Notes -- Unit 5 -- Reactions and Stoichiometry
... What is the atomic mass of Water (H2O)? 2H – 2 (1.0) = 2.0 a.m.u. 1O – 1(16.0) =16.0 a.m.u. 18.0 a.m.u What is the atomic mass of Ca(NO3)2? 1 Ca – 1(40.1) = 40.1 a.m.u 2 N – 2 (14.0) = 28.0 a.m.u. 6 O – 6 (16.0) = 96 a.m.u. 164.1 a.m.u. ...
... What is the atomic mass of Water (H2O)? 2H – 2 (1.0) = 2.0 a.m.u. 1O – 1(16.0) =16.0 a.m.u. 18.0 a.m.u What is the atomic mass of Ca(NO3)2? 1 Ca – 1(40.1) = 40.1 a.m.u 2 N – 2 (14.0) = 28.0 a.m.u. 6 O – 6 (16.0) = 96 a.m.u. 164.1 a.m.u. ...
H2-rich fluids from serpentinization: Geochemical and biotic
... (for example, metallic Fe), it is oxidized, producing hydrogen gas. Gas bubbles may build up in the fluid because the equilibrium does not depend on the amount of bubbles present. Reactions to the left of the solubility curve cannot saturate the fluid with H2(gas) at a total fluid pressure of 500 ba ...
... (for example, metallic Fe), it is oxidized, producing hydrogen gas. Gas bubbles may build up in the fluid because the equilibrium does not depend on the amount of bubbles present. Reactions to the left of the solubility curve cannot saturate the fluid with H2(gas) at a total fluid pressure of 500 ba ...
Ch 17 Equilibrium
... N2O4(g) 2NO2(g). • At some time, the color stops changing and we have a mixture of N2O4 and NO2. • Chemical equilibrium is the point at which the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction. At that point, the concentrations of all species are constant. • Using the co ...
... N2O4(g) 2NO2(g). • At some time, the color stops changing and we have a mixture of N2O4 and NO2. • Chemical equilibrium is the point at which the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction. At that point, the concentrations of all species are constant. • Using the co ...
U-6 Stoichiometry Notes
... In chemistry we make some measurements by counting and other measurements by weighing, determining volume, etc. Which technique we employ is determined, in large part, by our purpose. It is also necessary, when determining which technique to use, to consider what type of measurement is easiest to ma ...
... In chemistry we make some measurements by counting and other measurements by weighing, determining volume, etc. Which technique we employ is determined, in large part, by our purpose. It is also necessary, when determining which technique to use, to consider what type of measurement is easiest to ma ...
No Slide Title
... Therefore, for a process carried out at constant volume E = qV (V = constant) What does this mean? For a process carried out at constant volume, q is a state function, and so no information is needed concerning path. This makes it far easier to calculate and keep track of heat flow for these kinds ...
... Therefore, for a process carried out at constant volume E = qV (V = constant) What does this mean? For a process carried out at constant volume, q is a state function, and so no information is needed concerning path. This makes it far easier to calculate and keep track of heat flow for these kinds ...
I have put this in the format of the 1984 exam
... liquid, and vapor phases are all in equilibrium (D) Temperature at which liquid and vapor phases are in equilibrium at I atmosphere (E) lowest temperature above which a substance cnnot be liquified at any applied pressure 28. 2 A(g) + B(g) 2 C(g) When the concentration of substance B in the react ...
... liquid, and vapor phases are all in equilibrium (D) Temperature at which liquid and vapor phases are in equilibrium at I atmosphere (E) lowest temperature above which a substance cnnot be liquified at any applied pressure 28. 2 A(g) + B(g) 2 C(g) When the concentration of substance B in the react ...
Slide 1
... J/mol-K. The molar entropy values of substances in their standard state is called Standard molar entropies denoted as S°. Standard state of a pure ...
... J/mol-K. The molar entropy values of substances in their standard state is called Standard molar entropies denoted as S°. Standard state of a pure ...
Unit 5 - Chemical Reactions - Student
... The substances that undergo a chemical reaction are the reactants. The new substances formed are the products. Special symbols are written after formulas in equations to show a substance’s state. The designations for solid, liquid, or gas, are (s), (l), and (g), respectively. A substance dissolv ...
... The substances that undergo a chemical reaction are the reactants. The new substances formed are the products. Special symbols are written after formulas in equations to show a substance’s state. The designations for solid, liquid, or gas, are (s), (l), and (g), respectively. A substance dissolv ...
