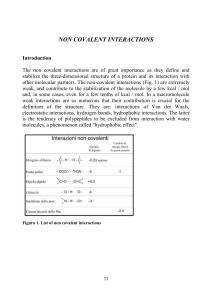
i principi di base - Structural Biology
... weak, and contribute to the stabilization of the molecule by a few kcal / mol and, in some cases, even for a few tenths of kcal / mol. In a macromolecule weak interactions are so numerous that their contribution is crucial for the definition of the structure. They are: interactions of Van der Waals, ...
... weak, and contribute to the stabilization of the molecule by a few kcal / mol and, in some cases, even for a few tenths of kcal / mol. In a macromolecule weak interactions are so numerous that their contribution is crucial for the definition of the structure. They are: interactions of Van der Waals, ...
Chemistry Module 1- Basic Revision Notes 1.1a Atomic Structure 1.1
... Plus the total number of electrons gives the atomic number. e.g. 2.1 = atomic number 3 2.5 = atomic number 7 Here are some more examples from the periodic table above:Element 3Li 15P 13Al 18Ar 20Ca ...
... Plus the total number of electrons gives the atomic number. e.g. 2.1 = atomic number 3 2.5 = atomic number 7 Here are some more examples from the periodic table above:Element 3Li 15P 13Al 18Ar 20Ca ...
9. Balancing Equations
... How many sodiums on the left? 2; how many on the right/ 1; put a coefficient 2 in front of the one on the right. How many oxygens on the left/ on the right/, etc. Na2O + BaCl2 - 2NaCl + BaO ...
... How many sodiums on the left? 2; how many on the right/ 1; put a coefficient 2 in front of the one on the right. How many oxygens on the left/ on the right/, etc. Na2O + BaCl2 - 2NaCl + BaO ...
N5 Chemistry Summary notes 2017
... The Noble gases are stable elements as they have a full outer electron shell. Other elements react until their atoms obtain a full outer shell and become stable. Non-metal atoms obtain a full outer shell by sharing their outer electrons with other nonmetal atoms. The sharing of outer electrons is ca ...
... The Noble gases are stable elements as they have a full outer electron shell. Other elements react until their atoms obtain a full outer shell and become stable. Non-metal atoms obtain a full outer shell by sharing their outer electrons with other nonmetal atoms. The sharing of outer electrons is ca ...
8.3 Bonding Theories
... 8.3 Bonding Theories > Key Concepts Just as an atomic orbital belongs to a particular atom, a molecular orbital belongs to a molecule as a whole. In order to explain the three-dimensional shape of molecules, scientists use the valence-shell electron-pair repulsion theory (VSEPR theory). Orbital hyb ...
... 8.3 Bonding Theories > Key Concepts Just as an atomic orbital belongs to a particular atom, a molecular orbital belongs to a molecule as a whole. In order to explain the three-dimensional shape of molecules, scientists use the valence-shell electron-pair repulsion theory (VSEPR theory). Orbital hyb ...
Ch08 Lesson08_3
... 8.3 Bonding Theories > Key Concepts Just as an atomic orbital belongs to a particular atom, a molecular orbital belongs to a molecule as a whole. In order to explain the three-dimensional shape of molecules, scientists use the valence-shell electron-pair repulsion theory (VSEPR theory). Orbital hyb ...
... 8.3 Bonding Theories > Key Concepts Just as an atomic orbital belongs to a particular atom, a molecular orbital belongs to a molecule as a whole. In order to explain the three-dimensional shape of molecules, scientists use the valence-shell electron-pair repulsion theory (VSEPR theory). Orbital hyb ...
Chapter 8: Periodic Properties of the Elements
... Homework: Read Chapter 8. Work out sample/practice exercises Suggested Chapter 8 Problems: 43, 45, 51, 55, 59, 63, 67, 71, 75, 79, 83, 99 Check for the MasteringChemistry.com assignment and complete before due date The Periodic Table: 1869 Dmitri Mendeleev (Russia) and Lothar Meyer (Germany) classif ...
... Homework: Read Chapter 8. Work out sample/practice exercises Suggested Chapter 8 Problems: 43, 45, 51, 55, 59, 63, 67, 71, 75, 79, 83, 99 Check for the MasteringChemistry.com assignment and complete before due date The Periodic Table: 1869 Dmitri Mendeleev (Russia) and Lothar Meyer (Germany) classif ...
How to Draw Orbital Overlap Diagrams
... time. • It’s too easy to miss something if you do the drawings with a different order to the steps. • You can change the order from what we show you here, but whatever order you use, use the same each tme. ...
