Chemical Bonding I: Lewis Theory
... • As with bond energies, these are averages since there are slight variations according to the molecular structure. • The next few slides give some typical values. • Nowadays, we use pm and the length unit. • Before that, we used the Ångstrom ...
... • As with bond energies, these are averages since there are slight variations according to the molecular structure. • The next few slides give some typical values. • Nowadays, we use pm and the length unit. • Before that, we used the Ångstrom ...
Chapter 7, 8, and 9 Exam 2014 Name I. 50% of your grade will come
... The energy required to convert a ground-state atom in the gas phase to a gaseous positive ion. ...
... The energy required to convert a ground-state atom in the gas phase to a gaseous positive ion. ...
Introduction_to_Geochemistry_Pre-Lecture_Quiz
... detach the loosest electron from atoms of that element. (e) All alkali metals have similar chemical properties. (f) Alkali earths have one electron in the outer shell. (g) Electronegativity is the amount of negative charge on an atom. (h) Ca has a valency of 2. (i) True ionic bonds are unknown and a ...
... detach the loosest electron from atoms of that element. (e) All alkali metals have similar chemical properties. (f) Alkali earths have one electron in the outer shell. (g) Electronegativity is the amount of negative charge on an atom. (h) Ca has a valency of 2. (i) True ionic bonds are unknown and a ...
chemical bond
... covalent bonds (sharing). i.e. must be a non-metal and a non-metal Molecular compound – a chemical compound whose simplest units are molecules. ...
... covalent bonds (sharing). i.e. must be a non-metal and a non-metal Molecular compound – a chemical compound whose simplest units are molecules. ...
Chemical Compounds
... S Take your ion and find someone you can bond with S Attempt to create the compound H2O, MgCl2..and so on S We will come together as a class and try to figure out if you ...
... S Take your ion and find someone you can bond with S Attempt to create the compound H2O, MgCl2..and so on S We will come together as a class and try to figure out if you ...
•What makes up an atom? Draw an atom
... • Isotope: different number of neutrons changes the mass, but NOT the element • EX. C12 vs C14 • Carbon 14 is heavier since it has two more neutrons ...
... • Isotope: different number of neutrons changes the mass, but NOT the element • EX. C12 vs C14 • Carbon 14 is heavier since it has two more neutrons ...
CHEMISTRY
... become IONS- they have a charge. Ex. a Hydrogen atom that loses it’s electron is called a hydrogen ion, H+, or a proton. ...
... become IONS- they have a charge. Ex. a Hydrogen atom that loses it’s electron is called a hydrogen ion, H+, or a proton. ...
Chemical Bonding I
... Now the real pHun! WriGng Lewis Structures!!! 1) Write the correct skeletal structure for the molecule. 2) Calculate the total number of electrons by summing the valence electrons of each atom. (Be ...
... Now the real pHun! WriGng Lewis Structures!!! 1) Write the correct skeletal structure for the molecule. 2) Calculate the total number of electrons by summing the valence electrons of each atom. (Be ...
The Chemical Basis of Life
... When the electron moves from one atom to another, the atoms now become charged (ions). What are the charges on each atom? ...
... When the electron moves from one atom to another, the atoms now become charged (ions). What are the charges on each atom? ...
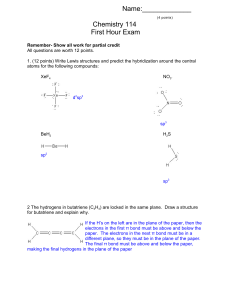
Name:______ Chemistry 114 First Hour Exam
... 3. One of the compounds you have met in the lab is NO gas, the nasty smelling brown gas that can come out of an internal combustion engine and that forms the brown haze of air pollution around big cities. NO uses the same series of molecular orbitals as C2 or N2. Show the occupied and unoccupied mo ...
... 3. One of the compounds you have met in the lab is NO gas, the nasty smelling brown gas that can come out of an internal combustion engine and that forms the brown haze of air pollution around big cities. NO uses the same series of molecular orbitals as C2 or N2. Show the occupied and unoccupied mo ...
