Thermodynamics and Equilibrium
... As we shall see, these two driving forces can act either in concert or in opposition. Figure 4.6 shows the effect that constraints (confinements or restrictions) on the degrees of freedom have on the density of states. The particles in Figure 4.6a are not constrained, so their energy is not constrai ...
... As we shall see, these two driving forces can act either in concert or in opposition. Figure 4.6 shows the effect that constraints (confinements or restrictions) on the degrees of freedom have on the density of states. The particles in Figure 4.6a are not constrained, so their energy is not constrai ...
Experiment #5 WHERE`S THE EVIDENCE
... b. Boiling water c. Burning wood d. Braiding hair 6. A change in matter that produces one or more new substances is a(n) __________________________. ...
... b. Boiling water c. Burning wood d. Braiding hair 6. A change in matter that produces one or more new substances is a(n) __________________________. ...
Teacher Background - Online Learning Exchange
... mole is equivalent to 6.02 1023 particles of a substance.) Ask: How can you determine the number of moles of a substance in a chemical equation? (The number of moles is represented by the substance’s coefficient.) Ask: What is molar mass? (Molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance.) ...
... mole is equivalent to 6.02 1023 particles of a substance.) Ask: How can you determine the number of moles of a substance in a chemical equation? (The number of moles is represented by the substance’s coefficient.) Ask: What is molar mass? (Molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance.) ...
Problem 14. MAGNESIUM DETERMINATION
... applied to macrosystems. To illustrate this idea, E. Schrödinger proposed the following mental experiment. Consider the Geiger counter which detects the entering electrons. The counter is connected to a device which breaks the glass with the poison when the particle enters the counter. Near the glas ...
... applied to macrosystems. To illustrate this idea, E. Schrödinger proposed the following mental experiment. Consider the Geiger counter which detects the entering electrons. The counter is connected to a device which breaks the glass with the poison when the particle enters the counter. Near the glas ...
Thermochem problems
... Yes, because it is just another elemental form of oxygen. No, because it is not the most stable form of the element oxygen at the given conditions. Yes, because changing the subscripts of an elemental formula does not change standard enthalpy of formation. No, because there is a temperature change w ...
... Yes, because it is just another elemental form of oxygen. No, because it is not the most stable form of the element oxygen at the given conditions. Yes, because changing the subscripts of an elemental formula does not change standard enthalpy of formation. No, because there is a temperature change w ...
Chemical Equilibrium - local.brookings.k12.sd.us
... and _________ ___________________, Chemical Equilibrium which states, at a given ___________, temperature a chemical state in which a system may reach a _____ ratio of _______ reactant and particular _____ product ____________ concentrations has a constant _______ _______ value Cato Maximilian Guldb ...
... and _________ ___________________, Chemical Equilibrium which states, at a given ___________, temperature a chemical state in which a system may reach a _____ ratio of _______ reactant and particular _____ product ____________ concentrations has a constant _______ _______ value Cato Maximilian Guldb ...
Slide 1
... ◦ More specifically, the first law states that the changes in internal energy is equal to the difference between the energy supplied to the system as heat and the energy removed from the system as work performed on the surroundings. ...
... ◦ More specifically, the first law states that the changes in internal energy is equal to the difference between the energy supplied to the system as heat and the energy removed from the system as work performed on the surroundings. ...
Topic 1: Quantitative chemistry (12
... An understanding of convergence is expected. Series should be considered in the ultraviolet, visible and infrared regions of the spectrum. Calculations, knowledge of quantum numbers and historical references will not be assessed. Aim 7: Interactive simulations modelling the behaviour of electrons in ...
... An understanding of convergence is expected. Series should be considered in the ultraviolet, visible and infrared regions of the spectrum. Calculations, knowledge of quantum numbers and historical references will not be assessed. Aim 7: Interactive simulations modelling the behaviour of electrons in ...
X1-1 - murov.info
... 2. How many protons, neutrons and electrons are in a.* Cl b. Cu 3. How many protons, neutrons and electrons are in a.* H b. C c. N d. O e. Br 4. How many protons, neutrons and electrons are in a.* Cu2+ b. Cl5. Except for small but very important differences in rates of chemical reactions, isotopes ( ...
... 2. How many protons, neutrons and electrons are in a.* Cl b. Cu 3. How many protons, neutrons and electrons are in a.* H b. C c. N d. O e. Br 4. How many protons, neutrons and electrons are in a.* Cu2+ b. Cl5. Except for small but very important differences in rates of chemical reactions, isotopes ( ...
H2-rich fluids from serpentinization: Geochemical and biotic
... pressure contours are thick gray lines. ...
... pressure contours are thick gray lines. ...
Document
... in a system of individual atoms than if the same atoms are united into molecules (∆S > 0). The key factor, then, is the temperature, T. At low temperatures, ∆H is the determining factor, dissociation into atoms is a nonspontaneous process, and therefore molecules are generally stable with respect to ...
... in a system of individual atoms than if the same atoms are united into molecules (∆S > 0). The key factor, then, is the temperature, T. At low temperatures, ∆H is the determining factor, dissociation into atoms is a nonspontaneous process, and therefore molecules are generally stable with respect to ...
Department of Chemistry, IIT-Delhi CY110N Tutorial
... 16. 100 g of ice at 0 o C is dropped into an insulated beaker containing 150 g of water at 100 o C. Calculate ∆S for this process. 17. Calculate the maximum work and the maximum non-expansion work that can be obtained from the freezing of supercooled water at −5 o C and 1.0 atm. The densities of wat ...
... 16. 100 g of ice at 0 o C is dropped into an insulated beaker containing 150 g of water at 100 o C. Calculate ∆S for this process. 17. Calculate the maximum work and the maximum non-expansion work that can be obtained from the freezing of supercooled water at −5 o C and 1.0 atm. The densities of wat ...
Study Guide for Test 2: Chapters 3 & 4... This is NOT a complete list of what will be... Revised March 4, 2014
... 11) Still know Avogadro’s Number (Chapter 2) and be able to convert between number of items (atoms, molecules, ions, etc.) and moles of that item. Be able to combine this calculation with molar mass. (1 mole items = 6.022 x 1023 items) 12) Be able to convert between moles of a compound and moles of ...
... 11) Still know Avogadro’s Number (Chapter 2) and be able to convert between number of items (atoms, molecules, ions, etc.) and moles of that item. Be able to combine this calculation with molar mass. (1 mole items = 6.022 x 1023 items) 12) Be able to convert between moles of a compound and moles of ...
Acid Rain - Controlled Assessment
... During the last century the rain water in some parts of the world has become far more acidic. This acid rain has been caused by the emission of pollutant gases such as carbon dioxide, sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides. When coal is burned in electricity power stations, gases are released into the ...
... During the last century the rain water in some parts of the world has become far more acidic. This acid rain has been caused by the emission of pollutant gases such as carbon dioxide, sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides. When coal is burned in electricity power stations, gases are released into the ...
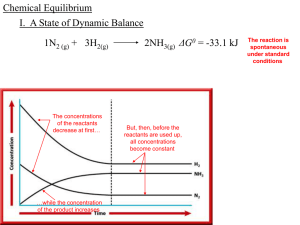
Chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which both reactants and products are present in concentrations which have no further tendency to change with time. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same rate as the reverse reaction. The reaction rates of the forward and backward reactions are generally not zero, but equal. Thus, there are no net changes in the concentrations of the reactant(s) and product(s). Such a state is known as dynamic equilibrium.