Final "I Can Statements" Answer Key
... percent composition of an element in a compound. _____24. I can convert between moles and numbers of particles ...
... percent composition of an element in a compound. _____24. I can convert between moles and numbers of particles ...
TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS AND SOLUTION CHEMISTRY
... 1. _________________________ is a technique for determining the amount of a certain substance by doing a titration. 2. A ____________________ involves delivery of a measured volume of a solution of known concentration, _______________, into a solution containing the substance being analyzed, _______ ...
... 1. _________________________ is a technique for determining the amount of a certain substance by doing a titration. 2. A ____________________ involves delivery of a measured volume of a solution of known concentration, _______________, into a solution containing the substance being analyzed, _______ ...
CH 115 Exam 2 - UAB General Chemistry Supplemental Instruction
... Assume the chemical equations on this exam are NOT balanced unless stated otherwise. 1. Balance the equation and give the stoichiometric coefficient for HCl ...
... Assume the chemical equations on this exam are NOT balanced unless stated otherwise. 1. Balance the equation and give the stoichiometric coefficient for HCl ...
Chemical Reactions - Waukee Community School District Blogs
... Explain the difference between ionization and dissociation. Ionization occurs when ions are formed from the solute particles due to the action of ...
... Explain the difference between ionization and dissociation. Ionization occurs when ions are formed from the solute particles due to the action of ...
Review Packet - Daigneault Chem.is.try
... There will be a total of 70 multiple-choice questions, given in a 1 hour and 45 minutes block of exam time. The exam time includes the time it takes to pass out exam materials at the start of the exam. You may use a non-programmable calculator. (No cell phones. No graphing calculators.) It is highly ...
... There will be a total of 70 multiple-choice questions, given in a 1 hour and 45 minutes block of exam time. The exam time includes the time it takes to pass out exam materials at the start of the exam. You may use a non-programmable calculator. (No cell phones. No graphing calculators.) It is highly ...
THE ELECTRON DENSITY DISTRIBUTION IN THE HYDROGEN
... The calculations on the water molecule in an electric field, on the water dimer, and on the oxalic acid dihydrate were performed within the framework of the density-functional theory. This is equivalent to solving the HartreeFock equations with an approximate exchange-correlation potential for which ...
... The calculations on the water molecule in an electric field, on the water dimer, and on the oxalic acid dihydrate were performed within the framework of the density-functional theory. This is equivalent to solving the HartreeFock equations with an approximate exchange-correlation potential for which ...
Atomic orbital An atomic orbital is a mathematical function that
... Jump to: navigation, search See also: Molecular orbital theory In chemistry, a molecular orbital (or MO) is a mathematical function describing the wave-like behavior of an electron in a molecule. This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of findi ...
... Jump to: navigation, search See also: Molecular orbital theory In chemistry, a molecular orbital (or MO) is a mathematical function describing the wave-like behavior of an electron in a molecule. This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of findi ...
know thy reference tables!
... in Period 3 on the Periodic Table are considered in order from left to right? (1) nonmetallic properties and atomic radius (2) nonmetallic properties and ionization energy (3) metallic properties and atomic radius (4) metallic properties and ionization energy An atom of argon in the ground state ten ...
... in Period 3 on the Periodic Table are considered in order from left to right? (1) nonmetallic properties and atomic radius (2) nonmetallic properties and ionization energy (3) metallic properties and atomic radius (4) metallic properties and ionization energy An atom of argon in the ground state ten ...
chemistry ii chapter 2- atoms, molecules, and ions
... of any object that has many components, but is recognized as a single object (car, phone, etc) ...
... of any object that has many components, but is recognized as a single object (car, phone, etc) ...
Subject Area Assessment Guides
... What the Science Frameworks states… A Lewis dot structure shows how valence electrons and covalent bonds are arranged between atoms in a molecule. Teachers should follow the rules for drawing Lewis dot diagrams provided in chemistry textbook. Students should be able to use the periodic table to dete ...
... What the Science Frameworks states… A Lewis dot structure shows how valence electrons and covalent bonds are arranged between atoms in a molecule. Teachers should follow the rules for drawing Lewis dot diagrams provided in chemistry textbook. Students should be able to use the periodic table to dete ...
File
... The idea of atoms did not become scientific theory until 1808. John Dalton (1766–1844) developed an atomic theory proposing that atoms were responsible for the combinations of elements in compounds. ...
... The idea of atoms did not become scientific theory until 1808. John Dalton (1766–1844) developed an atomic theory proposing that atoms were responsible for the combinations of elements in compounds. ...
Gas-Forming reactions Reactions that form a
... But they end up with the same number of electrons they start with. Every atom, ion or polyatomic ion has a formal oxidation number associated with it. This value compares the number of protons in an atom (positive charge) and the number of electrons assigned to that atom (negative charge). In many c ...
... But they end up with the same number of electrons they start with. Every atom, ion or polyatomic ion has a formal oxidation number associated with it. This value compares the number of protons in an atom (positive charge) and the number of electrons assigned to that atom (negative charge). In many c ...
chemistry
... Which type of molecular attraction accounts for the high boiling point of H2O? (1) molecule–ion (2) ion–ion (3) hydrogen bonding (4) van der Waals forces ...
