Discussion 9, Mahaffy et al., Chapter 15
... Oxidation Reduction Reactions a. Oxidation is loss of electrons (acts as a reducing agent) b.Reduction is gain of electrons (acts as a oxidizing agent) Assigning Oxidation numbers c. Oxidation number is 0 for atoms in an element. d.The sum of all oxidation numbers in a molecule or ion must add up to ...
... Oxidation Reduction Reactions a. Oxidation is loss of electrons (acts as a reducing agent) b.Reduction is gain of electrons (acts as a oxidizing agent) Assigning Oxidation numbers c. Oxidation number is 0 for atoms in an element. d.The sum of all oxidation numbers in a molecule or ion must add up to ...
B.Sc.-Chemistry
... reaction - concentration, temperature, pressure, solvent, light, catalyst, concentration dependence of rates, mathematical characteristics of simple chemical reactions - zero order, first order, second order, pseudo order, half life and mean life, Determination of the order of reaction - differentia ...
... reaction - concentration, temperature, pressure, solvent, light, catalyst, concentration dependence of rates, mathematical characteristics of simple chemical reactions - zero order, first order, second order, pseudo order, half life and mean life, Determination of the order of reaction - differentia ...
The five main types of redox reactions are combination
... Redox reactions are matched sets: if one species is oxidized in a reaction, another must be reduced. Keep this in mind as we look at the five main types of redox reactions: combination, decomposition, displacement, combustion, and disproportion. ...
... Redox reactions are matched sets: if one species is oxidized in a reaction, another must be reduced. Keep this in mind as we look at the five main types of redox reactions: combination, decomposition, displacement, combustion, and disproportion. ...
Document
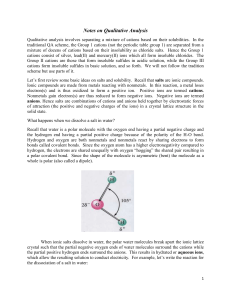
... • These acids contain more than one ionizable proton and release them sequentially. • For example, sulfuric acid, H2SO4 is a diprotic acid. • It is strong in its first ionizable proton, but weak in its ...
... • These acids contain more than one ionizable proton and release them sequentially. • For example, sulfuric acid, H2SO4 is a diprotic acid. • It is strong in its first ionizable proton, but weak in its ...
Energy
... Standard Enthalpies of Formation ∆Hfo values can be used to calculate the standard enthalpy changes for many reactions. In an application of Hess’s Law, it is as if the reactants are decomposed into their elements, and then the elements are recombined into the desired products. Since enthalpies of ...
... Standard Enthalpies of Formation ∆Hfo values can be used to calculate the standard enthalpy changes for many reactions. In an application of Hess’s Law, it is as if the reactants are decomposed into their elements, and then the elements are recombined into the desired products. Since enthalpies of ...
Download the paper in pdf format
... vacuo may represent a general technique for syntheses where small molecules are released and a crystal product is formed. Generally, the lower temperature range reduces the reaction velocity and the reduced pressure leads to lower concentrations. However, the efficient separation due to crystallisat ...
... vacuo may represent a general technique for syntheses where small molecules are released and a crystal product is formed. Generally, the lower temperature range reduces the reaction velocity and the reduced pressure leads to lower concentrations. However, the efficient separation due to crystallisat ...
Kinetics
... ln[A]t = -kt + ln[A]0 is the equation for a first order reaction. Note the similarity to y = mx + b. In this case , a plot of ln[A]t vs t yields a straight line with a slope –k and an intercept of ln[A]0 Half-life is the time required for the initial concentration of a reactant to decrease to on ...
... ln[A]t = -kt + ln[A]0 is the equation for a first order reaction. Note the similarity to y = mx + b. In this case , a plot of ln[A]t vs t yields a straight line with a slope –k and an intercept of ln[A]0 Half-life is the time required for the initial concentration of a reactant to decrease to on ...
6.5 Half-reactions and electrodes
... • A cell in which the overall reaction is at equilibrium can do no work with zero potential difference • The maximum non-expansion work a system can do is wadd,max = ΔG • Maximum work is produced when a change occurs reversibly • The reaction Gibbs energy is actually relating a specified composi ...
... • A cell in which the overall reaction is at equilibrium can do no work with zero potential difference • The maximum non-expansion work a system can do is wadd,max = ΔG • Maximum work is produced when a change occurs reversibly • The reaction Gibbs energy is actually relating a specified composi ...
AP Thermodynamics ppt.
... • Standard molar entropy, S: entropy of a substance in its standard state. Similar in concept to H. • Units: J/mol-K. Note units of H: kJ/mol. • Standard molar entropies of elements are not zero. • For a chemical reaction which produces n moles of products from m moles of reactants: ...
... • Standard molar entropy, S: entropy of a substance in its standard state. Similar in concept to H. • Units: J/mol-K. Note units of H: kJ/mol. • Standard molar entropies of elements are not zero. • For a chemical reaction which produces n moles of products from m moles of reactants: ...
Reactions and Balancing
... Don’t forget about the diatomic elements! (BrINClHOF) For example, Oxygen is O2 as an element. In a compound, it can’t be a diatomic element because it’s not an element anymore, it’s a compound! ...
... Don’t forget about the diatomic elements! (BrINClHOF) For example, Oxygen is O2 as an element. In a compound, it can’t be a diatomic element because it’s not an element anymore, it’s a compound! ...
+ H 2 O(l )
... What if the solution was basic? Notice that the method has assumed the solution was acidic - we added H+ to balance the equation. The [H+] in a basic solution is very small. The [OH-] is much greater. For this reason, we will add enough OH- ions to both sides of the equation to neutralize the H+ ad ...
... What if the solution was basic? Notice that the method has assumed the solution was acidic - we added H+ to balance the equation. The [H+] in a basic solution is very small. The [OH-] is much greater. For this reason, we will add enough OH- ions to both sides of the equation to neutralize the H+ ad ...
Thermodynamics
... (Homework) 2 moles of a certain ideal gas is allowed to expand adiabatically and reversibly to 5 atm pressure from an initial state of 20°C and 15 atm. What will be the final temperature and volume of the gas? What is the change in internal energy during this process? Assume a Cp of 8.58 cal/mole K ...
... (Homework) 2 moles of a certain ideal gas is allowed to expand adiabatically and reversibly to 5 atm pressure from an initial state of 20°C and 15 atm. What will be the final temperature and volume of the gas? What is the change in internal energy during this process? Assume a Cp of 8.58 cal/mole K ...
Chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which both reactants and products are present in concentrations which have no further tendency to change with time. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same rate as the reverse reaction. The reaction rates of the forward and backward reactions are generally not zero, but equal. Thus, there are no net changes in the concentrations of the reactant(s) and product(s). Such a state is known as dynamic equilibrium.