrons closer to the nucleus, therefore harder to remove regular increase in energy for each successive valence electron large increase in energy when start removing core electrons ...
... ◦ shrinkage in size due to having more protons than electrons ◦ outer electrons closer to the nucleus, therefore harder to remove regular increase in energy for each successive valence electron large increase in energy when start removing core electrons ...
Unit 4: Chemical Bonding Notes Chemical Bond—a mutual
... that binds the atoms together. Chemical bonds create more stable arrangements of matter. The goal of any atom is to gain, lose, or share valence electrons creating chemical bonds to provide a mor ...
... that binds the atoms together. Chemical bonds create more stable arrangements of matter. The goal of any atom is to gain, lose, or share valence electrons creating chemical bonds to provide a mor ...
Measuring and Calculating
... A period is likened to an energy level when completing energy level diagrams. Moving left to right, the attraction between the valence electrons and the nucleus increases, causing the atomic radius to decrease, and electronegativity and ionization energy to increase. ...
... A period is likened to an energy level when completing energy level diagrams. Moving left to right, the attraction between the valence electrons and the nucleus increases, causing the atomic radius to decrease, and electronegativity and ionization energy to increase. ...
Bonding Notes
... points or boiling points. (Remember in vapor pressures the liquid with the highest intermolecular forces of attraction had the highest boiling point!) Thus ionic solids have high melting points! -Also ionic compounds in the solids state are in the fixed geometric patterns or crystal lattice. In the ...
... points or boiling points. (Remember in vapor pressures the liquid with the highest intermolecular forces of attraction had the highest boiling point!) Thus ionic solids have high melting points! -Also ionic compounds in the solids state are in the fixed geometric patterns or crystal lattice. In the ...
CHEMISTRY 103 – Practice Problems #3 Chapters 8 – 10 http
... 17. A central atom with 2 lone pairs and 3 bonding pairs of e- will have a molecular shape of: a. linear b. trigonal pyramid c. trigonal planar d. T-shape e. trigonal bipyramid 18. In Lewis dot structures, which electron interactions repel the most? a. bonding pair–bonding pair b. bonding pair–lone ...
... 17. A central atom with 2 lone pairs and 3 bonding pairs of e- will have a molecular shape of: a. linear b. trigonal pyramid c. trigonal planar d. T-shape e. trigonal bipyramid 18. In Lewis dot structures, which electron interactions repel the most? a. bonding pair–bonding pair b. bonding pair–lone ...
power point notes
... Rutherford proposed that the atom consists of a tiny positively charged nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The nucleus contains almost all of the mass of the atom and consists of protons and neutrons. The number of electrons surrounding the nucleus, equals the number of p ...
... Rutherford proposed that the atom consists of a tiny positively charged nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The nucleus contains almost all of the mass of the atom and consists of protons and neutrons. The number of electrons surrounding the nucleus, equals the number of p ...
10th Grade Chemistry X (TJ) GRADE(S)/LEVELS SUBJECT Power
... Atoms are composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons have a positive charge, electrons are negative in charge, and neutrons have no net charge. Atoms of the same element have the same number of protons. The number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom determines the isotope of the element ...
... Atoms are composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons have a positive charge, electrons are negative in charge, and neutrons have no net charge. Atoms of the same element have the same number of protons. The number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom determines the isotope of the element ...
Key concepts of chemistry from high school chemistry
... than in high school, as well exams tend to cover more material than in high school. Most college courses will have cumulative final exams that can be worth 20-‐40% of your final grade depending o ...
... than in high school, as well exams tend to cover more material than in high school. Most college courses will have cumulative final exams that can be worth 20-‐40% of your final grade depending o ...
Molecular Geometry and Polarity1
... substances are solids, others liquids, and others gases. Some participate in sudden chemical reactions, whereas others are quite inert and unreactive. Perhaps most remarkably, this wonderful diversity occurs even though the substances are comprised of a limited number of elements. Indeed, only a ver ...
... substances are solids, others liquids, and others gases. Some participate in sudden chemical reactions, whereas others are quite inert and unreactive. Perhaps most remarkably, this wonderful diversity occurs even though the substances are comprised of a limited number of elements. Indeed, only a ver ...
