Atomic Theory - WaylandHighSchoolChemistry
... Schrödinger and Heisenberg, and many, many more. Used their brains to venture in the realm of inner space and found the world of the atom was a weird and wondrous place. ...
... Schrödinger and Heisenberg, and many, many more. Used their brains to venture in the realm of inner space and found the world of the atom was a weird and wondrous place. ...
C1403_Final Exam p. 1 Friday, January 23, 2004 Printed Last Name
... e. None of the above are correct 8. According to valence bond theory, methane (CH4), ammonia (NH3), and water (H2O) all involve sp3 hybridization. Why do these molecules have different bond angles? a. The central atom has a different number of valence electrons. b. These molecules can form a differe ...
... e. None of the above are correct 8. According to valence bond theory, methane (CH4), ammonia (NH3), and water (H2O) all involve sp3 hybridization. Why do these molecules have different bond angles? a. The central atom has a different number of valence electrons. b. These molecules can form a differe ...
CHM134 General Chemistry I Semester Review – Dr. Steel This list
... Quantum mechanical model of the atom Atomic orbitals ...
... Quantum mechanical model of the atom Atomic orbitals ...
Unit 2 Practice Exam exam_2p_08_matter
... a. When alpha particles are shot at gold foil some alpha particles are deflected slightly or at large angles. b. Each time an alpha particle hit this zinc sulfide coating, a flash of light was produced at the point of contact. c. Positively charged alpha particles were deflected rather than attracte ...
... a. When alpha particles are shot at gold foil some alpha particles are deflected slightly or at large angles. b. Each time an alpha particle hit this zinc sulfide coating, a flash of light was produced at the point of contact. c. Positively charged alpha particles were deflected rather than attracte ...
The Egyptian American International School
... 9.2 Using Chemical Equations to Calculate Mass To calculate masses from the moles of reactants needed or products formed, we can use the molar masses of substances for finding the masses (g) needed or formed. 9.3 Limiting Reactants and Percent Yield Often, reactants in a chemical reaction are n ...
... 9.2 Using Chemical Equations to Calculate Mass To calculate masses from the moles of reactants needed or products formed, we can use the molar masses of substances for finding the masses (g) needed or formed. 9.3 Limiting Reactants and Percent Yield Often, reactants in a chemical reaction are n ...
The Chemical Context of Life by Dr. Ty C.M. Hoffman
... associated with the nucleus of one of the bonded atoms than that pair spends associated with the other nucleus. This happens because different types of atoms attract electrons to different degrees. A me ...
... associated with the nucleus of one of the bonded atoms than that pair spends associated with the other nucleus. This happens because different types of atoms attract electrons to different degrees. A me ...
Revision topic 1-3
... Positive ions are smaller than their parent atoms (because of loss of the outer shell). Negative ions are larger than their parent atoms (because of increased electron repulsion by addition of electrons). The ionic radii decrease as a period is crossed from the left to the right (because of increase ...
... Positive ions are smaller than their parent atoms (because of loss of the outer shell). Negative ions are larger than their parent atoms (because of increased electron repulsion by addition of electrons). The ionic radii decrease as a period is crossed from the left to the right (because of increase ...
What do we call a substance with more than one kind of atom
... 42. Within a period, the atomic radius __________ as the atomic number increases. 43. As a nonmetal becomes an ion, its radius _________ 44. The ______________ are the family that contain the most reactive metals. 45. Examine the following electron configuration for element X and use it to answer th ...
... 42. Within a period, the atomic radius __________ as the atomic number increases. 43. As a nonmetal becomes an ion, its radius _________ 44. The ______________ are the family that contain the most reactive metals. 45. Examine the following electron configuration for element X and use it to answer th ...
Fall Exam 1
... A. chlorine and oxygen C. tin and lead B. calcium and scandium D. sulfur and arsenic 26. Gallium has an average atomic mass of 69.72 amu. Gallium exists as two naturally occurring isotopes, 69Ga and 71Ga with a natural abundance of 39.89% and an atomic mass of 70.92 amu. What is the atomic mass of 6 ...