PHY801: Survey of Atomic and Condensed Matter Physics
... the concentration n = N/V . Show that in the limit of very high temperatures, where µB B << kB T , the susceptibility is given by χ = 4nµ2B /(kB T ). 4.2. An exotic proposal to get nuclear fusion between two deuterons is to use the idea of muon catalysis. One constructs a “Hydrogen molecule ion”, on ...
... the concentration n = N/V . Show that in the limit of very high temperatures, where µB B << kB T , the susceptibility is given by χ = 4nµ2B /(kB T ). 4.2. An exotic proposal to get nuclear fusion between two deuterons is to use the idea of muon catalysis. One constructs a “Hydrogen molecule ion”, on ...
Chemistry I Honors
... Answer the following questions about the element selenium, Se (atomic number 34). c.In terms of atomic structure, explain why the first ionization energy of selenium is i. less than that of bromine (atomic number 35), and ii.greater than that of tellurium (atomic number 52). d.Selenium reacts with f ...
... Answer the following questions about the element selenium, Se (atomic number 34). c.In terms of atomic structure, explain why the first ionization energy of selenium is i. less than that of bromine (atomic number 35), and ii.greater than that of tellurium (atomic number 52). d.Selenium reacts with f ...
PHY 491: Atomic, Molecular, and Condensed Matter Physics
... concentration n = N/V . Show that in the limit of very high temperatures, where µB B << kB T , the susceptibility is given by χ = 8nµ2B /3kB T. 4.2. An exotic proposal to get nuclear fusion between two deuterons is to use the idea of muon catalysis. One constructs a “Hydrogen molecule ion”, only wit ...
... concentration n = N/V . Show that in the limit of very high temperatures, where µB B << kB T , the susceptibility is given by χ = 8nµ2B /3kB T. 4.2. An exotic proposal to get nuclear fusion between two deuterons is to use the idea of muon catalysis. One constructs a “Hydrogen molecule ion”, only wit ...
Microsoft Word
... 2. Calculate total number of electrons needed (N) to give each atom an octet (8 # non-hydrogen atoms + 2 # hydrogen atoms) 3. Calculate the number of bonding electrons (S): S=N-A 4. Draw a molecular skeleton for the substance and then assign two bonding electrons to each connection between atoms ...
... 2. Calculate total number of electrons needed (N) to give each atom an octet (8 # non-hydrogen atoms + 2 # hydrogen atoms) 3. Calculate the number of bonding electrons (S): S=N-A 4. Draw a molecular skeleton for the substance and then assign two bonding electrons to each connection between atoms ...
Chapter 6 Quiz
... ______ 4. The B—F bond in BF3 (electronegativity for B is 2.0; electronegativity for F is 4.0) is a. polar covalent. b. nonpolar covalent. c. ionic. d. metallic. ______ 5. The electron configuration of nitrogen is 1s2 2s2 2p3. How many more electrons does nitrogen need to satisfy the octet rule? a. ...
... ______ 4. The B—F bond in BF3 (electronegativity for B is 2.0; electronegativity for F is 4.0) is a. polar covalent. b. nonpolar covalent. c. ionic. d. metallic. ______ 5. The electron configuration of nitrogen is 1s2 2s2 2p3. How many more electrons does nitrogen need to satisfy the octet rule? a. ...
Ch. 8 Sections 8.1-8.3 Powerpoint
... •For atoms with very different electronegativity values, electron transfer occurs (ionic bond). •Intermediate cases give polar covalent bonds with unequal electron sharing. ...
... •For atoms with very different electronegativity values, electron transfer occurs (ionic bond). •Intermediate cases give polar covalent bonds with unequal electron sharing. ...
Ch 8 AP Practice
... (You must discuss both atoms in your response.) (c) Predict whether the first ionization energy of atomic xenon is greater than, less than, or equal to the first ionization energy of atomic fluorine. Justify your prediction. (d) Xenon can react with oxygen and fluorine to form compounds such as XeO3 ...
... (You must discuss both atoms in your response.) (c) Predict whether the first ionization energy of atomic xenon is greater than, less than, or equal to the first ionization energy of atomic fluorine. Justify your prediction. (d) Xenon can react with oxygen and fluorine to form compounds such as XeO3 ...
