Element Approx.
... of years for Earth to produce but humans are taking minerals out of Earth’s crust at a fast rate ...
... of years for Earth to produce but humans are taking minerals out of Earth’s crust at a fast rate ...
1 - WordPress.com
... What is the structure of a solid ionic compound? Crystal lattice (alternating positive and negative ions packed closely together in a crystalline structure) What are properties of ionic compounds? Hard, brittle, very high melting points, can conduct electricity if dissolved in water or melted 41. A ...
... What is the structure of a solid ionic compound? Crystal lattice (alternating positive and negative ions packed closely together in a crystalline structure) What are properties of ionic compounds? Hard, brittle, very high melting points, can conduct electricity if dissolved in water or melted 41. A ...
Chapter 5 notes
... Atoms tend to gain or lose electrons until they have achieved an outer shell that contains an octet (8) of electrons ...
... Atoms tend to gain or lose electrons until they have achieved an outer shell that contains an octet (8) of electrons ...
2003
... Explain the difference in electrical conductivity between substances C and D. (2 marks) OUTCOME – P 14 Substance C conducts electricity in solid and molten states due to free (delocalised) electrons which can move freely through the lattice. Substance D does not conduct electricity in the solid stat ...
... Explain the difference in electrical conductivity between substances C and D. (2 marks) OUTCOME – P 14 Substance C conducts electricity in solid and molten states due to free (delocalised) electrons which can move freely through the lattice. Substance D does not conduct electricity in the solid stat ...
Unit 3 Lesson 1
... Who developed the atomic theory? • In 1808, John Dalton published an atomic theory, stating that all matter is made up of atoms that cannot be created, divided, or destroyed. • This theory also stated that all atoms of a certain element are identical, but they differ from atoms of all other elements ...
... Who developed the atomic theory? • In 1808, John Dalton published an atomic theory, stating that all matter is made up of atoms that cannot be created, divided, or destroyed. • This theory also stated that all atoms of a certain element are identical, but they differ from atoms of all other elements ...
Chapter 3 Molecules, Compounds, and Chemical Equations
... 9 use lines to represent covalent bonds 9 Each line describes the number of electrons shared by the bonded atoms. ¾ single line = 2 shared electrons, a single covalent bond ¾ double line = 4 shared electrons, a double covalent bond ¾ triple line = 6 shared electrons, a triple covalent bond ...
... 9 use lines to represent covalent bonds 9 Each line describes the number of electrons shared by the bonded atoms. ¾ single line = 2 shared electrons, a single covalent bond ¾ double line = 4 shared electrons, a double covalent bond ¾ triple line = 6 shared electrons, a triple covalent bond ...
General Chemistry Questions
... 6. Use VSEPR theory to predict the ideal bond angles around the two carbon atoms in acetaldehyde, CH3CHO. (The first carbon has single bonds to three H atoms and one C atom; the second carbon has single bonds to C and H, and a double bond to O.) a. b. c. d. e. ...
... 6. Use VSEPR theory to predict the ideal bond angles around the two carbon atoms in acetaldehyde, CH3CHO. (The first carbon has single bonds to three H atoms and one C atom; the second carbon has single bonds to C and H, and a double bond to O.) a. b. c. d. e. ...
The radial part of the wavefunction, R(r)
... Let us now consider how we might represent atomic orbitals in three-dimensional space. We said earlier that a useful description of an electron in an atom is the probability of finding the electron in a given volume of space. The function Ψ2 is proportional to the probability density of the electron ...
... Let us now consider how we might represent atomic orbitals in three-dimensional space. We said earlier that a useful description of an electron in an atom is the probability of finding the electron in a given volume of space. The function Ψ2 is proportional to the probability density of the electron ...
CST Review Part 2
... principle of conservation of matter and the ability to calculate the mass of products and reactants. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know how to describe chemical reactions by writing balanced equations. b. Students know the quantity on mole is set by defining one mole of carb ...
... principle of conservation of matter and the ability to calculate the mass of products and reactants. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know how to describe chemical reactions by writing balanced equations. b. Students know the quantity on mole is set by defining one mole of carb ...
atom
... • Where are protons, neutrons, and electrons located in an atom? • How is the atomic number related to the number of protons in an atom? • What effect does changing the number of particles in an atom have on the ...
... • Where are protons, neutrons, and electrons located in an atom? • How is the atomic number related to the number of protons in an atom? • What effect does changing the number of particles in an atom have on the ...
Elements, Compounds and Mixtures.
... similar to those of the substances are different to those of the in a mixture. elements which reacted to form it. There are practically no energy Heat is usually given out or changes when a mixture is made taken in when a compound is formed. It is usually easy to separate the components of a mixture ...
... similar to those of the substances are different to those of the in a mixture. elements which reacted to form it. There are practically no energy Heat is usually given out or changes when a mixture is made taken in when a compound is formed. It is usually easy to separate the components of a mixture ...
KEY_Reaction Types WS
... Balance the Molecular Equation: In the “molecular” equation, nothing is broken up into ions. Salt formulas are written so that the cation charges exactly balance out the anion charges so that the salt is neutral. Then the equation is balanced for atoms. Balance the Total Ionic Equation: The first st ...
