Chemistry in Society Homework Booklet
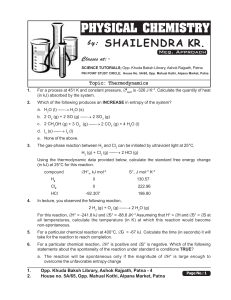
... (a) the effect on the Fe ion concentration of adding KCNS to the equilibrium mixture (b) why changing the pressure has no effect on this reaction. ...
... (a) the effect on the Fe ion concentration of adding KCNS to the equilibrium mixture (b) why changing the pressure has no effect on this reaction. ...
Chemistry - cloudfront.net
... 50. know the products of these common reactions: a. metal + acid b. metal carbonate + acid Unit 4: Stoichiometry; Properties of Solutions and Their Equations 51. be able to compute a Formula Weight from a named compound or a given chemical formula 52. be able to calculate the moles of an element or ...
... 50. know the products of these common reactions: a. metal + acid b. metal carbonate + acid Unit 4: Stoichiometry; Properties of Solutions and Their Equations 51. be able to compute a Formula Weight from a named compound or a given chemical formula 52. be able to calculate the moles of an element or ...
Physical Chemistry 3: — Chemical Kinetics - Christian
... students to repeat the material more economically. It covers basic material that all chemistry students should learn irrespective of their possible inclination towards inorganic, organic or physical chemistry, but goes beyond the standard Physical Chemistry textbooks used in the PC-1 and PC-2 course ...
... students to repeat the material more economically. It covers basic material that all chemistry students should learn irrespective of their possible inclination towards inorganic, organic or physical chemistry, but goes beyond the standard Physical Chemistry textbooks used in the PC-1 and PC-2 course ...
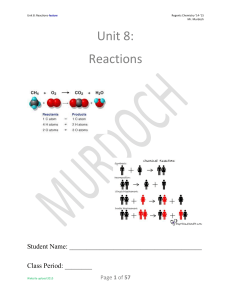
Unit 8: Reactions
... Objective: The amount of matter in reactants equals that in products! The mass on the reactants (left) side of the arrow and the mass on the products (right) side of the arrow MUST equal each other as the Law of Conservation of Mass states that mass may not be created or destroyed in any chemical re ...
... Objective: The amount of matter in reactants equals that in products! The mass on the reactants (left) side of the arrow and the mass on the products (right) side of the arrow MUST equal each other as the Law of Conservation of Mass states that mass may not be created or destroyed in any chemical re ...
Chapter_4_Reactions_in_Aqueous_Solution
... 500-mL volumetric flask to obtain the desired concentration. Check The initial volume is less than the final volume, so the answer is reasonable. ...
... 500-mL volumetric flask to obtain the desired concentration. Check The initial volume is less than the final volume, so the answer is reasonable. ...
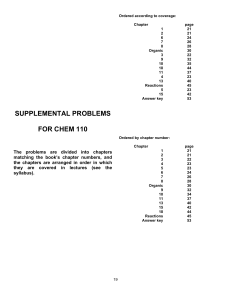
SUPPLEMENTAL PROBLEMS FOR CHEM 110
... 10. Which series of quantum numbers describes the orbital in which the highest energy electron in potassium resides in the ground state? ...
... 10. Which series of quantum numbers describes the orbital in which the highest energy electron in potassium resides in the ground state? ...
aq - Moodle@FCT
... 500-mL volumetric flask to obtain the desired concentration. Check The initial volume is less than the final volume, so the answer is reasonable. ...
... 500-mL volumetric flask to obtain the desired concentration. Check The initial volume is less than the final volume, so the answer is reasonable. ...
MC84 - Southchemistry.com
... The reaction of silver metal and dilute nitric acid proceeds according to the equation above. If 0.10 mole of powdered silver is added to 10. milliliters of 6.0-molar nitric acid, the number of moles of NO gas that can be formed is (A) 0.015 mole (B) 0.020 mole (C) 0.030 mole (D) 0.045 mole (E) 0.09 ...
... The reaction of silver metal and dilute nitric acid proceeds according to the equation above. If 0.10 mole of powdered silver is added to 10. milliliters of 6.0-molar nitric acid, the number of moles of NO gas that can be formed is (A) 0.015 mole (B) 0.020 mole (C) 0.030 mole (D) 0.045 mole (E) 0.09 ...
fahad h. ahmad - Fahad`s Academy
... - Metals lose electrons to form positive ions (cations) - Non-metals gain electrons to form negative ions (anions) The formation of ions is resulted from transfer of atoms from one atom to another atom(s), which the ions produced are of opposite charges, and unlike charges attract, causing them to b ...
... - Metals lose electrons to form positive ions (cations) - Non-metals gain electrons to form negative ions (anions) The formation of ions is resulted from transfer of atoms from one atom to another atom(s), which the ions produced are of opposite charges, and unlike charges attract, causing them to b ...
mass-mass problems.
... reaction (substance A) and asked to calculate the mass of a different substance in the reaction (substance B). This will be a 3-step dimensional analysis conversion. 1. Convert grams of A to moles of A using the molar mass of A. 2. Convert moles of A to moles of B using the coefficients from the bal ...
... reaction (substance A) and asked to calculate the mass of a different substance in the reaction (substance B). This will be a 3-step dimensional analysis conversion. 1. Convert grams of A to moles of A using the molar mass of A. 2. Convert moles of A to moles of B using the coefficients from the bal ...
