Midterm Review Answers
... Questions 52-53nrefer to the following types of energy A) Activation energy B) Free energy C) Ionization energy D) Kinetic energy E) Lattice energy 52. The energy required to convert a ground-state atom in the gas phase to a gaseous positive ion. C 53. The energy released when gas phase ions bond t ...
... Questions 52-53nrefer to the following types of energy A) Activation energy B) Free energy C) Ionization energy D) Kinetic energy E) Lattice energy 52. The energy required to convert a ground-state atom in the gas phase to a gaseous positive ion. C 53. The energy released when gas phase ions bond t ...
rev8thgrade - PAMS
... thermal energy between substances of different temperature. As thermal energy is added, the temperature of a substance increases. ...
... thermal energy between substances of different temperature. As thermal energy is added, the temperature of a substance increases. ...
chapter2 2012 (no naming)
... • Rays are composed of negatively charged particles called electrons • Electrons carry unit negative charge (-1) and have a very small mass (1/2000 the lightest atomic mass) ...
... • Rays are composed of negatively charged particles called electrons • Electrons carry unit negative charge (-1) and have a very small mass (1/2000 the lightest atomic mass) ...
The topic that fascinated me the most in my Science lessons this
... germanium, gallium and scandium were found and their physical and chemical ‘behaviour’ were just as Mendeleev predicted! Hence, even though Mendeleev did not physically stumble upon these elements, he could be said to have discovered them. Why is Mendeleev able to predict the properties of undiscove ...
... germanium, gallium and scandium were found and their physical and chemical ‘behaviour’ were just as Mendeleev predicted! Hence, even though Mendeleev did not physically stumble upon these elements, he could be said to have discovered them. Why is Mendeleev able to predict the properties of undiscove ...
Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi © 2016 Ebneshahidi
... (PE) is stored energy in matters ; Kinetic energy (KE) is working energy produced by the motion of matters. Energy occurs in 4 forms in the human body: chemical, electrical, radiant, and mechanical energy. Chemical energy is the most important form in terms of actually driving chemical reactions. ...
... (PE) is stored energy in matters ; Kinetic energy (KE) is working energy produced by the motion of matters. Energy occurs in 4 forms in the human body: chemical, electrical, radiant, and mechanical energy. Chemical energy is the most important form in terms of actually driving chemical reactions. ...
Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding
... octet (exceptions are H, Be, B, Al, elements on rows 3, 4, 5, and 6.) No electrons should be left unpaired (only in rare cases will a species contain an unpaired electron.) For those atoms that can have more than an octet, if all of its single electrons are used in a covalent bond, and there are sur ...
... octet (exceptions are H, Be, B, Al, elements on rows 3, 4, 5, and 6.) No electrons should be left unpaired (only in rare cases will a species contain an unpaired electron.) For those atoms that can have more than an octet, if all of its single electrons are used in a covalent bond, and there are sur ...
chapter_2_2009
... Creating different chemical substances by forming and breaking chemical bonds. Remember: Atoms form chemical bonds to fill their outermost electron energy levels, achieving ...
... Creating different chemical substances by forming and breaking chemical bonds. Remember: Atoms form chemical bonds to fill their outermost electron energy levels, achieving ...
Atomic Structure (history of atom)
... ATOMS of any one ELEMENT are different from those of any other element Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or chemically combine to form compounds Chemical reactions occur when atoms are joined, separated or rearranged Atoms of one element are never changed into atoms of another ...
... ATOMS of any one ELEMENT are different from those of any other element Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or chemically combine to form compounds Chemical reactions occur when atoms are joined, separated or rearranged Atoms of one element are never changed into atoms of another ...
apbio ch 2 study guide
... Hydrogen bonds form when a hydrogen atom that is already covalently bonded to one electronegative atom is attracted to another electronegative atom. o In cells, the electronegative partners are typically nitrogen or oxygen. o Hydrogen bonds form because a polar covalent bond leaves the hydrogen atom ...
... Hydrogen bonds form when a hydrogen atom that is already covalently bonded to one electronegative atom is attracted to another electronegative atom. o In cells, the electronegative partners are typically nitrogen or oxygen. o Hydrogen bonds form because a polar covalent bond leaves the hydrogen atom ...