... time. • It’s too easy to miss something if you do the drawings with a different order to the steps. • You can change the order from what we show you here, but whatever order you use, use the same each tme. ...
Document
... Waals forces are called “hydrogen bonding”—ie hydrogen bonding (or H-bonding) is a special case of van der Waals forces due to its rather strong nature coupled with its ubiquity in biological systems - Hydrogen bonding—represented by a dotted or dashed line—is the supreme attractive force that rende ...
... Waals forces are called “hydrogen bonding”—ie hydrogen bonding (or H-bonding) is a special case of van der Waals forces due to its rather strong nature coupled with its ubiquity in biological systems - Hydrogen bonding—represented by a dotted or dashed line—is the supreme attractive force that rende ...
File
... Name: _______________________________________________________________________ Period: ____ 11.2: Types of Chemical Reactions Part A: Completion Directions: Each blank can be completed with a term, short phrase, or number. It is possible to __1__ the products of some chemical ...
... Name: _______________________________________________________________________ Period: ____ 11.2: Types of Chemical Reactions Part A: Completion Directions: Each blank can be completed with a term, short phrase, or number. It is possible to __1__ the products of some chemical ...
Chemistry (CP) Final Exam Study Guide 1
... ____ 50. What is the maximum number of d orbitals in a principal energy level? a. 1 c. 3 b. 2 d. 5 ____ 51. What types of atomic orbitals are in the third principal energy level? a. s and p only c. s, p, and d only b. p and d only d. s, p, d, and f ____ 52. What is the next atomic orbital in the ser ...
... ____ 50. What is the maximum number of d orbitals in a principal energy level? a. 1 c. 3 b. 2 d. 5 ____ 51. What types of atomic orbitals are in the third principal energy level? a. s and p only c. s, p, and d only b. p and d only d. s, p, d, and f ____ 52. What is the next atomic orbital in the ser ...
Organic Chemistry 2014 finalzzz
... If more than one of the same branch exist, use a multiplier to show this (di, tri). Remember to include all numbers ...
... If more than one of the same branch exist, use a multiplier to show this (di, tri). Remember to include all numbers ...
Period:______ Table Number
... they are combined together in different ways and in different amounts. P. 9, 70, VCR: Atoms and Molecules 46. The smallest particle of any element that you can have which still possesses all of the physical and chemical properties of that element is a single ATOM of that element. P. 10, VCR: Atoms a ...
... they are combined together in different ways and in different amounts. P. 9, 70, VCR: Atoms and Molecules 46. The smallest particle of any element that you can have which still possesses all of the physical and chemical properties of that element is a single ATOM of that element. P. 10, VCR: Atoms a ...
Atoms, Molecules and Ions
... and closest to the bottom of a group on periodic table is placed first in formula − If more than one compound can be formed from the same elements, use prefixes to indicate number of each kind of atom − Last element name ends in -ide ...
... and closest to the bottom of a group on periodic table is placed first in formula − If more than one compound can be formed from the same elements, use prefixes to indicate number of each kind of atom − Last element name ends in -ide ...
CHM100PracticeExam2
... Do not begin the exam until you have been instructed to do so. You have 120 minutes to complete this exam. There are 50 multiple choice questions. You must use a number 2 pencil. You may use a scientific calculator. Make sure that you have written your name legibly on the scantron form. Circle bubbl ...
... Do not begin the exam until you have been instructed to do so. You have 120 minutes to complete this exam. There are 50 multiple choice questions. You must use a number 2 pencil. You may use a scientific calculator. Make sure that you have written your name legibly on the scantron form. Circle bubbl ...
Chemical bonding and structure
... as protons and electrons. This is because the number of protons (+) is equal to the number of electrons (−), and so their charges cancel each other out. The positively charged protons, located within the nucleus of the atom, are not transferred during chemical reactions. Electrons, however, position ...
... as protons and electrons. This is because the number of protons (+) is equal to the number of electrons (−), and so their charges cancel each other out. The positively charged protons, located within the nucleus of the atom, are not transferred during chemical reactions. Electrons, however, position ...
The ocean is a mixture.
... Transition elements have properties similar to one another and to other metals, but their properties do not fit in with those of any other family. Many transition metals combine chemically with oxygen to form compounds called oxides. They have one or two electrons in the outer level Reactivity: less ...
... Transition elements have properties similar to one another and to other metals, but their properties do not fit in with those of any other family. Many transition metals combine chemically with oxygen to form compounds called oxides. They have one or two electrons in the outer level Reactivity: less ...