Final Exam Review
... 22. Consider two identical flasks, both at 25 C and 1 atm pressure. One contains H2 gas and the other O2 gas. Which of the following statements about the gases contained in the two flasks is not true? (Ch. 13) a. The same number of molecules are contained in each flask. b. The average kinetic energ ...
... 22. Consider two identical flasks, both at 25 C and 1 atm pressure. One contains H2 gas and the other O2 gas. Which of the following statements about the gases contained in the two flasks is not true? (Ch. 13) a. The same number of molecules are contained in each flask. b. The average kinetic energ ...
File - Mr. L`s Room
... Matter Unit Test Study Guide with Answers This unit test is cumulative, so all three Study Guides—Characteristics of Science, Atoms and the Periodic Table Study Guide, and this one on Matter—should be completed and studied for this unit test. Characterisitcs of Science: Each of these items were cove ...
... Matter Unit Test Study Guide with Answers This unit test is cumulative, so all three Study Guides—Characteristics of Science, Atoms and the Periodic Table Study Guide, and this one on Matter—should be completed and studied for this unit test. Characterisitcs of Science: Each of these items were cove ...
Lecture 1 - Introduction to Semiconductors - Outline Introductions/Announcements Handouts:
... • Silicon in thermal equilibrium Intrinsic (pure) Si: no = po = ni(T) = 1010 cm-3 at RT Doped Si: nopo = ni2 always; no net charge (mobile + fixed = 0) If Nd > Na, then: no ≈ Nd – Na; po = ni2/no; called "n-type"; electrons are the majority carriers, holes the minority ...
... • Silicon in thermal equilibrium Intrinsic (pure) Si: no = po = ni(T) = 1010 cm-3 at RT Doped Si: nopo = ni2 always; no net charge (mobile + fixed = 0) If Nd > Na, then: no ≈ Nd – Na; po = ni2/no; called "n-type"; electrons are the majority carriers, holes the minority ...
Molecular Modeling Activity for Carbohydrates
... molecule has a molecular formula of ___________and is called _____________________________________ 9. Write the molecular formula for sucrose. _____________________________ 10. How many times larger is the number of hydrogen atoms than oxygen atoms in a disaccharide? ________ 11. How many monosaccha ...
... molecule has a molecular formula of ___________and is called _____________________________________ 9. Write the molecular formula for sucrose. _____________________________ 10. How many times larger is the number of hydrogen atoms than oxygen atoms in a disaccharide? ________ 11. How many monosaccha ...
Solution
... NF3 = 0.23 D, PF3 = 1.03 D, AsF3 = 2.57 D. Provide at least two arguments to explain this trend. (10 pts) The difference in electronegativity between the two atoms increases with increasing dipole moment. The bond distances also increase with increasing dipole moment due larger atomic radii of the c ...
... NF3 = 0.23 D, PF3 = 1.03 D, AsF3 = 2.57 D. Provide at least two arguments to explain this trend. (10 pts) The difference in electronegativity between the two atoms increases with increasing dipole moment. The bond distances also increase with increasing dipole moment due larger atomic radii of the c ...
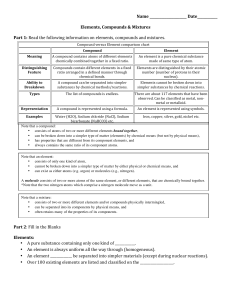
Compound vs Element chart
... • can be broken down into a simpler type of matter (elements) by chemical means (but not by physical means), • has properties that are different from its component elements, and • always contains the same ratio of its component atoms. Note that an element: • consists of only one kind of atom, • cann ...
... • can be broken down into a simpler type of matter (elements) by chemical means (but not by physical means), • has properties that are different from its component elements, and • always contains the same ratio of its component atoms. Note that an element: • consists of only one kind of atom, • cann ...
Atoms and Molecules
... 2. Atoms combine by chemical bonding to form molecules • Atoms with incomplete valence shells interact by either sharing or transferring valence electrons. • These interactions typically result in the atoms remaining close together, held by an attractions called chemical bonds. • The strongest chem ...
... 2. Atoms combine by chemical bonding to form molecules • Atoms with incomplete valence shells interact by either sharing or transferring valence electrons. • These interactions typically result in the atoms remaining close together, held by an attractions called chemical bonds. • The strongest chem ...
Inorganic Pharmaceutical Chemistry Hybrid Orbitals Hybridization
... If your visual imagination will cope, you may be able to see that this ion has no plane of symmetry. If you find this difficult to visualise, the only solution is to make the ion out of a lump of plasticene (or a bit of clay or dough) and three bits of cardboard cut to shape A substance with no plan ...
... If your visual imagination will cope, you may be able to see that this ion has no plane of symmetry. If you find this difficult to visualise, the only solution is to make the ion out of a lump of plasticene (or a bit of clay or dough) and three bits of cardboard cut to shape A substance with no plan ...
HL2-1
... molecule is the Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory. Q – Do electrons like to hang out together? ...
... molecule is the Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory. Q – Do electrons like to hang out together? ...
Training - Independent School District 196
... philosopher, first purposed the word ‘Atom’ around 375 BC. The atom was defined as a small round indivisible particle. Democritus described the atom by talking about the constant division of an object until the object could no longer be divided. The idea of the Atom had to wait for 2200 years to be ...
