Basic Physical Chemistry (12.4 MB ppt)
... AB 3. By inequal number of molls of starting compounds and final product in gaseous system (2A + B = C) the change of pressure 4. Change of temperature (exothermic – the rate decreases with increasing temperature; endothermic – the rate increases with increasing temperature) All reactions in liv ...
... AB 3. By inequal number of molls of starting compounds and final product in gaseous system (2A + B = C) the change of pressure 4. Change of temperature (exothermic – the rate decreases with increasing temperature; endothermic – the rate increases with increasing temperature) All reactions in liv ...
No Slide Title
... 1. How much heat is needed to warm 250 g of water from 22 C to 98 C? What is the molar heat capacity of water? The specific heat of water is 4.18 J/g K. 2. Large beds of rocks are used in some solar-heated homes to store heat. Calculate the quantity of heat absorbed by 50.0 kg of rocks if their te ...
... 1. How much heat is needed to warm 250 g of water from 22 C to 98 C? What is the molar heat capacity of water? The specific heat of water is 4.18 J/g K. 2. Large beds of rocks are used in some solar-heated homes to store heat. Calculate the quantity of heat absorbed by 50.0 kg of rocks if their te ...
CfE Higher Chemistry Unit 3: Chemistry in Society
... Industrial processes are designed to maximise profit and minimise the impact on the environment. "The Chemical Industry is not in existence to manufacture chemicals: like any other industry it exists to create wealth and wealth can only be created if it can make profits." So, the major determinant i ...
... Industrial processes are designed to maximise profit and minimise the impact on the environment. "The Chemical Industry is not in existence to manufacture chemicals: like any other industry it exists to create wealth and wealth can only be created if it can make profits." So, the major determinant i ...
Chemical Thermodynamics
... (For more information on matter, see Chapter 1 "Introduction to Chemistry".) The law of conservation of mass is the basis for all the stoichiometry and equilibrium calculations you have learned thus far in chemistry. The second, the law of conservation of energy, states that energy can be neither cr ...
... (For more information on matter, see Chapter 1 "Introduction to Chemistry".) The law of conservation of mass is the basis for all the stoichiometry and equilibrium calculations you have learned thus far in chemistry. The second, the law of conservation of energy, states that energy can be neither cr ...
`A` LEVEL H2 CHEMISTRY ORGANIC REACTIONS SUMMARY By
... Assuming ideal behavior, which of the following changes would cause the density of the gas to double? A B C D ...
... Assuming ideal behavior, which of the following changes would cause the density of the gas to double? A B C D ...
Chapter 15
... osmotic pressure as blood. There are three scenarios: (1) if the external solution is hypertonic, its osmotic pressure > Π(internal), and there is a net flow of water out of the cell. (2) if the external solution is isotonic, its osmotic pressure = Π(internal), and red blood cells in the isotonic so ...
... osmotic pressure as blood. There are three scenarios: (1) if the external solution is hypertonic, its osmotic pressure > Π(internal), and there is a net flow of water out of the cell. (2) if the external solution is isotonic, its osmotic pressure = Π(internal), and red blood cells in the isotonic so ...
Branham
... process in papermaking to near 100% by completely converting Na2SO4 to Na2S and Na2CO3 to NaOH. Kinetic data were collected, and it was determined that both reactions were overall first order with rate constants of 0.037s-1 for the formation of BaSO4 and 0.021s-1 for the formation of BaCO3. Also, it ...
... process in papermaking to near 100% by completely converting Na2SO4 to Na2S and Na2CO3 to NaOH. Kinetic data were collected, and it was determined that both reactions were overall first order with rate constants of 0.037s-1 for the formation of BaSO4 and 0.021s-1 for the formation of BaCO3. Also, it ...
5 SURFACE CHEMISTRY CATEGORY
... freezing point by 7.5°C? The freezing point depression constant, Kf , for water is 1.86 K kg mol–1. Assume van’t Hoff factor for NaCl is 1.87. 8. 18 g of glucose, C6H12O6 (Molar Mass = 180 g mol–1) is dissolved in 1 kg of water in a sauce pan. At what temperature will this solution boil? 9.Determine ...
... freezing point by 7.5°C? The freezing point depression constant, Kf , for water is 1.86 K kg mol–1. Assume van’t Hoff factor for NaCl is 1.87. 8. 18 g of glucose, C6H12O6 (Molar Mass = 180 g mol–1) is dissolved in 1 kg of water in a sauce pan. At what temperature will this solution boil? 9.Determine ...
Example 1-2
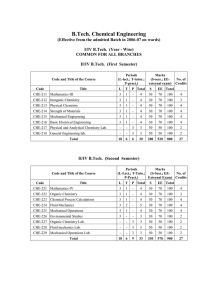
... central atom equals the periodic table family number. The only exceptions to this occur in the halogens, where the –ate and the –ic endings correspond to a +5 oxidation state and the noble gases where they correspond to +6. 5. Use solubility rules to predict products of reactions. The attached table ...
... central atom equals the periodic table family number. The only exceptions to this occur in the halogens, where the –ate and the –ic endings correspond to a +5 oxidation state and the noble gases where they correspond to +6. 5. Use solubility rules to predict products of reactions. The attached table ...
Chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which both reactants and products are present in concentrations which have no further tendency to change with time. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same rate as the reverse reaction. The reaction rates of the forward and backward reactions are generally not zero, but equal. Thus, there are no net changes in the concentrations of the reactant(s) and product(s). Such a state is known as dynamic equilibrium.