112- Unit I -Electrochem -pdf
... b) The substance is considered to be a strong oxidizing agent as the value of E° red becomes more positive. c) The more negative E° red , the weaker the tendency for the substance to be reduced. Actually, the greater the tendency of the substance to be oxidized and it is considered to be a strong re ...
... b) The substance is considered to be a strong oxidizing agent as the value of E° red becomes more positive. c) The more negative E° red , the weaker the tendency for the substance to be reduced. Actually, the greater the tendency of the substance to be oxidized and it is considered to be a strong re ...
5073 Chemistry (SPA)
... 440 BC, the Greek Leucippus and his pupil Democritus coined the term atomos to describe the smallest particle of matter. It translates to mean something that is indivisible. In the eighteenth century, chemist, John Dalton, revived the term when he suggested that each element was made up of unique at ...
... 440 BC, the Greek Leucippus and his pupil Democritus coined the term atomos to describe the smallest particle of matter. It translates to mean something that is indivisible. In the eighteenth century, chemist, John Dalton, revived the term when he suggested that each element was made up of unique at ...
GCE Chemistry Question Paper Unit 05 - Energetics, Redox
... The oxides nitrogen monoxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) both contribute to atmospheric pollution. The table gives some data for these oxides and for oxygen. S / J K–1 mol–1 ...
... The oxides nitrogen monoxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) both contribute to atmospheric pollution. The table gives some data for these oxides and for oxygen. S / J K–1 mol–1 ...
Net ionic equation
... Weak acids and bases - Molecular compounds that are weak acids or weak bases are also weak electrolytes. Note that an acid forms H+ ion when added to water, and a base forms OH- ion. ...
... Weak acids and bases - Molecular compounds that are weak acids or weak bases are also weak electrolytes. Note that an acid forms H+ ion when added to water, and a base forms OH- ion. ...
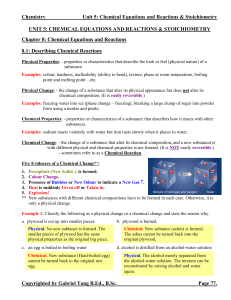
Unit 5: Chemical Equations and Reactions
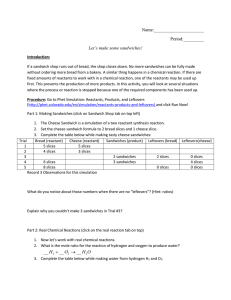
... 1. Write the correct chemical formulas for all products and reactants with proper subscripts. The presence of metals or ionic compounds indicates that we will need to use ions and charges to form any products. 2. For hydrocarbon combustion, balance in the order of C, H, and then O. The product, H2O, ...
... 1. Write the correct chemical formulas for all products and reactants with proper subscripts. The presence of metals or ionic compounds indicates that we will need to use ions and charges to form any products. 2. For hydrocarbon combustion, balance in the order of C, H, and then O. The product, H2O, ...
TEKS 8 - UNT College of Education
... A chemical reaction, also called a chemical change, is material changing from a beginning mass to a resulting substance. The process involves one or more reactants yielding one or more products different from the reactants. The characteristic of a chemical reaction is that new material or materials ...
... A chemical reaction, also called a chemical change, is material changing from a beginning mass to a resulting substance. The process involves one or more reactants yielding one or more products different from the reactants. The characteristic of a chemical reaction is that new material or materials ...
KEY + + - UIC Department of Chemistry
... 2. A reaction between an acid and a metal produces __________. (a) salt + water (b) salt + H2(g) (c) salt + CO2(g) (d) salt + CO2(g) + H 2 O 3. A compound was found to contain 54.5% carbon, 9.2% hydrogen, and 36.3% oxygen by mass. What is the empirical formula of the compound? (a) C6 HO4 (b) C4 H8 O ...
... 2. A reaction between an acid and a metal produces __________. (a) salt + water (b) salt + H2(g) (c) salt + CO2(g) (d) salt + CO2(g) + H 2 O 3. A compound was found to contain 54.5% carbon, 9.2% hydrogen, and 36.3% oxygen by mass. What is the empirical formula of the compound? (a) C6 HO4 (b) C4 H8 O ...
Presentation
... Balancing Chemical Equations Concept Check Which of the following are true concerning balanced chemical equations? There may be more than one true statement. I. The number of molecules is conserved. II. The coefficients tell you how much of each ...
