atomic number - Mrs.Yu Science Class
... the outermost orbital are called valence electrons. All the electrons in levels other than the outermost level are called inner electrons. ...
... the outermost orbital are called valence electrons. All the electrons in levels other than the outermost level are called inner electrons. ...
atom - BSCSChemistryA
... • Dalton’s Atomic Theory (1808) – All matter consists of atoms which cannot be created, destroyed or split ...
... • Dalton’s Atomic Theory (1808) – All matter consists of atoms which cannot be created, destroyed or split ...
Types of reactions: redox reactions
... As a reactant, chlorine has an oxidation number of zero, but as part of the product magnesium chloride, the element has an oxidation number of -1. Each chlorine atom has gained an electron and the element has therefore been reduced. The half-reaction for this change is: ...
... As a reactant, chlorine has an oxidation number of zero, but as part of the product magnesium chloride, the element has an oxidation number of -1. Each chlorine atom has gained an electron and the element has therefore been reduced. The half-reaction for this change is: ...
Elements and the Periodic Table
... • Group 15, the nitrogen family, contains two nonmetals: nitrogen and phosphorus. These non-metals usually gain or share three electrons when reacting with atoms of other elements. • Nitrogen is an example of an element that occurs in nature in the form of diatomic molecules, as N2. • A diatomic mol ...
... • Group 15, the nitrogen family, contains two nonmetals: nitrogen and phosphorus. These non-metals usually gain or share three electrons when reacting with atoms of other elements. • Nitrogen is an example of an element that occurs in nature in the form of diatomic molecules, as N2. • A diatomic mol ...
atomicstructure IONincluded
... Rutherford had discovered that the volume of the nucleus was very small compared to the total volume of the atom, suggesting that there was a lot of empty space. ...
... Rutherford had discovered that the volume of the nucleus was very small compared to the total volume of the atom, suggesting that there was a lot of empty space. ...
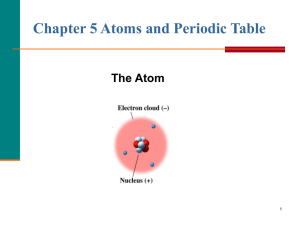
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure
... atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. (3.) Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine to form compounds. ...
... atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. (3.) Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine to form compounds. ...
Worksheet 2 Structure of matter Task 2.1.
... A. Read the text provided and underline in red the sentences, which state what makes the atoms of two different elements different from each other. B. Underline in blue the sentences, which state why all atoms of an element do not have the same number of neutrons All matter, such as solids, liquids ...
... A. Read the text provided and underline in red the sentences, which state what makes the atoms of two different elements different from each other. B. Underline in blue the sentences, which state why all atoms of an element do not have the same number of neutrons All matter, such as solids, liquids ...
LESSON PLAN Subject: Chemistry Topic: Matter matters!
... A. Read the text provided and underline in red the sentences, which state what makes the atoms of two different elements different from each other. B. Underline in blue the sentences, which state why all atoms of an element do not have the same number of neutrons All matter, such as solids, liquids ...
... A. Read the text provided and underline in red the sentences, which state what makes the atoms of two different elements different from each other. B. Underline in blue the sentences, which state why all atoms of an element do not have the same number of neutrons All matter, such as solids, liquids ...
File
... While all the protons and neutrons are packed tightly together in the central nucleus, the electrons are arranged in a very specific pattern, according to a set of rules. 1. The electrons can orbit (go around) the nucleus as if they are on rings or shells around the nucleus 2. Only two electrons can ...
... While all the protons and neutrons are packed tightly together in the central nucleus, the electrons are arranged in a very specific pattern, according to a set of rules. 1. The electrons can orbit (go around) the nucleus as if they are on rings or shells around the nucleus 2. Only two electrons can ...
TEST on Atomic Structure
... _B__ 48) Which of the forces of molecular attraction is the weakest? (dispersion is just from the moving e-) a. dipole interaction b. dispersion c. hydrogen bond d. single covalent bond 49) Compare and Contrast Ionic and covalent bonds. 3 points ...
... _B__ 48) Which of the forces of molecular attraction is the weakest? (dispersion is just from the moving e-) a. dipole interaction b. dispersion c. hydrogen bond d. single covalent bond 49) Compare and Contrast Ionic and covalent bonds. 3 points ...