... Which type of molecular attraction accounts for the high boiling point of H2O? (1) molecule–ion (2) ion–ion (3) hydrogen bonding (4) van der Waals forces ...
FREE Sample Here
... http://testbankwizard.eu/Test-Bank-for-Campbell-Biology-with-MasteringBiology-9th-Edition-by-Reec e 24) What is the maximum number of electrons in a single 2 p orbital of an atom? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 E) 5 Answer: B Topic: Concept 2.2 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension 25) The organic molecules in living ...
... http://testbankwizard.eu/Test-Bank-for-Campbell-Biology-with-MasteringBiology-9th-Edition-by-Reec e 24) What is the maximum number of electrons in a single 2 p orbital of an atom? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 E) 5 Answer: B Topic: Concept 2.2 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension 25) The organic molecules in living ...
Chemical Equations and Reactions
... greater the activity is. • Metals: the greater the activity, the greater it loses electrons (to form cations) • Non-metals: the greater the activity, the greater it gains electrons (to form anions) • Activity series: a list of which elements a particular element can replace in a single replacement r ...
... greater the activity is. • Metals: the greater the activity, the greater it loses electrons (to form cations) • Non-metals: the greater the activity, the greater it gains electrons (to form anions) • Activity series: a list of which elements a particular element can replace in a single replacement r ...
PHYSICAL SETTING CHEMISTRY
... and chemical properties of diamond, graphite has (1) a different molecular structure and different properties (2) a different molecular structure and the same properties (3) the same molecular structure and different properties (4) the same molecular structure and the same properties ...
... and chemical properties of diamond, graphite has (1) a different molecular structure and different properties (2) a different molecular structure and the same properties (3) the same molecular structure and different properties (4) the same molecular structure and the same properties ...
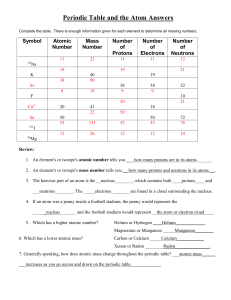
Periodic Table and the Atom Answers
... 13) Which of these elements has the highest first ionization energy? a) oxygen b) oxygen c) fluorine d) carbon e) boron 14) Which of these elements has the highest electronegativity? a) lithium b) nitrogen c) potassium d) arsenic e) beryllium ...
... 13) Which of these elements has the highest first ionization energy? a) oxygen b) oxygen c) fluorine d) carbon e) boron 14) Which of these elements has the highest electronegativity? a) lithium b) nitrogen c) potassium d) arsenic e) beryllium ...
ATOMS
... Theory of Matter The Atomic - Molecular Theory of Matter states that all matter is composed of small, fast moving particles called atoms. These atoms can join together to form molecules. This theory is really thousands of individual theories that provide evidence for the whole theory. ...
... Theory of Matter The Atomic - Molecular Theory of Matter states that all matter is composed of small, fast moving particles called atoms. These atoms can join together to form molecules. This theory is really thousands of individual theories that provide evidence for the whole theory. ...
Chapter 5
... can occur when atoms, ions, and molecules collide Activation energy is needed to disrupt electronic configurations Reaction rate is the frequency of collisions with enough energy to bring about a reaction. Reaction rate can be increased by enzymes or by increasing temperature or pressure ...
... can occur when atoms, ions, and molecules collide Activation energy is needed to disrupt electronic configurations Reaction rate is the frequency of collisions with enough energy to bring about a reaction. Reaction rate can be increased by enzymes or by increasing temperature or pressure ...
Topic 1 Review - Capital High School
... 5. What happens when magnesium metal reacts with chlorine gas? A. Each magnesium atom loses two electrons and each chlorine atom gains two electrons. B. Each magnesium atom gains one electron and each chlorine atom loses one electron. C. Each magnesium atom loses two electrons and each chlorine atom ...
... 5. What happens when magnesium metal reacts with chlorine gas? A. Each magnesium atom loses two electrons and each chlorine atom gains two electrons. B. Each magnesium atom gains one electron and each chlorine atom loses one electron. C. Each magnesium atom loses two electrons and each chlorine atom ...
IB Chemistry Review. Unit I. Topics 2
... 5. What happens when magnesium metal reacts with chlorine gas? A. Each magnesium atom loses two electrons and each chlorine atom gains two electrons. B. Each magnesium atom gains one electron and each chlorine atom loses one electron. C. Each magnesium atom loses two electrons and each chlorine atom ...
... 5. What happens when magnesium metal reacts with chlorine gas? A. Each magnesium atom loses two electrons and each chlorine atom gains two electrons. B. Each magnesium atom gains one electron and each chlorine atom loses one electron. C. Each magnesium atom loses two electrons and each chlorine atom ...
CHEM 1405 Practice Exam 3 (2015)
... 3) What is the volume of oxygen gas at STP from the decomposition of 10.8 g of mercuric oxide (216.59 g/mol)? __HgO(s) → __Hg(l) + __O2(g) ...
... 3) What is the volume of oxygen gas at STP from the decomposition of 10.8 g of mercuric oxide (216.59 g/mol)? __HgO(s) → __Hg(l) + __O2(g) ...