... philosopher, first purposed the word ‘Atom’ around 375 BC. The atom was defined as a small round indivisible particle. Democritus described the atom by talking about the constant division of an object until the object could no longer be divided. The idea of the Atom had to wait for 2200 years to be ...
Thermochemistry only Sp 12 unit I
... reaction in which one mole of the compound in its standard state is formed from its elements in their standard states. For example, C(s) + H2 (g) CH4 (g) ΔHf°= - 74.9 kj/mole The above elements are in their standard states. ΔHf° are important since they can be used to calculate heats of reaction t ...
... reaction in which one mole of the compound in its standard state is formed from its elements in their standard states. For example, C(s) + H2 (g) CH4 (g) ΔHf°= - 74.9 kj/mole The above elements are in their standard states. ΔHf° are important since they can be used to calculate heats of reaction t ...
Glossary: Chemical bonds
... CA, CB, CC, CD are concentrations of gaseous or dissolved substances. Chemical equilibrium is a dynamic one, so it can be shifted according to le Chateleu’s principle (principle of counteraction): if an equilibrium system is affected by any factor (change in concentrations, pressure or temperature), ...
... CA, CB, CC, CD are concentrations of gaseous or dissolved substances. Chemical equilibrium is a dynamic one, so it can be shifted according to le Chateleu’s principle (principle of counteraction): if an equilibrium system is affected by any factor (change in concentrations, pressure or temperature), ...
CBSE/12th Class/2010/CHEMISTRY
... (ii)The E0 value for the Mn3/Mn2+ couple is much more positive than that for Cr3/Cr2+ couple or Fe3+/Fe2+ couple.Because Mn3+ has the outer electronic configuration of 3d4 and Mn2+ has the outer electronic configuration of 3d5. Thus, the conversion of Mn3+ to Mn2+ will be a favourable reaction since ...
... (ii)The E0 value for the Mn3/Mn2+ couple is much more positive than that for Cr3/Cr2+ couple or Fe3+/Fe2+ couple.Because Mn3+ has the outer electronic configuration of 3d4 and Mn2+ has the outer electronic configuration of 3d5. Thus, the conversion of Mn3+ to Mn2+ will be a favourable reaction since ...
Exam Review
... A) Subatomic particles a. What are the atomic mass units for protons, neutrons, and electrons? Protons and neutrons = 1 amu; electrons about 0 amu What does the atomic number represent? # of protons b. What does the mass number represent? # of protons + # of neutrons c. What particles are in equal n ...
... A) Subatomic particles a. What are the atomic mass units for protons, neutrons, and electrons? Protons and neutrons = 1 amu; electrons about 0 amu What does the atomic number represent? # of protons b. What does the mass number represent? # of protons + # of neutrons c. What particles are in equal n ...
Chemical Composition Notes
... _______ - formed when electrons are lost or gained in ordinary chemical reactions; affect size of atoms dramatically __________ - (+) ions; often metals since metals lose electrons to become positively charged ________ - (—) ions; often nonmetals since nonmetals gain electrons to become negatively c ...
... _______ - formed when electrons are lost or gained in ordinary chemical reactions; affect size of atoms dramatically __________ - (+) ions; often metals since metals lose electrons to become positively charged ________ - (—) ions; often nonmetals since nonmetals gain electrons to become negatively c ...
IE EA
... f) SF6 Neither; the coordination number of six is rarely exceeded so that this molecule does not act as a Lewis acid and the high electronegativity of fluorine does not allow for it to act as a base. g) PCl5 Acidic; this compound reacts with a wide variety of Lewis bases to form adducts. h) (CH3)3N ...
... f) SF6 Neither; the coordination number of six is rarely exceeded so that this molecule does not act as a Lewis acid and the high electronegativity of fluorine does not allow for it to act as a base. g) PCl5 Acidic; this compound reacts with a wide variety of Lewis bases to form adducts. h) (CH3)3N ...
OCR_AS_Level_Chemistry_Unit_F321_Atoms
... another molecule. o The more electrons, the stronger the van der Waal’s forces o Occur in all simple covalent substances b) Dipole-dipole o Attraction between molecules with permanent dipoles o δ+ ends attracted to δ- ends c) Hydrogen bonds o Need H attached to N/O/F (highly electronegative elements ...
... another molecule. o The more electrons, the stronger the van der Waal’s forces o Occur in all simple covalent substances b) Dipole-dipole o Attraction between molecules with permanent dipoles o δ+ ends attracted to δ- ends c) Hydrogen bonds o Need H attached to N/O/F (highly electronegative elements ...
Functional Groups
... thiourea –both N & S) 2. Compounds that contain a functional group consisting of sulfur and oxygen. (Sulfoxides, sulfones). 3. Sulfur heterocyclics: where sulfur is attached at one of the points in a cyclic carbon molecule. ...
... thiourea –both N & S) 2. Compounds that contain a functional group consisting of sulfur and oxygen. (Sulfoxides, sulfones). 3. Sulfur heterocyclics: where sulfur is attached at one of the points in a cyclic carbon molecule. ...