... A. chlorine and oxygen C. tin and lead B. calcium and scandium D. sulfur and arsenic 26. Gallium has an average atomic mass of 69.72 amu. Gallium exists as two naturally occurring isotopes, 69Ga and 71Ga with a natural abundance of 39.89% and an atomic mass of 70.92 amu. What is the atomic mass of 6 ...
File
... b.) The second ionization energy of K is greater than the second ionization energy of Ca. 2003B 7. Account for the following observations using principles of atomic structure and/or chemical bonding. In each part, your answer must include specific information about both substances. a. The Ca2+ and C ...
... b.) The second ionization energy of K is greater than the second ionization energy of Ca. 2003B 7. Account for the following observations using principles of atomic structure and/or chemical bonding. In each part, your answer must include specific information about both substances. a. The Ca2+ and C ...
2. Covalent network
... 1. The particles are so small compared with the distances between them that the volume of the individual particles can be assumed to be zero 2. The particles are in constant motion. Collisions of the particles with the walls of the container cause pressure 3. Assume that the particles exert no force ...
... 1. The particles are so small compared with the distances between them that the volume of the individual particles can be assumed to be zero 2. The particles are in constant motion. Collisions of the particles with the walls of the container cause pressure 3. Assume that the particles exert no force ...
Eighth Grade Review - PAMS-Doyle
... Matter can also be described by its chemical properties, which include acidity, basicity, combustibility, and reactivity. A chemical property indicates whether a substance can undergo a chemical change. ...
... Matter can also be described by its chemical properties, which include acidity, basicity, combustibility, and reactivity. A chemical property indicates whether a substance can undergo a chemical change. ...
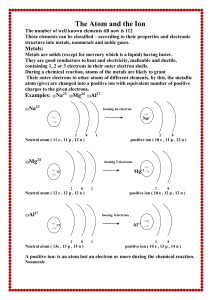
The Atom and the Ion
... Some of nonmetals are solids, others are gases and only there is one liquid element which is bromine. They have no luster, not malleable or ductile (brittle), they are bad conductors to heat and electricity, except graphite which is good conductor to electricity. Most of nonmetals contain 5,6 or 7 ...
... Some of nonmetals are solids, others are gases and only there is one liquid element which is bromine. They have no luster, not malleable or ductile (brittle), they are bad conductors to heat and electricity, except graphite which is good conductor to electricity. Most of nonmetals contain 5,6 or 7 ...
Unit 3: Bonding and Nomenclature Content Outline: Chemical
... A. The term refers to any electrically neutral group of atoms that are bound together. 1. It can be 2 or more atoms of the same element or composed of different elements. For example: N2 (nitrogen gas) or NH3 (Ammonia) A. Molecular Compound This term is used to refer to a chemical compound (2 or mor ...
... A. The term refers to any electrically neutral group of atoms that are bound together. 1. It can be 2 or more atoms of the same element or composed of different elements. For example: N2 (nitrogen gas) or NH3 (Ammonia) A. Molecular Compound This term is used to refer to a chemical compound (2 or mor ...
File
... 24. What are Valence electrons? Electrons on the outermost energy level of an atom 25. How many electrons can the 1st, 2nd and 3rd energy levels hold? 1st level can hold up to 2; 2nd level can hold up to 8; 3rd level can up hold up to 8 (with exceptions with periods past the 3rd level) 26. Which gro ...
... 24. What are Valence electrons? Electrons on the outermost energy level of an atom 25. How many electrons can the 1st, 2nd and 3rd energy levels hold? 1st level can hold up to 2; 2nd level can hold up to 8; 3rd level can up hold up to 8 (with exceptions with periods past the 3rd level) 26. Which gro ...
普通化学 (全英文) 教学大纲
... (b).Pictures of the orbitals: s, px, py, pz (c).How to fill electrons in different orbitals (d).Be able to draw the electron configuration of the first 20 elements (e).Unpaired electrons, Spin, Paramagnetic and Diamagnetism 2.5.Comparing the atomic orbitals with Bohr’s model of atoms (Classical but ...
... (b).Pictures of the orbitals: s, px, py, pz (c).How to fill electrons in different orbitals (d).Be able to draw the electron configuration of the first 20 elements (e).Unpaired electrons, Spin, Paramagnetic and Diamagnetism 2.5.Comparing the atomic orbitals with Bohr’s model of atoms (Classical but ...
