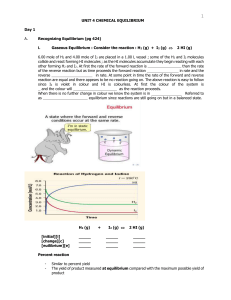
Unit 4 - Chemical Equilibrium
... of reactants and hardly _ _ _ products. As _ _ _ _ goes on, however, the concentration of reactants falls and the concentration of products rises. The forward reaction gets gradually slower and the _ _ _ _ _ _ _ reaction gets gradually faster. It follows that there must come a time when the reaction ...
... of reactants and hardly _ _ _ products. As _ _ _ _ goes on, however, the concentration of reactants falls and the concentration of products rises. The forward reaction gets gradually slower and the _ _ _ _ _ _ _ reaction gets gradually faster. It follows that there must come a time when the reaction ...
Ch 13 kinetics
... a) If a reaction of 2A → B is 1st order and has a rate constant of 0.150 s–1, how much time will it take for [A] to equal 0.0100 M if [A]0 = 0.0500 M? What is the value of [A] at 27.0 seconds? b) If a reaction of 2A → B is 2nd order and has a rate constant of 0.150 M–1 s–1, how much time will it tak ...
... a) If a reaction of 2A → B is 1st order and has a rate constant of 0.150 s–1, how much time will it take for [A] to equal 0.0100 M if [A]0 = 0.0500 M? What is the value of [A] at 27.0 seconds? b) If a reaction of 2A → B is 2nd order and has a rate constant of 0.150 M–1 s–1, how much time will it tak ...
18.3 Standard Entropies and the Third Law of
... terms are italicized in the text. Where a term does not fall directly under a text section heading, additional information is given for you to locate it. thermodynamics* study of the relationship between heat and other forms of energy involved in a chemical or physical process (chapter introduction) ...
... terms are italicized in the text. Where a term does not fall directly under a text section heading, additional information is given for you to locate it. thermodynamics* study of the relationship between heat and other forms of energy involved in a chemical or physical process (chapter introduction) ...
Chapter 6
... there may be a change in pressure, but if there is no change in volume, the atmosphere outside the container didn’t “move” and without movement, no work is done by or on the system. • If there is no change in volume (V= 0), then no work is done by or on the system (w= 0) and the change in internal e ...
... there may be a change in pressure, but if there is no change in volume, the atmosphere outside the container didn’t “move” and without movement, no work is done by or on the system. • If there is no change in volume (V= 0), then no work is done by or on the system (w= 0) and the change in internal e ...
model paper-1 - WordPress.com
... Name four quantum numbers and what are their significance. 5M OR a) State Heisenberg Uncertainty principle. b) What is the energy in joules, required to shift the electron of the hydrogen atom from the first Bohr orbit to the fifth Bohr orbit, and what is the wavelength of the light emitted when the ...
... Name four quantum numbers and what are their significance. 5M OR a) State Heisenberg Uncertainty principle. b) What is the energy in joules, required to shift the electron of the hydrogen atom from the first Bohr orbit to the fifth Bohr orbit, and what is the wavelength of the light emitted when the ...
Document
... is 1.2 . The reaction is started with [H2 ]0 = 0.76 M, [N2]0 = 0.60 M and [NH3]0= 0.48 M. Which of the following is correct as the reaction comes to equilibrium? A) The concentration of N2will increase B) The concentration of H2will decrease C) The concentration of NH3will decrease D) The concentrat ...
... is 1.2 . The reaction is started with [H2 ]0 = 0.76 M, [N2]0 = 0.60 M and [NH3]0= 0.48 M. Which of the following is correct as the reaction comes to equilibrium? A) The concentration of N2will increase B) The concentration of H2will decrease C) The concentration of NH3will decrease D) The concentrat ...
Unit 12 Worksheet Answers
... 3. What is the difference between a nonelectrolyte, a strong electrolyte and a weak electrolyte? Nonelectrolyte does not conduct electricity (no ions) Weak electrolyte conducts electricity a little (little ions) Strong electrolyte conducts electricity well (a lot of ions) 4. What is the difference b ...
... 3. What is the difference between a nonelectrolyte, a strong electrolyte and a weak electrolyte? Nonelectrolyte does not conduct electricity (no ions) Weak electrolyte conducts electricity a little (little ions) Strong electrolyte conducts electricity well (a lot of ions) 4. What is the difference b ...
Document
... To predict products of SR reactions, create a new compound with the lone metal ion and the anion from the reactanct compound. The cation from the reacctant compound becomes a lone element on the product side. ...
... To predict products of SR reactions, create a new compound with the lone metal ion and the anion from the reactanct compound. The cation from the reacctant compound becomes a lone element on the product side. ...
Many thermal and chemical reactions occur during the roasting
... relative quality. System Energy: At any given environment temperature, the amount of ...
... relative quality. System Energy: At any given environment temperature, the amount of ...
chapter 4 lecture slides
... Therefore Cu will displace Ag+ from a solution of AgNO3. • Silver metal will come out of the solution (reduction.) • The solution will begin to turn blue from the presence of Cu2+ as the copper metal reacts ...
... Therefore Cu will displace Ag+ from a solution of AgNO3. • Silver metal will come out of the solution (reduction.) • The solution will begin to turn blue from the presence of Cu2+ as the copper metal reacts ...
PDF (Size: 41K)
... Cyanogen, (CN)2, is a gas which is soluble in water to give the weak acid hydrocyanic acid, HCN (CN)2(g) + H2O(1) ...
... Cyanogen, (CN)2, is a gas which is soluble in water to give the weak acid hydrocyanic acid, HCN (CN)2(g) + H2O(1) ...
lecture slides of chap19_FU
... Electrochemical processes are oxidation-reduction reactions in which: ...
... Electrochemical processes are oxidation-reduction reactions in which: ...
Chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which both reactants and products are present in concentrations which have no further tendency to change with time. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same rate as the reverse reaction. The reaction rates of the forward and backward reactions are generally not zero, but equal. Thus, there are no net changes in the concentrations of the reactant(s) and product(s). Such a state is known as dynamic equilibrium.