Zn + HCl → ZnCl 2 + H2 NaOH + H3PO4 → Na3PO4 + H2O N2 +
... Look at only one type of atom at a time. Start with atoms that appear only once on each side of the equation. Once those are balanced, try to balance atoms that appear in more than one species on either side of the reaction. Tip: If there is a molecule with only one type of atom (eg, O2), so ...
... Look at only one type of atom at a time. Start with atoms that appear only once on each side of the equation. Once those are balanced, try to balance atoms that appear in more than one species on either side of the reaction. Tip: If there is a molecule with only one type of atom (eg, O2), so ...
Biol 1020 Ch. 2 Chemistry
... Together and Store Energy In aqueous systems (such as living organisms), the effective relative bond strengths are: ...
... Together and Store Energy In aqueous systems (such as living organisms), the effective relative bond strengths are: ...
Problem Set 3_Chem165_Sp2014
... For (c), which isomer of the alcohol product do you think you get from the hydration reaction, or do you think you get both isomers? 7. Predict the products of the following reactions. (No reaction could be the correct answer.) (a) 1-octene + MeOH (with an acid catalyst) (b) styrene + excess H2 (ove ...
... For (c), which isomer of the alcohol product do you think you get from the hydration reaction, or do you think you get both isomers? 7. Predict the products of the following reactions. (No reaction could be the correct answer.) (a) 1-octene + MeOH (with an acid catalyst) (b) styrene + excess H2 (ove ...
Semester 1 Final Review Powerpoint
... steal electrons from pure silver. Think about it . . . Do you see potassium in its pure form in nature? No! Do you typically see silver corrode and quickly rust away? No! These observations imply that K is very reactive and Ag is not. ...
... steal electrons from pure silver. Think about it . . . Do you see potassium in its pure form in nature? No! Do you typically see silver corrode and quickly rust away? No! These observations imply that K is very reactive and Ag is not. ...
www.xtremepapers.net
... Dot-and-cross structures for the molecules mentioned (outer shells only). Emphasise that bonds are stable entities, so give out heat when they form. This stability is due to attraction of the bonding electrons to two nuclei rather than just one. The use of two dots (or two crosses) in a dative bond ...
... Dot-and-cross structures for the molecules mentioned (outer shells only). Emphasise that bonds are stable entities, so give out heat when they form. This stability is due to attraction of the bonding electrons to two nuclei rather than just one. The use of two dots (or two crosses) in a dative bond ...
chemistry i - surrattchemistry
... Use the chart below on questions 18 and 19. A student is determining the density of a U.S. nickel. His data is shown below: # of ...
... Use the chart below on questions 18 and 19. A student is determining the density of a U.S. nickel. His data is shown below: # of ...
Standards Practice
... B. hydrogen bond. C. ionic bond. D. metallic bond. 2. When atoms combine to form a molecule by sharing electrons, what type of bonds are formed? A. covalent B. hydrogen C. ionic D. polar ionic 3. Which is the best way to express the relationship between hydrogen and fluorine when they combine? ...
... B. hydrogen bond. C. ionic bond. D. metallic bond. 2. When atoms combine to form a molecule by sharing electrons, what type of bonds are formed? A. covalent B. hydrogen C. ionic D. polar ionic 3. Which is the best way to express the relationship between hydrogen and fluorine when they combine? ...
The Basics - I`m a faculty member, and I need web space. What
... • The mole ratios can be obtained from the coefficients in the balanced chemical equation. • What are the mole ratios in this problem? • Mole ratios can be used as conversion factors to predict the amount of any reactant or product involved in a reaction if the amount of another reactant and/or prod ...
... • The mole ratios can be obtained from the coefficients in the balanced chemical equation. • What are the mole ratios in this problem? • Mole ratios can be used as conversion factors to predict the amount of any reactant or product involved in a reaction if the amount of another reactant and/or prod ...
Document
... – No chemical bonding between components – Can be separated by physical means, such as straining or filtering – Heterogeneous or homogeneous ...