Enzymes - WordPress.com
... Enzymes Enzymes are important biological macromolecules that do work in all living things. Plants, animals, and prokaryotes all depend on enzymes to break down large molecules or build new ones. ENZYMES are proteins that act as catalysts and help chemical reactions occur. In order for these chemical ...
... Enzymes Enzymes are important biological macromolecules that do work in all living things. Plants, animals, and prokaryotes all depend on enzymes to break down large molecules or build new ones. ENZYMES are proteins that act as catalysts and help chemical reactions occur. In order for these chemical ...
Document
... reduce H+(aq) to H2(g) and be oxidized to Cu2+(aq). Looking at it the other way, H+ is not a strong enough oxidizing agent to oxidize Cu(s) to Cu 2+(aq). Chloride ion in HCl(aq) can only be a reducing agent. As neither H+ nor Cl– can oxidize Cu, we expect no reaction between Cu(s) and HCl(aq). (b) I ...
... reduce H+(aq) to H2(g) and be oxidized to Cu2+(aq). Looking at it the other way, H+ is not a strong enough oxidizing agent to oxidize Cu(s) to Cu 2+(aq). Chloride ion in HCl(aq) can only be a reducing agent. As neither H+ nor Cl– can oxidize Cu, we expect no reaction between Cu(s) and HCl(aq). (b) I ...
Introduction to Computational Chemistry
... • All the methods which employ quantum mechanics (QM) are based on solving the Schrödinger equation (to some level of approximation) for the molecular system of interest. • Ab initio ("from the beginning") methods involve no empirical parameters and therefore are the most accurate techniques (and th ...
... • All the methods which employ quantum mechanics (QM) are based on solving the Schrödinger equation (to some level of approximation) for the molecular system of interest. • Ab initio ("from the beginning") methods involve no empirical parameters and therefore are the most accurate techniques (and th ...
Mr. Dehne AP Chem Name: ___________ Date: Per#: ___ AP
... 35. A student added 50.0mL of NaOH solution to 100.0mL of 0.400M HCl. The solution was then treated with an excess of aqueous chromium (III) nitrate, resulting in formation of 2.06g of precipitate. Determine the concentration of the NaOH solution? 36. A 10.00mL sample of vinegar, an aqueous solution ...
... 35. A student added 50.0mL of NaOH solution to 100.0mL of 0.400M HCl. The solution was then treated with an excess of aqueous chromium (III) nitrate, resulting in formation of 2.06g of precipitate. Determine the concentration of the NaOH solution? 36. A 10.00mL sample of vinegar, an aqueous solution ...
www.fahadsacademy.com
... because the ions are arrnged in straight rows in strong ionic bonds. 2. Ionic compounds have very high melting points and boiling points. 3. The strong forces holding ionic compounds prevents them to evaporate easily. Hence, ionic compounds have no smell. 4. Solid ionic compounds don’t conduct elect ...
... because the ions are arrnged in straight rows in strong ionic bonds. 2. Ionic compounds have very high melting points and boiling points. 3. The strong forces holding ionic compounds prevents them to evaporate easily. Hence, ionic compounds have no smell. 4. Solid ionic compounds don’t conduct elect ...
Regents Chemistry Topic Review Packet
... in a substance; no new types of particles result from this type of change. A chemical change results in the formation of different particles with changed properties. Distinguish between chemical and physical changes based on whether new substances form or not. ...
... in a substance; no new types of particles result from this type of change. A chemical change results in the formation of different particles with changed properties. Distinguish between chemical and physical changes based on whether new substances form or not. ...
ch14 lecture 7e
... Carbon in Organic Chemistry The large number and wide variety of organic compounds is due to the ability of C to bond to itself, and to form multiple bonds. Catenation is the process whereby carbon bonds to itself to form stable chains, branches, and rings. Since C is small, the C-C bond is short e ...
... Carbon in Organic Chemistry The large number and wide variety of organic compounds is due to the ability of C to bond to itself, and to form multiple bonds. Catenation is the process whereby carbon bonds to itself to form stable chains, branches, and rings. Since C is small, the C-C bond is short e ...
Chemical reaction

A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive elements where both electronic and nuclear changes may occur.The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more products, which usually have properties different from the reactants. Reactions often consist of a sequence of individual sub-steps, the so-called elementary reactions, and the information on the precise course of action is part of the reaction mechanism. Chemical reactions are described with chemical equations, which symbolically present the starting materials, end products, and sometimes intermediate products and reaction conditions.Chemical reactions happen at a characteristic reaction rate at a given temperature and chemical concentration. Typically, reaction rates increase with increasing temperature because there is more thermal energy available to reach the activation energy necessary for breaking bonds between atoms.Reactions may proceed in the forward or reverse direction until they go to completion or reach equilibrium. Reactions that proceed in the forward direction to approach equilibrium are often described as spontaneous, requiring no input of free energy to go forward. Non-spontaneous reactions require input of free energy to go forward (examples include charging a battery by applying an external electrical power source, or photosynthesis driven by absorption of electromagnetic radiation in the form of sunlight).Different chemical reactions are used in combinations during chemical synthesis in order to obtain a desired product. In biochemistry, a consecutive series of chemical reactions (where the product of one reaction is the reactant of the next reaction) form metabolic pathways. These reactions are often catalyzed by protein enzymes. Enzymes increase the rates of biochemical reactions, so that metabolic syntheses and decompositions impossible under ordinary conditions can occur at the temperatures and concentrations present within a cell.The general concept of a chemical reaction has been extended to reactions between entities smaller than atoms, including nuclear reactions, radioactive decays, and reactions between elementary particles as described by quantum field theory.