+ 2 HCL(aq) CaCl2(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
... Chemical Formula: States what elements a compound contains and the exact number of atoms of these elements. Oxidation Number: positive or negative number on the periodic table that indicates how many electrons an element has gained, lost or shared when bonding with another element. Polyatomic Atom: ...
... Chemical Formula: States what elements a compound contains and the exact number of atoms of these elements. Oxidation Number: positive or negative number on the periodic table that indicates how many electrons an element has gained, lost or shared when bonding with another element. Polyatomic Atom: ...
Chemistry
... will contain between eight and ten compulsory questions of the fill-in type requiring short answers; Section B will consist of between four and sixcompulsory structured questions; Section C will require candidates to choose two out of four long questions. Each of section A and B will carry 30 marks ...
... will contain between eight and ten compulsory questions of the fill-in type requiring short answers; Section B will consist of between four and sixcompulsory structured questions; Section C will require candidates to choose two out of four long questions. Each of section A and B will carry 30 marks ...
Chapter 10 (Hill/Petrucci/McCreary/Perry Bonding Theory and
... “Precise molecular geometry can be determined only by experiment but the shapes of many molecules and polyatomic ions can be predicted fairly well …” (Hill, p. 388) “As the name implies, the valence-shell electron pair repulsion method is based on the idea that pairs of valence electrons in bonded a ...
... “Precise molecular geometry can be determined only by experiment but the shapes of many molecules and polyatomic ions can be predicted fairly well …” (Hill, p. 388) “As the name implies, the valence-shell electron pair repulsion method is based on the idea that pairs of valence electrons in bonded a ...
Regents_Chem_Core_for_review
... IV.2 Two major categories of compounds are ionic and molecular (covalent) compounds. (5.2g) IV.3 Chemical bonds are formed when valence electrons are (5.2a): • transferred from one atom to another (ionic) • shared between atoms (covalent) • mobile within a metal (metallic) IV.4 In a multiple covalen ...
... IV.2 Two major categories of compounds are ionic and molecular (covalent) compounds. (5.2g) IV.3 Chemical bonds are formed when valence electrons are (5.2a): • transferred from one atom to another (ionic) • shared between atoms (covalent) • mobile within a metal (metallic) IV.4 In a multiple covalen ...
Honors Midterm - Stamford High School
... Metallic bonds consist of the attractions of the free-floating valence electrons for the positively charged metal ions. The free floating valence electrons make metals good conductors and light reflecting off of the free floating valence electrons that travel around the outside of metal give metal ...
... Metallic bonds consist of the attractions of the free-floating valence electrons for the positively charged metal ions. The free floating valence electrons make metals good conductors and light reflecting off of the free floating valence electrons that travel around the outside of metal give metal ...
Chemistry
... will contain between eight and ten compulsory questions of the fill-in type requiring short answers; Section B will consist of between four and sixcompulsory structured questions; Section C will require candidates to choose two out of four long questions. Each of section A and B will carry 30 marks ...
... will contain between eight and ten compulsory questions of the fill-in type requiring short answers; Section B will consist of between four and sixcompulsory structured questions; Section C will require candidates to choose two out of four long questions. Each of section A and B will carry 30 marks ...
Importance of Molecular Simulation for Studying Structural Properties
... Discovery of the active site of these molecules would be performed by quantum mechanical simulations using density functional theory method [21]. DFT is an approach for the description of ground state properties of metals, semiconductors, and insulators. The success of DFT not only encompasses stand ...
... Discovery of the active site of these molecules would be performed by quantum mechanical simulations using density functional theory method [21]. DFT is an approach for the description of ground state properties of metals, semiconductors, and insulators. The success of DFT not only encompasses stand ...
Mock Final Exam
... b. One resonance structure corresponds to the observed structure. c. The observed structure is an average of the various resonance structures. d. The same atoms need not be bonded to each other in all resonance forms. e. There cannot be more than two resonance structures for a given species. 7.5: Ex ...