... – No chemical bonding between components – Can be separated by physical means, such as straining or filtering – Heterogeneous or homogeneous ...
Chapter 2 Notes
... 2. compounds- when 2 or more substances combine chemically; has properties different from the properties of each of the elements in it; example: water (H2O) 3. chemical properties = describe how one substance changes when it reacts with other substances; example: iron changes to rust when it reacts ...
... 2. compounds- when 2 or more substances combine chemically; has properties different from the properties of each of the elements in it; example: water (H2O) 3. chemical properties = describe how one substance changes when it reacts with other substances; example: iron changes to rust when it reacts ...
Study Guide 1st Semester
... 31. What is a valence electron? 32. Where are the alkali metal elements found? How do their electron configurations end? What are some typical behaviors of alkali metals? 33. Where are the alkaline earth metals found? How do their electron configurations end? What are some typical behaviors of alkal ...
... 31. What is a valence electron? 32. Where are the alkali metal elements found? How do their electron configurations end? What are some typical behaviors of alkali metals? 33. Where are the alkaline earth metals found? How do their electron configurations end? What are some typical behaviors of alkal ...
2012 Coaches Institute Presentation
... Assume AgCrO4 dissociates completely in water at 25oC. [Ag+] = 1.3 x 10-4 AgCrO4(s) ⇔ 2Ag+(aq) + CrO4-2(aq) Ksp = [Ag+]2[CrO4-2] [CrO4-2] = 1.3 x 10-4 mol Ag+ x 1 mol CrO4-2 ...
... Assume AgCrO4 dissociates completely in water at 25oC. [Ag+] = 1.3 x 10-4 AgCrO4(s) ⇔ 2Ag+(aq) + CrO4-2(aq) Ksp = [Ag+]2[CrO4-2] [CrO4-2] = 1.3 x 10-4 mol Ag+ x 1 mol CrO4-2 ...
23.32 KB - KFUPM Resources v3
... A) The hydrogen atom has only one orbital. B) The size of the hydrogen 1s orbital is defined as the surface that contains 90% of the total electron probability. C) The square of the wave function represents the probability distribution of the elctron in the orbital. D) In the quantum mechanical mode ...
... A) The hydrogen atom has only one orbital. B) The size of the hydrogen 1s orbital is defined as the surface that contains 90% of the total electron probability. C) The square of the wave function represents the probability distribution of the elctron in the orbital. D) In the quantum mechanical mode ...
4. bonding - New Hartford Central Schools
... Elements with more than one positive oxidation number (Transition Metals) (This is called the Stock System) When the oxidation number varies we us a Roman numeral in parentheses to indicate the charge. Roman number is used for the positive element only!!! ...
... Elements with more than one positive oxidation number (Transition Metals) (This is called the Stock System) When the oxidation number varies we us a Roman numeral in parentheses to indicate the charge. Roman number is used for the positive element only!!! ...
Intermolecular Attractions
... Draw the electron dot formula. Then state how many bonding and unbonding pairs are present. A) NBr3 B) Water C) Chlorite ion (ClO2- ) D) CF2Cl2 ...
... Draw the electron dot formula. Then state how many bonding and unbonding pairs are present. A) NBr3 B) Water C) Chlorite ion (ClO2- ) D) CF2Cl2 ...
Preliminary Course Atomic Structure 1 + 2
... Molecules are discrete entities with discrete properties Atoms form molecules in a very predictable way, based on their elements ...
... Molecules are discrete entities with discrete properties Atoms form molecules in a very predictable way, based on their elements ...
Intro to Atoms - Freehold Borough Schools
... protons and neutrons In the nucleus are: • Proton: small, positively charged particle in the nucleus of an atom ( + symbol) • Neutron: Neutral charged particle in the nucleus of an atom Outside the Nucleus: • Electron: tiny, negatively charged particle that moves around the nucleus of an atom ...