... Balance the Molecular Equation: In the “molecular” equation, nothing is broken up into ions. Salt formulas are written so that the cation charges exactly balance out the anion charges so that the salt is neutral. Then the equation is balanced for atoms. Balance the Total Ionic Equation: The first st ...
1 - Groupfusion.net
... What is the structure of a solid ionic compound? Crystal lattice (alternating positive and negative ions packed closely together in a crystalline structure) What are properties of ionic compounds? Hard, brittle, very high melting points, can conduct electricity if dissolved in water or melted 41. A ...
... What is the structure of a solid ionic compound? Crystal lattice (alternating positive and negative ions packed closely together in a crystalline structure) What are properties of ionic compounds? Hard, brittle, very high melting points, can conduct electricity if dissolved in water or melted 41. A ...
Chapter 23 (Section 3) Pregnancy, Birth, and
... of Triads stated there were groups of “3” ELEMENTS where the middle ELEMENT’S atomic MASS was the average of the other “2” ELEMENTS *a. (e.g.) calcium [Ca] = 40.08; strontium [Sr] = 87.62; barium [Ba] = 137.33 *2. In 1856, Newlands proposed the Law of Octaves stated that some of the 56 ELEMENTS ...
... of Triads stated there were groups of “3” ELEMENTS where the middle ELEMENT’S atomic MASS was the average of the other “2” ELEMENTS *a. (e.g.) calcium [Ca] = 40.08; strontium [Sr] = 87.62; barium [Ba] = 137.33 *2. In 1856, Newlands proposed the Law of Octaves stated that some of the 56 ELEMENTS ...
Part II Biochemistry
... • The word carbohydrate arose because molecular formulas of these compounds can be expressed as hydrates of carbon. • Glucose, for example, has the molecular formula C6H12O6, which might be written as C6(H2O)6. • Carbohydrates are now defined as: 1. polyhydroxyaldehydes, 2. polyhydroxyketones, or 3 ...
... • The word carbohydrate arose because molecular formulas of these compounds can be expressed as hydrates of carbon. • Glucose, for example, has the molecular formula C6H12O6, which might be written as C6(H2O)6. • Carbohydrates are now defined as: 1. polyhydroxyaldehydes, 2. polyhydroxyketones, or 3 ...
CHAPtER 9 Properties and reactions of organic compounds
... than the cis isomers, making the intermolecular forces more effective. cis and trans isomers can also occur in ring structures. cis–trans isomers belong to a larger group of stereoisomers called diastereomers, which includes other stereoisomers that are not mirror images of each other. Some molecule ...
... than the cis isomers, making the intermolecular forces more effective. cis and trans isomers can also occur in ring structures. cis–trans isomers belong to a larger group of stereoisomers called diastereomers, which includes other stereoisomers that are not mirror images of each other. Some molecule ...
Atoms and bonds in molecules and chemical explanations
... This example shows that several causal processes may be invoked to explain a fact. In the present case all answers are relevant and complementary since they partially address the question. This example insists on the cultural differences between scientific communities. Chemical explanations of the s ...
... This example shows that several causal processes may be invoked to explain a fact. In the present case all answers are relevant and complementary since they partially address the question. This example insists on the cultural differences between scientific communities. Chemical explanations of the s ...
Spectrum05
... Copper reacts with chlorine to form copper (II) chloride. In a word equation Methane + oxygen water +carbon dioxide Arrow means “yields” or “makes” The plus sign means “and” Can use formulas CH4 +O2 CO2 +H2O ...
... Copper reacts with chlorine to form copper (II) chloride. In a word equation Methane + oxygen water +carbon dioxide Arrow means “yields” or “makes” The plus sign means “and” Can use formulas CH4 +O2 CO2 +H2O ...
model paper-1 - WordPress.com
... A reagent that takes away an electron pair is called an electrophile (E+) i.e., electron seeking and the reaction is called electrophilic. Example: carbocations and neutral molecules having functional groups like carbonyl group or alkyl halides. b) This is because if sulphuric acid is used, it will ...
... A reagent that takes away an electron pair is called an electrophile (E+) i.e., electron seeking and the reaction is called electrophilic. Example: carbocations and neutral molecules having functional groups like carbonyl group or alkyl halides. b) This is because if sulphuric acid is used, it will ...
File
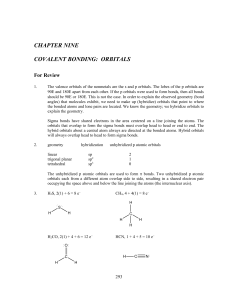
... We use the valence s and the three degenerate p valence atomic orbitals for four of the five orbitals; the fifth is an empty d orbital close in energy to the valence atomic orbitals. We call this hybridization dsp3. For octahedral geometry, we need six hybrid orbitals to account for the locations of ...
... We use the valence s and the three degenerate p valence atomic orbitals for four of the five orbitals; the fifth is an empty d orbital close in energy to the valence atomic orbitals. We call this hybridization dsp3. For octahedral geometry, we need six hybrid orbitals to account for the locations of ...