Intro to the Periodic Table
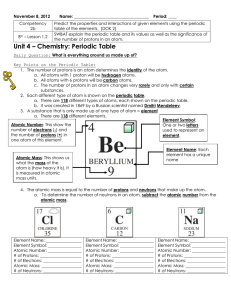
... 7. Find the element with the atomic number of 8. a. What is the element name? _________________________ b. What is the element symbol? _________________________ c. How many protons are in one atom of this element? __________________ d. How many electrons are in one atom of this element? ____________ ...
... 7. Find the element with the atomic number of 8. a. What is the element name? _________________________ b. What is the element symbol? _________________________ c. How many protons are in one atom of this element? __________________ d. How many electrons are in one atom of this element? ____________ ...
Atomic Structure Atomic_Structure
... 1. What is meant when an atom is said to be in its ground state? CORRECT: The state an atom is found naturally. 3. The subatomic particle(s) found in the nucleus of an atom are CORRECT: protons and neutrons. 5. What is the maximum number of electrons that can occupy an atomic orbital? CORRECT: 2, 6 ...
... 1. What is meant when an atom is said to be in its ground state? CORRECT: The state an atom is found naturally. 3. The subatomic particle(s) found in the nucleus of an atom are CORRECT: protons and neutrons. 5. What is the maximum number of electrons that can occupy an atomic orbital? CORRECT: 2, 6 ...
ATOMIC STRUCTURE
... • Said that all matter is composed of tiny, _____________ particles called __________ (atoms) In 1803, _______________ studied experiments and concluded that the properties of matter could be explained in terms of __________. Dalton’s _________________ was based on the following ideas: o Each __ ...
... • Said that all matter is composed of tiny, _____________ particles called __________ (atoms) In 1803, _______________ studied experiments and concluded that the properties of matter could be explained in terms of __________. Dalton’s _________________ was based on the following ideas: o Each __ ...
1 | Page Chemistry Lecture #19: Atomic Number, Isotopes, and
... For now, ignore the 14.0067 (I’ll explain what this number is in another lecture). The number 7 is the atomic number of nitrogen. Thus, nitrogen has 7 protons in the nucleus. In a neutral atom, the number of protons in the nucleus is equal to the number of electrons. ...
... For now, ignore the 14.0067 (I’ll explain what this number is in another lecture). The number 7 is the atomic number of nitrogen. Thus, nitrogen has 7 protons in the nucleus. In a neutral atom, the number of protons in the nucleus is equal to the number of electrons. ...
Mixtures, Pure Substance and Isotopes
... from atomic number of N = 7 7 protons isotope number – atomic number (= 16-7) 9 neutrons number of protons = no. of electrons 7 electrons ...
... from atomic number of N = 7 7 protons isotope number – atomic number (= 16-7) 9 neutrons number of protons = no. of electrons 7 electrons ...
Name:
... metallic solid. Scientists think that electrons in the outer energy levels of the bonding metallic atoms are free to move from one atom to the next. As a result, electricity will flow quite easily. This means that metals are good _________. ...
... metallic solid. Scientists think that electrons in the outer energy levels of the bonding metallic atoms are free to move from one atom to the next. As a result, electricity will flow quite easily. This means that metals are good _________. ...
11 atomic number
... -Contributes to an elements atomic mass - The number of ________ determine the isotope of the element -Have a weight of 1.6749 × 10−27 kg -Discovered by James Chadwick Atomic mass- the mass of an atom at rest - expressed in amu’s - equal to the mass of protons, neutrons and electrons (when the atom ...
... -Contributes to an elements atomic mass - The number of ________ determine the isotope of the element -Have a weight of 1.6749 × 10−27 kg -Discovered by James Chadwick Atomic mass- the mass of an atom at rest - expressed in amu’s - equal to the mass of protons, neutrons and electrons (when the atom ...
The Structure of the Atom- Chapter 4, 3
... placed in the first shell, up to 8 in the 2nd shell, up to 18 in the 3rd shell, etc. Only 8 electrons can be placed in the 3rd shell at first, then 2 electrons will move into the 4th shell and the remaining of the 18 will be placed back in the 3rd shell for a total of 18. **( Just know this : it wil ...
... placed in the first shell, up to 8 in the 2nd shell, up to 18 in the 3rd shell, etc. Only 8 electrons can be placed in the 3rd shell at first, then 2 electrons will move into the 4th shell and the remaining of the 18 will be placed back in the 3rd shell for a total of 18. **( Just know this : it wil ...
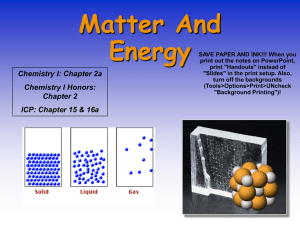
Matter and Energy
... 6. Which of the following are types of matter? (1) elements only (2) compounds only (3) mixtures only (4) all of these 7. Which of the following is a type of mixture? (1) elements only(2) compounds only (3) solutions only (4) elements and Compounds 8. Which of the following is NOT composed of two or ...
... 6. Which of the following are types of matter? (1) elements only (2) compounds only (3) mixtures only (4) all of these 7. Which of the following is a type of mixture? (1) elements only(2) compounds only (3) solutions only (4) elements and Compounds 8. Which of the following is NOT composed of two or ...