... protons and neutrons In the nucleus are: • Proton: small, positively charged particle in the nucleus of an atom ( + symbol) • Neutron: Neutral charged particle in the nucleus of an atom Outside the Nucleus: • Electron: tiny, negatively charged particle that moves around the nucleus of an atom ...
www.theallpapers.com
... Dot-and-cross structures for the molecules mentioned (outer shells only). Emphasise that bonds are stable entities, so give out heat when they form. This stability is due to attraction of the bonding electrons to two nuclei rather than just one. The use of two dots (or two crosses) in a dative bond ...
... Dot-and-cross structures for the molecules mentioned (outer shells only). Emphasise that bonds are stable entities, so give out heat when they form. This stability is due to attraction of the bonding electrons to two nuclei rather than just one. The use of two dots (or two crosses) in a dative bond ...
Electron Arrangement
... Group 7 elements (Halogens). In molecular compounds When non-metal atoms join! Eg. Water (H2O), ammonia (NH3), Methane (CH4). These have specific shapes because of the covalent bonds. Covalent molecular substances tend to have low melting and boiling points because they only have Van der Waals’ forc ...
... Group 7 elements (Halogens). In molecular compounds When non-metal atoms join! Eg. Water (H2O), ammonia (NH3), Methane (CH4). These have specific shapes because of the covalent bonds. Covalent molecular substances tend to have low melting and boiling points because they only have Van der Waals’ forc ...
Science-M2-Basic-Che..
... physical environment around us—are held together by chemical bonds, which dictate the structure of matter. The explanation of these physical attractive forces is a complex area, and there are a few varieties of chemical bonds. Covalent and Ionic Bonds In an ionic bond, the atoms are bound by attract ...
... physical environment around us—are held together by chemical bonds, which dictate the structure of matter. The explanation of these physical attractive forces is a complex area, and there are a few varieties of chemical bonds. Covalent and Ionic Bonds In an ionic bond, the atoms are bound by attract ...
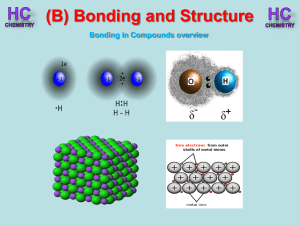
Lesson 1 - Bonding in compounds overview
... Silicon, like carbon, can form giant covalent networks. Silicon carbide exist in a similar structure to diamond. Tetrahedral shape ...
... Silicon, like carbon, can form giant covalent networks. Silicon carbide exist in a similar structure to diamond. Tetrahedral shape ...
SEMESTER 1 EXAM Prblms/Short Ans
... 16.Write the formulas for the following binary compounds formed between the following elements: (#1 p. 223) a. Sodium and sulfur _______________________ d. aluminum and nitrogen __________________ Name the binary ionic compound as indicated by the following formulas: (#2 p. 223) b. AgCl ___________ ...
... 16.Write the formulas for the following binary compounds formed between the following elements: (#1 p. 223) a. Sodium and sulfur _______________________ d. aluminum and nitrogen __________________ Name the binary ionic compound as indicated by the following formulas: (#2 p. 223) b. AgCl ___________ ...
Resonance (chemistry)
In chemistry, resonance or mesomerism is a way of describing delocalized electrons within certain molecules or polyatomic ions where the bonding cannot be expressed by one single Lewis formula. A molecule or ion with such delocalized electrons is represented by several contributing structures (also called resonance structures or canonical forms).Each contributing structure can be represented by a Lewis structure, with only an integer number of covalent bonds between each pair of atoms within the structure. Several Lewis structures are used collectively to describe the actual molecular structure, which is an approximate intermediate between the canonical forms called a resonance hybrid. Contributing structures differ only in the position of electrons, not in the position of nuclei.Electron delocalization lowers the potential energy of the substance and thus makes it more stable than any of the contributing structures. The difference between the potential energy of the actual structure and that of the contributing structure with the lowest potential energy is called the resonance energy or delocalization energy.Resonance is distinguished from tautomerism and conformational isomerism, which involve the formation of isomers, thus the rearrangement of the nuclear positions.