lecture slides file
... An element is a fundamental or elementary substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. Each element has a number. Beginning with hydrogen as 1, the elements are numbered in order of increasing complexity. An atom is the smallest particle of an element that can exis ...
... An element is a fundamental or elementary substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. Each element has a number. Beginning with hydrogen as 1, the elements are numbered in order of increasing complexity. An atom is the smallest particle of an element that can exis ...
Predissociation dynamics of lithium iodide
... points. Due to the avoided X-A curve crossing, part of the wave packet escapes outwards along the dissociative diabatic potential to form free Li + I fragments each time the wave packet comes near the crossing point. Since the ionization energy of atomic Li (5.39 eV) exceeds the photon energy (∼4.6 ...
... points. Due to the avoided X-A curve crossing, part of the wave packet escapes outwards along the dissociative diabatic potential to form free Li + I fragments each time the wave packet comes near the crossing point. Since the ionization energy of atomic Li (5.39 eV) exceeds the photon energy (∼4.6 ...
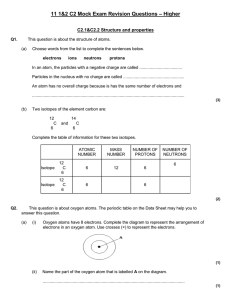
Year 11 C2 Mock Exam Revision Questions
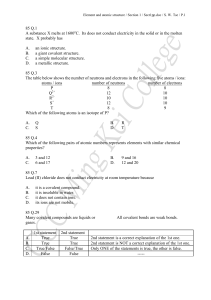
... sentences below which are about this compound. Phosphorus trifluoride is made up of phosphorus and fluorine ................................ These are joined together by sharing pairs of ............................................... to form ...
... sentences below which are about this compound. Phosphorus trifluoride is made up of phosphorus and fluorine ................................ These are joined together by sharing pairs of ............................................... to form ...
Momentum-resolved tunneling into fractional
... FIG. 1. Schematic picture of tunneling geometry. Two mutually perpendicular two-dimensional electron systems are realized, e.g., in a semiconductor heterostructure. An external magnetic field is applied such that it is perpendicular to one of them (2DES⬜ ) but in plane for the other one (2DES储 ). Wh ...
... FIG. 1. Schematic picture of tunneling geometry. Two mutually perpendicular two-dimensional electron systems are realized, e.g., in a semiconductor heterostructure. An external magnetic field is applied such that it is perpendicular to one of them (2DES⬜ ) but in plane for the other one (2DES储 ). Wh ...
Quantized conductance for neutral matter
... because deleterious effects such as reflection and interHELIUM When an electrochemical potential difference (i.e., a voltage) is appliedLIQUID has been observed in both electron and neutral-atom mode nonadiabatic transitions are minimized [12], allowacross a metal wire whose transverse dimensions ar ...
... because deleterious effects such as reflection and interHELIUM When an electrochemical potential difference (i.e., a voltage) is appliedLIQUID has been observed in both electron and neutral-atom mode nonadiabatic transitions are minimized [12], allowacross a metal wire whose transverse dimensions ar ...
Models of electrodes and contacts in molecular
... We consider different models for the leads and leadmolecule contacts of a Au-benzenedithiol-Au system: 共A兲 leads with different finite cross sections, 共B兲 leads of infinite periodic surfaces, 共C兲 periodic surface leads with a nanowire connection of different lengths to the molecule, and 共D兲 similar ...
... We consider different models for the leads and leadmolecule contacts of a Au-benzenedithiol-Au system: 共A兲 leads with different finite cross sections, 共B兲 leads of infinite periodic surfaces, 共C兲 periodic surface leads with a nanowire connection of different lengths to the molecule, and 共D兲 similar ...
as a PDF
... of irradiation pulses prevents this kind of redox process through electron transfer. It was shown that in the same mixed ion system the metal clusters obtained change with increasing dose rate from a bilayered core/shell structure to an alloyed structure or bimetallic solid solution.10 In the litera ...
... of irradiation pulses prevents this kind of redox process through electron transfer. It was shown that in the same mixed ion system the metal clusters obtained change with increasing dose rate from a bilayered core/shell structure to an alloyed structure or bimetallic solid solution.10 In the litera ...
Barrier-free intermolecular proton transfer induced by excess
... Such a mechanism of a single-strand break has been computationally studied by Barrios et al., who suggested that only a small barrier would have to be overcome to create a sugarphosphate C–O bond rupture initiated by an excess electron attachment to a DNA base.6 Negatively charged clusters of biolog ...
... Such a mechanism of a single-strand break has been computationally studied by Barrios et al., who suggested that only a small barrier would have to be overcome to create a sugarphosphate C–O bond rupture initiated by an excess electron attachment to a DNA base.6 Negatively charged clusters of biolog ...
