1.8 M - Thierry Karsenti
... copyright free, relevant, compulsory resources other than a written text or a web site. These could be a video file, an audio file, a set of images, etc. For each resource, Module Developers need to write the complete reference (APA style), as well as a 50 word abstract written in a way to motivate ...
... copyright free, relevant, compulsory resources other than a written text or a web site. These could be a video file, an audio file, a set of images, etc. For each resource, Module Developers need to write the complete reference (APA style), as well as a 50 word abstract written in a way to motivate ...
Folie 1
... solute divided by the volume of the solution. Molar concentration is usually expressed in moles per litre (mol L-1 or mol dm-3). A molar concentration of x mol L-1 is widely called ‘x molar’ and denoted x M. The term molality refers to the amount of substance of the solute divided by the mass of t ...
... solute divided by the volume of the solution. Molar concentration is usually expressed in moles per litre (mol L-1 or mol dm-3). A molar concentration of x mol L-1 is widely called ‘x molar’ and denoted x M. The term molality refers to the amount of substance of the solute divided by the mass of t ...
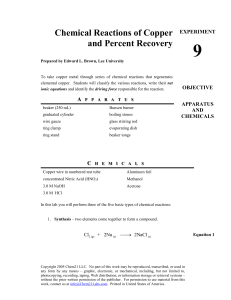
Chemical Reactions of Copper and Percent Recovery
... 6. Either you or your instructor will place ~ 5 mL of concentrated nitric acid (conc HNO3 is very CAUSTIC – Avoid Contact!! Use gloves!!) in the beaker. The copper metal will be oxidized to copper ions (~5 minutes). The noxious gas, NO2, is produced in this reaction so the beaker must be kept inside ...
... 6. Either you or your instructor will place ~ 5 mL of concentrated nitric acid (conc HNO3 is very CAUSTIC – Avoid Contact!! Use gloves!!) in the beaker. The copper metal will be oxidized to copper ions (~5 minutes). The noxious gas, NO2, is produced in this reaction so the beaker must be kept inside ...
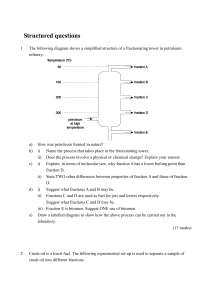
Structured questions
... ii) A component of the heavy fraction of petroleum has a molecular formula C12H26. In one of the reactions in Process 2, only a hydrocarbon and compound B are formed from this component. Write a chemical equation for the reaction involved. Catalytic hydration is employed to convert compound B into e ...
... ii) A component of the heavy fraction of petroleum has a molecular formula C12H26. In one of the reactions in Process 2, only a hydrocarbon and compound B are formed from this component. Write a chemical equation for the reaction involved. Catalytic hydration is employed to convert compound B into e ...
PIB - Unit 6 - Chemical Reactions - Student
... The substances that undergo a chemical reaction are the reactants. The new substances formed are the products. Special symbols are written after formulas in equations to show a substance’s state. The designations for solid, liquid, or gas, are (s), (l), and (g), respectively. A substance dissolv ...
... The substances that undergo a chemical reaction are the reactants. The new substances formed are the products. Special symbols are written after formulas in equations to show a substance’s state. The designations for solid, liquid, or gas, are (s), (l), and (g), respectively. A substance dissolv ...
AP Chemistry: Total Notes Review
... o Elements in the same group on the Periodic Table have the same type of electron arrangement in their outermost shells ex) F, [He]2s22p5; and Cl[Ne]3s23p5 ~ Outer-shell electrons: those that lie outside the orbitals occupied in the nextlowest noble gas element ex)[He]2s22p5 ~ Valence electrons: out ...
... o Elements in the same group on the Periodic Table have the same type of electron arrangement in their outermost shells ex) F, [He]2s22p5; and Cl[Ne]3s23p5 ~ Outer-shell electrons: those that lie outside the orbitals occupied in the nextlowest noble gas element ex)[He]2s22p5 ~ Valence electrons: out ...
answers to part a of the canadian chemistry
... The people involved in preparing the CCC very much appreciate all the comments and feedback that we get from teachers. We have tried to incorporate some of these comments in with the solutions. We have also tried to indicate how students did in particular questions, although, unfortunately, we have ...
... The people involved in preparing the CCC very much appreciate all the comments and feedback that we get from teachers. We have tried to incorporate some of these comments in with the solutions. We have also tried to indicate how students did in particular questions, although, unfortunately, we have ...