Chem Review
... 25Mg (24.985837amu) with a percent abundance of 10.00%, and 26Mg (25.982593amu) with a percent abundance of 11.01%. Calculate the average atomic mass of Magnesium to 3 decimal places. 21. Boron has two naturally occurring isotopes: 10B with a mass of 10.013amu and 11B with a mass of 11.009amu. Deter ...
... 25Mg (24.985837amu) with a percent abundance of 10.00%, and 26Mg (25.982593amu) with a percent abundance of 11.01%. Calculate the average atomic mass of Magnesium to 3 decimal places. 21. Boron has two naturally occurring isotopes: 10B with a mass of 10.013amu and 11B with a mass of 11.009amu. Deter ...
Chemistry Cram Sheet
... John’s lab group compared the effect of different aged grass compost on bean plants. Because decomposition is necessary for release of nutrients, the group hypothesized that older grass compost would produce taller bean plants. Three flats of bean plants (25 plants/flat) were grown for five days. Th ...
... John’s lab group compared the effect of different aged grass compost on bean plants. Because decomposition is necessary for release of nutrients, the group hypothesized that older grass compost would produce taller bean plants. Three flats of bean plants (25 plants/flat) were grown for five days. Th ...
Unit 1 Powerpoint
... Science aims to be objective, but scientists are human, too. Sometimes scientific data can be misinterpreted or misapplied by scientists who want to prove a particular point. Recommendations made by scientists with personal biases may or may not be in the public interest. But if enough of us underst ...
... Science aims to be objective, but scientists are human, too. Sometimes scientific data can be misinterpreted or misapplied by scientists who want to prove a particular point. Recommendations made by scientists with personal biases may or may not be in the public interest. But if enough of us underst ...
Chapter 4 Notes
... Electrons as Waves and Particles • Electrons have wavelike properties • Consider the electron as a wave confined to a space that can have only certain frequencies ...
... Electrons as Waves and Particles • Electrons have wavelike properties • Consider the electron as a wave confined to a space that can have only certain frequencies ...
The Atomic Theory of Matter
... gold foil a few thousand atoms thick. He found that most passed right through the gold foil while some were deflected. This was later concluded that there is a lot of empty space in an atom and that they mostly passed through the empty space ,sometimes getting deflected by the later discovered nucle ...
... gold foil a few thousand atoms thick. He found that most passed right through the gold foil while some were deflected. This was later concluded that there is a lot of empty space in an atom and that they mostly passed through the empty space ,sometimes getting deflected by the later discovered nucle ...
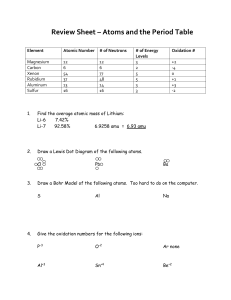
Review Sheet Filled Out
... Electrons closest to the nucleus have the least amount of energy Electrons farthest away from the nucleus have the most energy – valence e Have a negative charge Have insignificant mass and volume Reside in the 99.996% of the atom outside the nucleus Can’t tell where an electron is at any ...
... Electrons closest to the nucleus have the least amount of energy Electrons farthest away from the nucleus have the most energy – valence e Have a negative charge Have insignificant mass and volume Reside in the 99.996% of the atom outside the nucleus Can’t tell where an electron is at any ...
Ch9_10notes maroon edition
... zero. When a negative charge exists, it should be placed on the most electronegative atom. ...
... zero. When a negative charge exists, it should be placed on the most electronegative atom. ...
Resonance (chemistry)
In chemistry, resonance or mesomerism is a way of describing delocalized electrons within certain molecules or polyatomic ions where the bonding cannot be expressed by one single Lewis formula. A molecule or ion with such delocalized electrons is represented by several contributing structures (also called resonance structures or canonical forms).Each contributing structure can be represented by a Lewis structure, with only an integer number of covalent bonds between each pair of atoms within the structure. Several Lewis structures are used collectively to describe the actual molecular structure, which is an approximate intermediate between the canonical forms called a resonance hybrid. Contributing structures differ only in the position of electrons, not in the position of nuclei.Electron delocalization lowers the potential energy of the substance and thus makes it more stable than any of the contributing structures. The difference between the potential energy of the actual structure and that of the contributing structure with the lowest potential energy is called the resonance energy or delocalization energy.Resonance is distinguished from tautomerism and conformational isomerism, which involve the formation of isomers, thus the rearrangement of the nuclear positions.