Chemistry Test Review - Greenslime Home Page
... 4. How many valence electrons exist in an electrically neutral atom of Aluminum? What does this tell you about the Boron Family? a. 3 b. this tells you that the Boron Family has 3 valence electrons 5. Describe possible evidence that would suggest that a chemical change has ...
... 4. How many valence electrons exist in an electrically neutral atom of Aluminum? What does this tell you about the Boron Family? a. 3 b. this tells you that the Boron Family has 3 valence electrons 5. Describe possible evidence that would suggest that a chemical change has ...
Study Guide Answers
... two valence electrons, many are minerals Halogens – Group 17, most reactive nonmetals, have 7 valence electrons many are used as disinfectants Noble Gases – Group 18, least reactive elements, full outer electron cloud, many are used in neon signs. Boron Family – Group 13, have 3 valence electrons ...
... two valence electrons, many are minerals Halogens – Group 17, most reactive nonmetals, have 7 valence electrons many are used as disinfectants Noble Gases – Group 18, least reactive elements, full outer electron cloud, many are used in neon signs. Boron Family – Group 13, have 3 valence electrons ...
MYP Chemistry: Final Review
... How are elements in the same group (column) related? How are the alkali metals all related? The noble gases? All have the same final electron configuration number; all have same number of valence electrons Alkali Metals: end in s1 configuration, have 1 valence electron Noble gases: end in s2p6, have ...
... How are elements in the same group (column) related? How are the alkali metals all related? The noble gases? All have the same final electron configuration number; all have same number of valence electrons Alkali Metals: end in s1 configuration, have 1 valence electron Noble gases: end in s2p6, have ...
Band Theory of Solids
... 3. Hydrogen bonded crystals are transparent. 4. These crystal have peculiar directional properties. 5. Lose structure. ...
... 3. Hydrogen bonded crystals are transparent. 4. These crystal have peculiar directional properties. 5. Lose structure. ...
Midterm Review Date
... experiment” and the resulting model of the atom? A) An atom is mainly empty space, and the nucleus has a positive charge. B) An atom is mainly empty space, and the nucleus has a negative charge. C) An atom has hardly any empty space, and the nucleus has a positive charge. D) An atom has hardly any e ...
... experiment” and the resulting model of the atom? A) An atom is mainly empty space, and the nucleus has a positive charge. B) An atom is mainly empty space, and the nucleus has a negative charge. C) An atom has hardly any empty space, and the nucleus has a positive charge. D) An atom has hardly any e ...
High School Physical Science Glossary
... (F) is F = ma Newton's 3rd law- for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction, thus forces occur in pairs noble gas- any of the six gases helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon; the outermost electron shell of atoms of these gases is full, so they do not react chemically with othe ...
... (F) is F = ma Newton's 3rd law- for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction, thus forces occur in pairs noble gas- any of the six gases helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon; the outermost electron shell of atoms of these gases is full, so they do not react chemically with othe ...
Chemical Equations and Reactions
... – Some form of energy is given off by the reaction • Heat given off causes reaction mixture to feel hot • Examples-burning wood, dynamite explosion ...
... – Some form of energy is given off by the reaction • Heat given off causes reaction mixture to feel hot • Examples-burning wood, dynamite explosion ...
Resonance (chemistry)
In chemistry, resonance or mesomerism is a way of describing delocalized electrons within certain molecules or polyatomic ions where the bonding cannot be expressed by one single Lewis formula. A molecule or ion with such delocalized electrons is represented by several contributing structures (also called resonance structures or canonical forms).Each contributing structure can be represented by a Lewis structure, with only an integer number of covalent bonds between each pair of atoms within the structure. Several Lewis structures are used collectively to describe the actual molecular structure, which is an approximate intermediate between the canonical forms called a resonance hybrid. Contributing structures differ only in the position of electrons, not in the position of nuclei.Electron delocalization lowers the potential energy of the substance and thus makes it more stable than any of the contributing structures. The difference between the potential energy of the actual structure and that of the contributing structure with the lowest potential energy is called the resonance energy or delocalization energy.Resonance is distinguished from tautomerism and conformational isomerism, which involve the formation of isomers, thus the rearrangement of the nuclear positions.