551Lect03
... In an ionic bond, atom A holds electrons weakly, and atom B holds them strongly. In a covalent bond, both atoms hold electrons strongly. In a metallic bond, both atoms hold electrons weakly. The transitions between the three types of bonding are continuous, since the electronegativities vary gradual ...
... In an ionic bond, atom A holds electrons weakly, and atom B holds them strongly. In a covalent bond, both atoms hold electrons strongly. In a metallic bond, both atoms hold electrons weakly. The transitions between the three types of bonding are continuous, since the electronegativities vary gradual ...
First Semester Final - Review Questions
... 42. What type of instrument is best for measuring mass, volume, and length? 43. How is the uncertainty of an instrument determined? 44. State the Atlantic-Pacific Rule for determining significant figures. 45. How many significant figures are in the following measurements? a. 0.000653 g c. 8.50x10-9 ...
... 42. What type of instrument is best for measuring mass, volume, and length? 43. How is the uncertainty of an instrument determined? 44. State the Atlantic-Pacific Rule for determining significant figures. 45. How many significant figures are in the following measurements? a. 0.000653 g c. 8.50x10-9 ...
Biol 1441
... Polar covalent bond: the electrons of the bond are not shared equally. Ex: HCl Ionic Bonds: Two atoms are so unequal in their attraction for valence electrons that the more electronegative atom strips an electron completely away from its partner. Ion: a charged atom (or molecule) Cation: a positive ...
... Polar covalent bond: the electrons of the bond are not shared equally. Ex: HCl Ionic Bonds: Two atoms are so unequal in their attraction for valence electrons that the more electronegative atom strips an electron completely away from its partner. Ion: a charged atom (or molecule) Cation: a positive ...
2.1 The Nature of Matter - Sonoma Valley High School
... neutrons and different mass. All isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties b/c their electrons are the same. ...
... neutrons and different mass. All isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties b/c their electrons are the same. ...
Advanced Chemistry Midterm
... 23. What are the electronegativity difference ranges for nonpolar bonds? For polar bonds? For ionic bonds? ...
... 23. What are the electronegativity difference ranges for nonpolar bonds? For polar bonds? For ionic bonds? ...
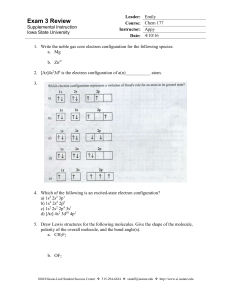
Exam 3 Review - Iowa State University
... 15. Which substance should form an acidic solution in water? a. Na2O b. SO2 c. CO d. BaO 16. Which of the following is the largest in size? a. Clb. Cl c. I+ d. I17. When an alkali metal reacts with water, a metal hydroxide and a gas form. Which gas forms? a. Carbon dioxide b. Oxygen c. Ozone d. Hydr ...
... 15. Which substance should form an acidic solution in water? a. Na2O b. SO2 c. CO d. BaO 16. Which of the following is the largest in size? a. Clb. Cl c. I+ d. I17. When an alkali metal reacts with water, a metal hydroxide and a gas form. Which gas forms? a. Carbon dioxide b. Oxygen c. Ozone d. Hydr ...
Resonance (chemistry)
In chemistry, resonance or mesomerism is a way of describing delocalized electrons within certain molecules or polyatomic ions where the bonding cannot be expressed by one single Lewis formula. A molecule or ion with such delocalized electrons is represented by several contributing structures (also called resonance structures or canonical forms).Each contributing structure can be represented by a Lewis structure, with only an integer number of covalent bonds between each pair of atoms within the structure. Several Lewis structures are used collectively to describe the actual molecular structure, which is an approximate intermediate between the canonical forms called a resonance hybrid. Contributing structures differ only in the position of electrons, not in the position of nuclei.Electron delocalization lowers the potential energy of the substance and thus makes it more stable than any of the contributing structures. The difference between the potential energy of the actual structure and that of the contributing structure with the lowest potential energy is called the resonance energy or delocalization energy.Resonance is distinguished from tautomerism and conformational isomerism, which involve the formation of isomers, thus the rearrangement of the nuclear positions.