Chapter 1 Matter and Change
... Mixtures are a physical blend of at least two substances; have variable composition. They can be either: 1) Heterogeneous – the mixture is not uniform in composition • Chocolate chip cookie, gravel, soil. 2) Homogeneous - same composition throughout; called “solutions” • Kool-aid, air, salt water ...
... Mixtures are a physical blend of at least two substances; have variable composition. They can be either: 1) Heterogeneous – the mixture is not uniform in composition • Chocolate chip cookie, gravel, soil. 2) Homogeneous - same composition throughout; called “solutions” • Kool-aid, air, salt water ...
Department of Chemistry First Year Syllabus
... Account for the horizontal and vertical trends for some atomic properties such as atomic size, ionisation potential, electron affinity and electronegativity Know how to describe chemical bonding in small molecules of the main group elements Be familiar with the three different models describing thos ...
... Account for the horizontal and vertical trends for some atomic properties such as atomic size, ionisation potential, electron affinity and electronegativity Know how to describe chemical bonding in small molecules of the main group elements Be familiar with the three different models describing thos ...
Questions
... If alanine is made from propanoic acid the product mixture does not show optical activity. Explain why this is so. ...
... If alanine is made from propanoic acid the product mixture does not show optical activity. Explain why this is so. ...
Chapter 19 CHEMICAL THERMODYNAMICS 19.1 SPONTANEOUS
... 1. Unlike enthalpies of formation, standard molar entropies of elements at the reference temperature of 298 K are not zero. 2. The standard molar entropies of gases are greater than those of liquids and solids, consistent with our interpretation of experimental observations, as represented in Figure ...
... 1. Unlike enthalpies of formation, standard molar entropies of elements at the reference temperature of 298 K are not zero. 2. The standard molar entropies of gases are greater than those of liquids and solids, consistent with our interpretation of experimental observations, as represented in Figure ...
LIQUIDS
... Definition: An atom is the smallest particle of an element that can exist or take part in a chemical change. MOLECULES All elements are made up of atoms. In some gaseous elements (e.g. argon) single atoms move around freely. But in other gaseous elements, single atoms cannot exist on their own at or ...
... Definition: An atom is the smallest particle of an element that can exist or take part in a chemical change. MOLECULES All elements are made up of atoms. In some gaseous elements (e.g. argon) single atoms move around freely. But in other gaseous elements, single atoms cannot exist on their own at or ...
File
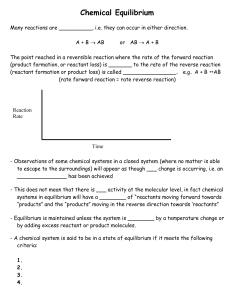
... Examples of chemical systems in equilibrium: 1. Solubility Equilibrium • in solubility equilibrium the ________ solute particles continuously dissolve into solution, while an equal number of dissolved solute particles in solution crystallize or _________ out of solution 2. Phase Equilibrium - in ph ...
... Examples of chemical systems in equilibrium: 1. Solubility Equilibrium • in solubility equilibrium the ________ solute particles continuously dissolve into solution, while an equal number of dissolved solute particles in solution crystallize or _________ out of solution 2. Phase Equilibrium - in ph ...
Chemical reaction

A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive elements where both electronic and nuclear changes may occur.The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more products, which usually have properties different from the reactants. Reactions often consist of a sequence of individual sub-steps, the so-called elementary reactions, and the information on the precise course of action is part of the reaction mechanism. Chemical reactions are described with chemical equations, which symbolically present the starting materials, end products, and sometimes intermediate products and reaction conditions.Chemical reactions happen at a characteristic reaction rate at a given temperature and chemical concentration. Typically, reaction rates increase with increasing temperature because there is more thermal energy available to reach the activation energy necessary for breaking bonds between atoms.Reactions may proceed in the forward or reverse direction until they go to completion or reach equilibrium. Reactions that proceed in the forward direction to approach equilibrium are often described as spontaneous, requiring no input of free energy to go forward. Non-spontaneous reactions require input of free energy to go forward (examples include charging a battery by applying an external electrical power source, or photosynthesis driven by absorption of electromagnetic radiation in the form of sunlight).Different chemical reactions are used in combinations during chemical synthesis in order to obtain a desired product. In biochemistry, a consecutive series of chemical reactions (where the product of one reaction is the reactant of the next reaction) form metabolic pathways. These reactions are often catalyzed by protein enzymes. Enzymes increase the rates of biochemical reactions, so that metabolic syntheses and decompositions impossible under ordinary conditions can occur at the temperatures and concentrations present within a cell.The general concept of a chemical reaction has been extended to reactions between entities smaller than atoms, including nuclear reactions, radioactive decays, and reactions between elementary particles as described by quantum field theory.