Chemical Thermodynamics presentation 1
... Because ΔG° is positive, the reaction is not spontaneous under standard conditions at 298 K. Note: We had to convert the units of the T ΔS term to kJ sp that it could be added to the ΔH term whose units are kJ ...
... Because ΔG° is positive, the reaction is not spontaneous under standard conditions at 298 K. Note: We had to convert the units of the T ΔS term to kJ sp that it could be added to the ΔH term whose units are kJ ...
[SESSION-2014-2015] SUBJECT - SCIENCE PATNA REGION
... 1)Chemical reaction— Chemical changes or chemical reactions are the changes in which one or more new substances are formed. 2)Chemical Equations – Representation of a chemical reaction in terms of symbols and formulae of the reactants and products is known as chemical equation. 3)Balanced Chemical e ...
... 1)Chemical reaction— Chemical changes or chemical reactions are the changes in which one or more new substances are formed. 2)Chemical Equations – Representation of a chemical reaction in terms of symbols and formulae of the reactants and products is known as chemical equation. 3)Balanced Chemical e ...
Class XII Chemistry IMPORTANT QUESTIONS and COMMON
... conductivity decreases. In case of semiconductors, with increase of temperature, more electrons can shift from valence band to conduction band. Hence conductivity increases. 4. What type of substances would make better permanent magnets, ferromagnetic or ferromagnetic,Why? AnsFerromagnetic substance ...
... conductivity decreases. In case of semiconductors, with increase of temperature, more electrons can shift from valence band to conduction band. Hence conductivity increases. 4. What type of substances would make better permanent magnets, ferromagnetic or ferromagnetic,Why? AnsFerromagnetic substance ...
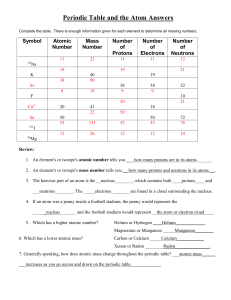
Periodic Table and the Atom Answers
... a) At a smaller volume the atoms will move faster and hit the sides more often. b) At a smaller volume the atoms will slow down and so they will have more contact with the walls of the container. c) At a smaller volume the atoms will have less room to move around, so they will collide with the sides ...
... a) At a smaller volume the atoms will move faster and hit the sides more often. b) At a smaller volume the atoms will slow down and so they will have more contact with the walls of the container. c) At a smaller volume the atoms will have less room to move around, so they will collide with the sides ...
1.8 M - Thierry Karsenti
... copyright free, relevant, compulsory resources other than a written text or a web site. These could be a video file, an audio file, a set of images, etc. For each resource, Module Developers need to write the complete reference (APA style), as well as a 50 word abstract written in a way to motivate ...
... copyright free, relevant, compulsory resources other than a written text or a web site. These could be a video file, an audio file, a set of images, etc. For each resource, Module Developers need to write the complete reference (APA style), as well as a 50 word abstract written in a way to motivate ...
Chemical reaction

A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive elements where both electronic and nuclear changes may occur.The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more products, which usually have properties different from the reactants. Reactions often consist of a sequence of individual sub-steps, the so-called elementary reactions, and the information on the precise course of action is part of the reaction mechanism. Chemical reactions are described with chemical equations, which symbolically present the starting materials, end products, and sometimes intermediate products and reaction conditions.Chemical reactions happen at a characteristic reaction rate at a given temperature and chemical concentration. Typically, reaction rates increase with increasing temperature because there is more thermal energy available to reach the activation energy necessary for breaking bonds between atoms.Reactions may proceed in the forward or reverse direction until they go to completion or reach equilibrium. Reactions that proceed in the forward direction to approach equilibrium are often described as spontaneous, requiring no input of free energy to go forward. Non-spontaneous reactions require input of free energy to go forward (examples include charging a battery by applying an external electrical power source, or photosynthesis driven by absorption of electromagnetic radiation in the form of sunlight).Different chemical reactions are used in combinations during chemical synthesis in order to obtain a desired product. In biochemistry, a consecutive series of chemical reactions (where the product of one reaction is the reactant of the next reaction) form metabolic pathways. These reactions are often catalyzed by protein enzymes. Enzymes increase the rates of biochemical reactions, so that metabolic syntheses and decompositions impossible under ordinary conditions can occur at the temperatures and concentrations present within a cell.The general concept of a chemical reaction has been extended to reactions between entities smaller than atoms, including nuclear reactions, radioactive decays, and reactions between elementary particles as described by quantum field theory.

















![[SESSION-2014-2015] SUBJECT - SCIENCE PATNA REGION](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008930072_1-5a35e1ae8e3204ea88999f1418a93013-300x300.png)