... Balancing Chemical Equations Concept Check Which of the following are true concerning balanced chemical equations? There may be more than one true statement. I. The number of molecules is conserved. II. The coefficients tell you how much of each ...
Study Modules XII Chemistry 2017
... 7. The electrical conductivity of a metal decreases with rise in temperature while that of a semiconductor increases.Explain. In metals with increase of temperature, the kernels start vibrating and thus offer resistance to the flow of electrons.Hence conductivity decreases. In case of semiconductors ...
... 7. The electrical conductivity of a metal decreases with rise in temperature while that of a semiconductor increases.Explain. In metals with increase of temperature, the kernels start vibrating and thus offer resistance to the flow of electrons.Hence conductivity decreases. In case of semiconductors ...
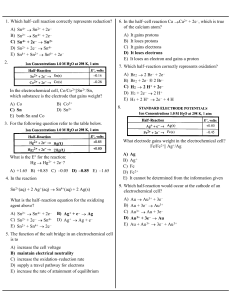
A) Sn4+ → Sn2+ + 2e
... B) Anode: 2 Cl – ® Cl 2 + 2e – Cathode: 2 H 2O + 2e – ® H 2 + 2 OH – C) Anode: 2 H 2O ® O 2 + 4 H+ + 4e – Cathode: 2 Zn2+ + 4e – ® 2 Zn D) Anode: 2 H2O ® O2 + 4 H+ + 4e – Cathode: 4 H 2 O + 4e – ® 2 H 2 + 4 OH – E) Anode: Cl 2 + 2e – ® 2 Cl – Cathode: Zn ® Zn 2+ + 2e – 69. What are the anode and cat ...
... B) Anode: 2 Cl – ® Cl 2 + 2e – Cathode: 2 H 2O + 2e – ® H 2 + 2 OH – C) Anode: 2 H 2O ® O 2 + 4 H+ + 4e – Cathode: 2 Zn2+ + 4e – ® 2 Zn D) Anode: 2 H2O ® O2 + 4 H+ + 4e – Cathode: 4 H 2 O + 4e – ® 2 H 2 + 4 OH – E) Anode: Cl 2 + 2e – ® 2 Cl – Cathode: Zn ® Zn 2+ + 2e – 69. What are the anode and cat ...
Problem 1: A brief history of life in the universe
... atoms escape more readily than nitrogen molecules even though the escape velocity is independent of the mass of the escaping object. The chemical composition of the atmosphere of a planet depends on the temperature of the planet’s atmosphere (which in turn depends on the distance from the sun, inter ...
... atoms escape more readily than nitrogen molecules even though the escape velocity is independent of the mass of the escaping object. The chemical composition of the atmosphere of a planet depends on the temperature of the planet’s atmosphere (which in turn depends on the distance from the sun, inter ...
Chemical reaction

A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive elements where both electronic and nuclear changes may occur.The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more products, which usually have properties different from the reactants. Reactions often consist of a sequence of individual sub-steps, the so-called elementary reactions, and the information on the precise course of action is part of the reaction mechanism. Chemical reactions are described with chemical equations, which symbolically present the starting materials, end products, and sometimes intermediate products and reaction conditions.Chemical reactions happen at a characteristic reaction rate at a given temperature and chemical concentration. Typically, reaction rates increase with increasing temperature because there is more thermal energy available to reach the activation energy necessary for breaking bonds between atoms.Reactions may proceed in the forward or reverse direction until they go to completion or reach equilibrium. Reactions that proceed in the forward direction to approach equilibrium are often described as spontaneous, requiring no input of free energy to go forward. Non-spontaneous reactions require input of free energy to go forward (examples include charging a battery by applying an external electrical power source, or photosynthesis driven by absorption of electromagnetic radiation in the form of sunlight).Different chemical reactions are used in combinations during chemical synthesis in order to obtain a desired product. In biochemistry, a consecutive series of chemical reactions (where the product of one reaction is the reactant of the next reaction) form metabolic pathways. These reactions are often catalyzed by protein enzymes. Enzymes increase the rates of biochemical reactions, so that metabolic syntheses and decompositions impossible under ordinary conditions can occur at the temperatures and concentrations present within a cell.The general concept of a chemical reaction has been extended to reactions between entities smaller than atoms, including nuclear reactions, radioactive decays, and reactions between elementary particles as described by quantum field theory.