Atoms Development of the Atomic Theory
... 1915- English scientist that developed the periodic table that we use today Sorted the chemical elements of the periodic table of the elements in a logical order based on their physics- on their atomic number (how many protons an element has) ...
... 1915- English scientist that developed the periodic table that we use today Sorted the chemical elements of the periodic table of the elements in a logical order based on their physics- on their atomic number (how many protons an element has) ...
atom
... • # of electrons = # of protons in an uncharged atom • electron cloud- entire space that the electrons occupy – 1st energy level is full with 2 – 2nd energy level is full with 8 – 3rd energy level is full at 8, but can hold up to 18 in all the sublevels ...
... • # of electrons = # of protons in an uncharged atom • electron cloud- entire space that the electrons occupy – 1st energy level is full with 2 – 2nd energy level is full with 8 – 3rd energy level is full at 8, but can hold up to 18 in all the sublevels ...
PIB and HH - Unit 4 - Chemical Names and Formulas
... from the valence shell of a neutral atom.” 2. Restate in one or two words: “The tendency of an atom to hold on to its valence electrons while engaged in a chemical bond.” 3. Restate in one or two words: “The actions of the non-valence electrons, diluting the force of the attraction between nucleus a ...
... from the valence shell of a neutral atom.” 2. Restate in one or two words: “The tendency of an atom to hold on to its valence electrons while engaged in a chemical bond.” 3. Restate in one or two words: “The actions of the non-valence electrons, diluting the force of the attraction between nucleus a ...
C14- Atomic Orbitals and Energy Levels
... The timeline shows the development of atomic models from 1803 to 1911. ...
... The timeline shows the development of atomic models from 1803 to 1911. ...
Honors Midterm - Stamford High School
... Metallic bonds consist of the attractions of the free-floating valence electrons for the positively charged metal ions. The free floating valence electrons make metals good conductors and light reflecting off of the free floating valence electrons that travel around the outside of metal give metal ...
... Metallic bonds consist of the attractions of the free-floating valence electrons for the positively charged metal ions. The free floating valence electrons make metals good conductors and light reflecting off of the free floating valence electrons that travel around the outside of metal give metal ...
objectives chm 1025 - Miami Dade College
... The student will demonstrate an ability to understand several of the intricacies of the periodic table by: a. Showing how to obtain an element’s average atomic mass and atomic number from the periodic table. b. Using the structure of the periodic table to classify elements (e.g., metal, nonmetal, me ...
... The student will demonstrate an ability to understand several of the intricacies of the periodic table by: a. Showing how to obtain an element’s average atomic mass and atomic number from the periodic table. b. Using the structure of the periodic table to classify elements (e.g., metal, nonmetal, me ...
GO 3.1 Evolution of Atomic Theory PPT
... element are all identical to one another but different from the atoms of all other elements, and (2) atoms of different elements can combine to form more complex substances. Although the two theories that speculated atoms couldn't be divided were false, Dalton contributed greatly to the advances of ...
... element are all identical to one another but different from the atoms of all other elements, and (2) atoms of different elements can combine to form more complex substances. Although the two theories that speculated atoms couldn't be divided were false, Dalton contributed greatly to the advances of ...
Chapter 4 Notes
... ____________________ - smallest particle of an element that retains the ____________________ of that element. ____________________ is the man credited with the discovery of the electrons in the late _____, using cathode ray tubes. ____________________ discovered the mass of the electron. Knowledge o ...
... ____________________ - smallest particle of an element that retains the ____________________ of that element. ____________________ is the man credited with the discovery of the electrons in the late _____, using cathode ray tubes. ____________________ discovered the mass of the electron. Knowledge o ...
atom atomic symbol atomic number # protons atomic mass
... Number of Protons = Atomic Number (Use the large colored marshmallows for protons) Number of Neutrons = Atomic Mass – Atomic Number (Use the large white marshmallows for neutrons) Number of Electrons = Number of Protons (Use the small colored marshmallows for electrons) ...
... Number of Protons = Atomic Number (Use the large colored marshmallows for protons) Number of Neutrons = Atomic Mass – Atomic Number (Use the large white marshmallows for neutrons) Number of Electrons = Number of Protons (Use the small colored marshmallows for electrons) ...
Relative Atomic Mass
... Vertical columns, Gp I – alkali metals; Gp II – alkaline earth metals , Gp VII – halogens Gp 0 – Noble gases – same number of electrons in out shell – similar properties ...
... Vertical columns, Gp I – alkali metals; Gp II – alkaline earth metals , Gp VII – halogens Gp 0 – Noble gases – same number of electrons in out shell – similar properties ...
Atoms - Cloudfront.net
... Going back as far as 400 BCE. Greek philosophers suggested that the universe was made of small invisible particles they named atomos. Atomos is Greek and means unable to be divided (loose translation). ...
... Going back as far as 400 BCE. Greek philosophers suggested that the universe was made of small invisible particles they named atomos. Atomos is Greek and means unable to be divided (loose translation). ...
Taking a Look Inside the Atom
... electrons Has fewer electrons than protons Called a cation Ex. ...
... electrons Has fewer electrons than protons Called a cation Ex. ...
Basic Structure of the Atom
... Radioactive materials - In your body Carbon 14 emits beta particles and decays into ...
... Radioactive materials - In your body Carbon 14 emits beta particles and decays into ...