... b. One resonance structure corresponds to the observed structure. c. The observed structure is an average of the various resonance structures. d. The same atoms need not be bonded to each other in all resonance forms. e. There cannot be more than two resonance structures for a given species. 7.5: Ex ...
CHEMISTRY IM 06 SYLLABUS 1
... will contain between eight and ten compulsory questions of the fill-in type requiring short answers; Section B will consist of between four and sixcompulsory structured questions; Section C will require candidates to choose two out of four long questions. Each of section A and B will carry 30 marks ...
... will contain between eight and ten compulsory questions of the fill-in type requiring short answers; Section B will consist of between four and sixcompulsory structured questions; Section C will require candidates to choose two out of four long questions. Each of section A and B will carry 30 marks ...
CH. 15 Notes
... to the right of the chemical symbols are called Subscripts, and notes the number of atoms of that element. A number in front of a chemical formula is a coefficient and it is multiplied by the subscript of all the atoms that are in the formula ...
... to the right of the chemical symbols are called Subscripts, and notes the number of atoms of that element. A number in front of a chemical formula is a coefficient and it is multiplied by the subscript of all the atoms that are in the formula ...
K,7th Grade Test Review: Atoms and Chemical Reactions PART
... 12. A _______________ shows how many atoms of what elements are in a molecule. 13. An atom with more electrons than protons has a _____________ charge and is called an anion. ...
... 12. A _______________ shows how many atoms of what elements are in a molecule. 13. An atom with more electrons than protons has a _____________ charge and is called an anion. ...
Chapter 13 Spectroscopy NMR, IR, MS, UV-Vis
... Since nuclei produce magnetic fields (the ones we’ve been talking about aligning with and against the field), those fields would affect the effective field felt by the hydrogen being measured. In the high energy state they would oppose (reduce) the field and in the low energy state reinforce (increa ...
... Since nuclei produce magnetic fields (the ones we’ve been talking about aligning with and against the field), those fields would affect the effective field felt by the hydrogen being measured. In the high energy state they would oppose (reduce) the field and in the low energy state reinforce (increa ...
Chapter 18 Resource: Matter
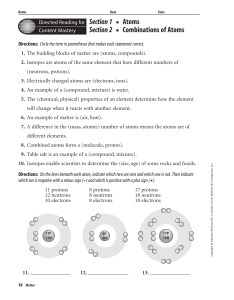
... 1. The building blocks of matter are (atoms, compounds). 2. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of (neutrons, protons). 3. Electrically charged atoms are (electrons, ions). 4. An example of a (compound, mixture) is water. 5. The (chemical, physical) properties of an el ...
... 1. The building blocks of matter are (atoms, compounds). 2. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of (neutrons, protons). 3. Electrically charged atoms are (electrons, ions). 4. An example of a (compound, mixture) is water. 5. The (chemical, physical) properties of an el ...
Chapter 8 Test Review
... Writing Formulas • Sulfur difluoride • Silicon tetrachloride • Chlorine trifluoride • Tetrasulfur heptanitride ...
... Writing Formulas • Sulfur difluoride • Silicon tetrachloride • Chlorine trifluoride • Tetrasulfur heptanitride ...
Resonance (chemistry)
In chemistry, resonance or mesomerism is a way of describing delocalized electrons within certain molecules or polyatomic ions where the bonding cannot be expressed by one single Lewis formula. A molecule or ion with such delocalized electrons is represented by several contributing structures (also called resonance structures or canonical forms).Each contributing structure can be represented by a Lewis structure, with only an integer number of covalent bonds between each pair of atoms within the structure. Several Lewis structures are used collectively to describe the actual molecular structure, which is an approximate intermediate between the canonical forms called a resonance hybrid. Contributing structures differ only in the position of electrons, not in the position of nuclei.Electron delocalization lowers the potential energy of the substance and thus makes it more stable than any of the contributing structures. The difference between the potential energy of the actual structure and that of the contributing structure with the lowest potential energy is called the resonance energy or delocalization energy.Resonance is distinguished from tautomerism and conformational isomerism, which involve the formation of isomers, thus the rearrangement of the nuclear positions.