Early-stage relaxation of hot electrons by LO phonon emission Herve´ Castella
... 共SBE’s兲, which give the time evolution of the density distributions in both bands, and of the interband polarization.4 The scattering processes, however, are taken into account by instantaneous scattering rates as in Boltzmann equations, thus treating relaxation as totally incoherent and energy cons ...
... 共SBE’s兲, which give the time evolution of the density distributions in both bands, and of the interband polarization.4 The scattering processes, however, are taken into account by instantaneous scattering rates as in Boltzmann equations, thus treating relaxation as totally incoherent and energy cons ...
Core_Class_Science_Chemistry_for_the_web 838.3 KB
... Atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons are called isotopes. Isotopes that give off radiation are called radioactive isotopes. A compound is a pure substance formed when two or more different elements combine. Compounds are always formed from a specific combination of elem ...
... Atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons are called isotopes. Isotopes that give off radiation are called radioactive isotopes. A compound is a pure substance formed when two or more different elements combine. Compounds are always formed from a specific combination of elem ...
Collective State Measurement of Mesoscopic Ensembles with Single-Atom Resolution
... order red sideband is approximately resonant with the cavity, while the carrier serves as a phase reference. The reflected signal is heterodyned with the modulation source to produce a dispersive frequency-dependent signal in the vicinity of the cavity resonance. Compared to previous transmission me ...
... order red sideband is approximately resonant with the cavity, while the carrier serves as a phase reference. The reflected signal is heterodyned with the modulation source to produce a dispersive frequency-dependent signal in the vicinity of the cavity resonance. Compared to previous transmission me ...
CHE 110 Dr. Nicholas Bizier Office DS 337b email
... Lysine is an amino acid which has the following elemental composition: C, H, O, N. In one experiment, 2.175 g of lysine was combusted to produce 3.94 g of CO2 and 1.89 g H2O. In a separate experiment, 1.873 g of lysine was burned to produce 0.436 g of NH2. The molar mass of lysine is 150 g/mol. Dete ...
... Lysine is an amino acid which has the following elemental composition: C, H, O, N. In one experiment, 2.175 g of lysine was combusted to produce 3.94 g of CO2 and 1.89 g H2O. In a separate experiment, 1.873 g of lysine was burned to produce 0.436 g of NH2. The molar mass of lysine is 150 g/mol. Dete ...
GCE Getting Started - Edexcel
... Atoms of metallic elements in Groups 1,2 and 3 can form positive ions when they take part in reactions since they are readily able to lose electrons. Atoms of Group 1 metals lose one electron and form ions with a 1+ charge, e.g. Na+ Atoms of Group 2 metals lose two electrons and form ions with a 2+ ...
... Atoms of metallic elements in Groups 1,2 and 3 can form positive ions when they take part in reactions since they are readily able to lose electrons. Atoms of Group 1 metals lose one electron and form ions with a 1+ charge, e.g. Na+ Atoms of Group 2 metals lose two electrons and form ions with a 2+ ...
Chapter 4 The Two Slit Experiment
... slit 2 is opened or closed as those electrons would go nowhere near slit 2. In other words, we have to expect that P12 (x) = P1 (x) + P2 (x), but this not what is observed. It appears that we must abandon the idea that the particles go through one slit or the other. But if we want to retain the ment ...
... slit 2 is opened or closed as those electrons would go nowhere near slit 2. In other words, we have to expect that P12 (x) = P1 (x) + P2 (x), but this not what is observed. It appears that we must abandon the idea that the particles go through one slit or the other. But if we want to retain the ment ...
Nonlinear atom optics - University of Arizona
... is the dipole potential due to the light. E(r, t) is the electric field at the center-of-mass location of the atom and q = −e is the electron charge. The force F(r, t) is often called the dipole force, or the gradient force. It indicates that it is possible to use light to manipulate atomic trajecto ...
... is the dipole potential due to the light. E(r, t) is the electric field at the center-of-mass location of the atom and q = −e is the electron charge. The force F(r, t) is often called the dipole force, or the gradient force. It indicates that it is possible to use light to manipulate atomic trajecto ...
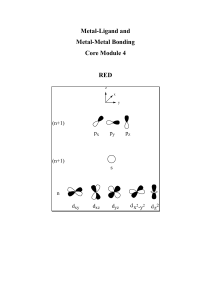
Section 8.10 Lewis Structures
... • Second-row elements never exceed the octet rule. • Third-row and heavier elements often satisfy the octet rule but can exceed the octet rule by using their empty valence d orbitals. Return to TOC ...
... • Second-row elements never exceed the octet rule. • Third-row and heavier elements often satisfy the octet rule but can exceed the octet rule by using their empty valence d orbitals. Return to TOC ...
Chapters_38-39
... photoelectric effect is used in many devices, including TV cameras, camcorders, and night vision viewers. Einstein supported his photon concept by using it to explain this effect, which simply cannot be understood without quantum physics. Let us analyze two basic photoelectric experiments, each usin ...
... photoelectric effect is used in many devices, including TV cameras, camcorders, and night vision viewers. Einstein supported his photon concept by using it to explain this effect, which simply cannot be understood without quantum physics. Let us analyze two basic photoelectric experiments, each usin ...
Chapter 8 and 9
... Lysine is an amino acid which has the following elemental composition: C, H, O, N. In one experiment, 2.175 g of lysine was combusted to produce 3.94 g of CO2 and 1.89 g H2O. In a separate experiment, 1.873 g of lysine was burned to produce 0.436 g of NH2. The molar mass of lysine is 150 g/mol. Dete ...
... Lysine is an amino acid which has the following elemental composition: C, H, O, N. In one experiment, 2.175 g of lysine was combusted to produce 3.94 g of CO2 and 1.89 g H2O. In a separate experiment, 1.873 g of lysine was burned to produce 0.436 g of NH2. The molar mass of lysine is 150 g/mol. Dete ...
Ionization

Ionization is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons to form ions, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. Ionization can result from the loss of an electron after collisions with sub atomic particles, collisions with other atoms, molecules and ions, or through the interaction with light. Heterolytic bond cleavage and heterolytic substitution reactions can result in the formation of ion pairs. Ionization can occur through radioactive decay by the internal conversion process, in which an excited nucleus transfers its energy to one of the inner-shell electrons causing it to be ejected.