File - ARC: Chemistry
... ____ 13. The octet rule states that, in chemical compounds, atoms tend to have ____. a. eight electrons in their principal energy level b. more protons than electrons c. the electron configuration of a noble gas d. more electrons than protons ____ 14. When naming a transition metal ion that can hav ...
... ____ 13. The octet rule states that, in chemical compounds, atoms tend to have ____. a. eight electrons in their principal energy level b. more protons than electrons c. the electron configuration of a noble gas d. more electrons than protons ____ 14. When naming a transition metal ion that can hav ...
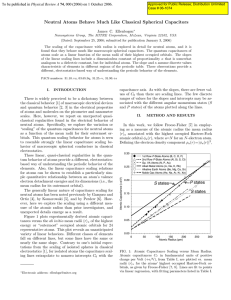
Neutral Atoms Behave Much Like Classical Spherical Capacitors
... atoms like Be, N, or the noble gas atoms, with relatively small dielectric constants and small mean radii, do not have sufficiently polarizable electrons in the valence region, nor sufficient surface area on which to distribute an additional electron to produce a stable anion. In summary, it has been de ...
... atoms like Be, N, or the noble gas atoms, with relatively small dielectric constants and small mean radii, do not have sufficiently polarizable electrons in the valence region, nor sufficient surface area on which to distribute an additional electron to produce a stable anion. In summary, it has been de ...
No Slide Title
... wave and particle terms. • Solving the equation leads to wave functions, ψ (orbitals). • ψ2 gives the probability of finding the electron • Orbital in the quantum model is different from Bohr’s orbit Prentice Hall © 2003 ...
... wave and particle terms. • Solving the equation leads to wave functions, ψ (orbitals). • ψ2 gives the probability of finding the electron • Orbital in the quantum model is different from Bohr’s orbit Prentice Hall © 2003 ...
Ex. = 1s 1 , 0 to (1-1)
... So the address for all 3 electrons of Li is: 1s2 2s1 This is called the electron configuration for Li and basically says that the first two electrons of Li are in the s sublevel with its one spherical shape with the 3rd electron in the 2 energy level, s sublevel with its bigger spherical shape. The ...
... So the address for all 3 electrons of Li is: 1s2 2s1 This is called the electron configuration for Li and basically says that the first two electrons of Li are in the s sublevel with its one spherical shape with the 3rd electron in the 2 energy level, s sublevel with its bigger spherical shape. The ...
AP Chap 2
... • Atoms with incomplete valence shells can share or transfer valence electrons with certain other atoms • These interactions usually result in atoms staying close together, held by attractions called chemical bonds ...
... • Atoms with incomplete valence shells can share or transfer valence electrons with certain other atoms • These interactions usually result in atoms staying close together, held by attractions called chemical bonds ...
Ex. = 1s 1 , 0 to (1-1)
... The Third Quantum Number - m In the address analogy, this would be the street on which the electron would probably be found. In the first state there is one city. In this first city there would be one street. In the second state there are two cities. The first city with its one street and a second ...
... The Third Quantum Number - m In the address analogy, this would be the street on which the electron would probably be found. In the first state there is one city. In this first city there would be one street. In the second state there are two cities. The first city with its one street and a second ...
Quantum Hall Effect
... Since the Hall voltage is being held constant,the fact that the current does not change as the magnetic eld is varied implies that the Hall resistance also remains constant. Whenever the Fermi level is in the sub-band of localized states, then, the Hall Resistance remains the same even when the mag ...
... Since the Hall voltage is being held constant,the fact that the current does not change as the magnetic eld is varied implies that the Hall resistance also remains constant. Whenever the Fermi level is in the sub-band of localized states, then, the Hall Resistance remains the same even when the mag ...
double-slit teacher
... If we don’t know what state an object is in, then it is in a combination or superposition of those states and these possibilities can interfere with each other. If we don’t try to detect which slit the electron goes through then electron can be in more than one place at a time. The probability of wh ...
... If we don’t know what state an object is in, then it is in a combination or superposition of those states and these possibilities can interfere with each other. If we don’t try to detect which slit the electron goes through then electron can be in more than one place at a time. The probability of wh ...
Chemistry Unit Summaries - Oak Park Unified School District
... orbital. The sublevel quantum number l is indicated by the letters s, p, d, and f, which correspond to l = 0, 1, 2, and 3 respectively. The l quantum number defines the shape of the orbital. For a given value of n, l can have integer values from 0 to (n – 1). The orbital quantum number ml relates t ...
... orbital. The sublevel quantum number l is indicated by the letters s, p, d, and f, which correspond to l = 0, 1, 2, and 3 respectively. The l quantum number defines the shape of the orbital. For a given value of n, l can have integer values from 0 to (n – 1). The orbital quantum number ml relates t ...
Atom-Light Interactions - Durham University Community
... monochromatic external light field. The processes that exchange energy with the driving field are known as absorption and stimulated emission. In this picture, an atom prepared in the excited state at t = 0 remains in the excited state, unless the external field is present to drive the atom. In real ...
... monochromatic external light field. The processes that exchange energy with the driving field are known as absorption and stimulated emission. In this picture, an atom prepared in the excited state at t = 0 remains in the excited state, unless the external field is present to drive the atom. In real ...
Atoms and Nuclei PA 322
... • Non-equivalent electrons: those which belong to different (n,l) subshells (e.g. orthohelium 1s2s) • Any (s, l) combination allowed without violating Pauli Exclusion Principle • Terms can be worked out using relationships for L, S and J applying rule for vector addition: – for two active electr ...
... • Non-equivalent electrons: those which belong to different (n,l) subshells (e.g. orthohelium 1s2s) • Any (s, l) combination allowed without violating Pauli Exclusion Principle • Terms can be worked out using relationships for L, S and J applying rule for vector addition: – for two active electr ...
Ionization

Ionization is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons to form ions, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. Ionization can result from the loss of an electron after collisions with sub atomic particles, collisions with other atoms, molecules and ions, or through the interaction with light. Heterolytic bond cleavage and heterolytic substitution reactions can result in the formation of ion pairs. Ionization can occur through radioactive decay by the internal conversion process, in which an excited nucleus transfers its energy to one of the inner-shell electrons causing it to be ejected.