1 Basics of Semiconductor and Spin Physics
... or maximum. However this concept has a more profound meaning. In many cases we are interested in what happens to an electron, or a hole, under the action of some external forces due to, for example, electric and magnetic fields, deformation of the crystal, etc. It can be shown, that if the spatial v ...
... or maximum. However this concept has a more profound meaning. In many cases we are interested in what happens to an electron, or a hole, under the action of some external forces due to, for example, electric and magnetic fields, deformation of the crystal, etc. It can be shown, that if the spatial v ...
Quantum Mechanics of Many-Particle Systems: Atoms, Molecules
... wavefunctions can correctly predict the observed properties of the system. More generally, this is accepted as a fundamental property of electronic systems. ...
... wavefunctions can correctly predict the observed properties of the system. More generally, this is accepted as a fundamental property of electronic systems. ...
Chemistry - RESONANCE PCCP IDEAL for NTSE, IJSO, Olympiads
... Mol wt. or At. wt No. of electrons lost or gained by one molecule of the substance ...
... Mol wt. or At. wt No. of electrons lost or gained by one molecule of the substance ...
A study of the electron structure of endohedrally confined atoms
... finite-element methodology. The results are then compared with previous ones obtained by using other short-range model potentials. ...
... finite-element methodology. The results are then compared with previous ones obtained by using other short-range model potentials. ...
Preprint
... necessary - the combination of magnetic trapping and ultrahigh vacuum provides sufficient insulation. Atoms interact Bose condensed atoms are distinguished from photons in a laser by their interactions. The atomic condensates have turned out to be an unexpectedly valuable testing ground for the stud ...
... necessary - the combination of magnetic trapping and ultrahigh vacuum provides sufficient insulation. Atoms interact Bose condensed atoms are distinguished from photons in a laser by their interactions. The atomic condensates have turned out to be an unexpectedly valuable testing ground for the stud ...
Nanoelectromechanical systems
... charging energy gives the net energy gained by the tunnelling electron, which must be positive. Because of the small sizes of the electrodes, their mutual capacitances are small and so the charging energy is large. Hence, a large enough drain-source voltage must be applied in order to meet this char ...
... charging energy gives the net energy gained by the tunnelling electron, which must be positive. Because of the small sizes of the electrodes, their mutual capacitances are small and so the charging energy is large. Hence, a large enough drain-source voltage must be applied in order to meet this char ...
ABSTRACT PHOTON PAIR PRODUCTION FROM A HOT ATOMIC ENSEMBLE IN THE DIAMOND CONFIGURATION
... us to use very high quality interference filters to remove pump contamination from the pair modes. The diamond level structure in alkali atoms also allows for pair generation where one photon is at a telecommunications wavelength while the second ...
... us to use very high quality interference filters to remove pump contamination from the pair modes. The diamond level structure in alkali atoms also allows for pair generation where one photon is at a telecommunications wavelength while the second ...
Quantum Tweezer for Atoms
... atoms are left in it. Note that only one atom is allowed to leak out of the dot at each crossing with the ground state, due to the diminishing repulsion between atoms in the dot as there are less atoms in it (see Fig. 1). The next atom would have a chance of leaking to the condensate as the dot move ...
... atoms are left in it. Note that only one atom is allowed to leak out of the dot at each crossing with the ground state, due to the diminishing repulsion between atoms in the dot as there are less atoms in it (see Fig. 1). The next atom would have a chance of leaking to the condensate as the dot move ...
Quantum nanophotonic phase switch with a single atom.
... The finite Pon w0 without a gate field arises from imperfect atomic-state preparation and readout fidelity (Supplementary Information). Also, ...
... The finite Pon w0 without a gate field arises from imperfect atomic-state preparation and readout fidelity (Supplementary Information). Also, ...
Bose-Glass Phases of Ultracold Atoms due to Cavity Backaction Hessam Habibian,
... Bragg diffraction is a manifestation of the wave properties of light and provides a criterion for the existence of long-range order in the scattering medium [1]. Bragg diffraction of light by atoms in optical lattices was measured for various geometries and settings, from gratings of laser-cooled at ...
... Bragg diffraction is a manifestation of the wave properties of light and provides a criterion for the existence of long-range order in the scattering medium [1]. Bragg diffraction of light by atoms in optical lattices was measured for various geometries and settings, from gratings of laser-cooled at ...
Ionization

Ionization is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons to form ions, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. Ionization can result from the loss of an electron after collisions with sub atomic particles, collisions with other atoms, molecules and ions, or through the interaction with light. Heterolytic bond cleavage and heterolytic substitution reactions can result in the formation of ion pairs. Ionization can occur through radioactive decay by the internal conversion process, in which an excited nucleus transfers its energy to one of the inner-shell electrons causing it to be ejected.