Practice Multiple Choice Questions for the Chemistry Final Exam
... a) gas-liquid b) liquid-liquid c) solid-liquid d) liquid-solid 96. Solutions that conduct electricity are called a) ions b) super solutions c) electrolytes d) nonelectrolytes 97. If the amount of solute present in a solution at a given temperature is less than the maximum amount that can dissolve at ...
... a) gas-liquid b) liquid-liquid c) solid-liquid d) liquid-solid 96. Solutions that conduct electricity are called a) ions b) super solutions c) electrolytes d) nonelectrolytes 97. If the amount of solute present in a solution at a given temperature is less than the maximum amount that can dissolve at ...
Valence Electrons and Lewis Dot Diagrams
... Valence Electrons and Lewis Dot Diagrams Purpose: To illustrate the number of valence electrons for any given atom using Lewis Dot Structures. Background Information Valence electrons are the electrons in the highest energy level for an atom. They are the electrons involved with bonding between atom ...
... Valence Electrons and Lewis Dot Diagrams Purpose: To illustrate the number of valence electrons for any given atom using Lewis Dot Structures. Background Information Valence electrons are the electrons in the highest energy level for an atom. They are the electrons involved with bonding between atom ...
Energy - Biology
... • The innermost shell - or lowest energy level - is filled first. Each succeeding shell can only hold a certain number of electrons before it becomes full. • The innermost shell can hold a maximum of two electrons, the second shell a maximum of eight, and so on. • Look at the diagram of the chlorine ...
... • The innermost shell - or lowest energy level - is filled first. Each succeeding shell can only hold a certain number of electrons before it becomes full. • The innermost shell can hold a maximum of two electrons, the second shell a maximum of eight, and so on. • Look at the diagram of the chlorine ...
Chapter 4 Homework 4 File
... Adding together the numbers of electrons and protons Subtracting the number of protons from the number of electrons Subtracting the number of protons from the mass number Adding the mass number to the number of protons ...
... Adding together the numbers of electrons and protons Subtracting the number of protons from the number of electrons Subtracting the number of protons from the mass number Adding the mass number to the number of protons ...
Chem 220 In Class Socrative Qs: atomic orbitals 28/09/2016 1
... For the 3p orbitals in phosphorus (P), Zeff = 4.89. Which of the following statements is true? a) The 3p orbitals of S must have Zeff < 4.89, because S has more electrons to screen the charge than P b) The 2p orbitals of N must have Zeff > 4.89, because they are lower energy than 3p orbitals c) Th ...
... For the 3p orbitals in phosphorus (P), Zeff = 4.89. Which of the following statements is true? a) The 3p orbitals of S must have Zeff < 4.89, because S has more electrons to screen the charge than P b) The 2p orbitals of N must have Zeff > 4.89, because they are lower energy than 3p orbitals c) Th ...
Defining the Atom
... A. teaching that all matter is composed of tiny particles called atoms B. theorizing that all atoms of the same element are identical C. using experimental methods to establish a scientific theory D. not relating atoms to chemical change ...
... A. teaching that all matter is composed of tiny particles called atoms B. theorizing that all atoms of the same element are identical C. using experimental methods to establish a scientific theory D. not relating atoms to chemical change ...
Symbols of Elements - Chemistry with Mr. Patmos
... Are tiny particles of matter. of an element are similar and different from other elements. of two or more different elements combine in whole number ratios to form compounds. are separated, joined, or rearranged in a chemical reaction. ...
... Are tiny particles of matter. of an element are similar and different from other elements. of two or more different elements combine in whole number ratios to form compounds. are separated, joined, or rearranged in a chemical reaction. ...
s - RCSD
... could live in one house at a time, but the quantum model made it clear that, like a studio apartment with an unfriendly landlord, only two can live in one at the same time. ...
... could live in one house at a time, but the quantum model made it clear that, like a studio apartment with an unfriendly landlord, only two can live in one at the same time. ...
Unit 3 - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... 1. Elements are made of indivisible particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are exactly alike; in particular, they have the same mass. 3. Compounds are formed by the joining of atoms of two or more elements in fixed, whole number ratios. e.g., 1:1, 2:1, 3:1, 2:3, 1:2:1 Dalton’s was the ...
... 1. Elements are made of indivisible particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are exactly alike; in particular, they have the same mass. 3. Compounds are formed by the joining of atoms of two or more elements in fixed, whole number ratios. e.g., 1:1, 2:1, 3:1, 2:3, 1:2:1 Dalton’s was the ...