Lesson 1 - Working With Chemicals
... o A nucleus – a central region that is positively charged and contains most of the mass - protons are heavy positive particles within the nucleus o Electrons – particles with a negative charge and are very light (compared to protons). - Electrons circle around the nucleus o Empty space surrounding t ...
... o A nucleus – a central region that is positively charged and contains most of the mass - protons are heavy positive particles within the nucleus o Electrons – particles with a negative charge and are very light (compared to protons). - Electrons circle around the nucleus o Empty space surrounding t ...
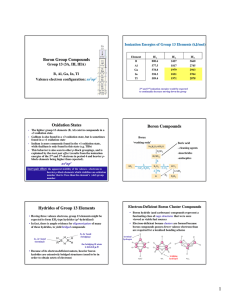
Boron Group Compounds Oxidation States Boron
... while thallium is only found in this state (e.g. TlBr) This behavior is also seen in other p-block groupings, and is explained by the inert pair effect (results from the ionization energies of the 2nd and 3rd electrons in period 4 and heavier pblock elements being higher than expected). ...
... while thallium is only found in this state (e.g. TlBr) This behavior is also seen in other p-block groupings, and is explained by the inert pair effect (results from the ionization energies of the 2nd and 3rd electrons in period 4 and heavier pblock elements being higher than expected). ...
Inside an Atom - Mrs. Ericka Williams
... They are identified by the number or protons because this number never changes without changing the identity of the element Are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons; for example, the three isotopes of carbon differ in the number of neutrons in each nucleus such as Carbon ...
... They are identified by the number or protons because this number never changes without changing the identity of the element Are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons; for example, the three isotopes of carbon differ in the number of neutrons in each nucleus such as Carbon ...
Chapter 3: Atom Powerpoint
... of the same two elements, then the ratio of the masses of the second element combined with a certain masses of the first element is always a ratio of small whole numbers. An example of the law of multiple proportions is the existence of A) FeCl3 and Fe(S04)3 C) CO and CO2 B) O2 and O3 D) FeCl2 and F ...
... of the same two elements, then the ratio of the masses of the second element combined with a certain masses of the first element is always a ratio of small whole numbers. An example of the law of multiple proportions is the existence of A) FeCl3 and Fe(S04)3 C) CO and CO2 B) O2 and O3 D) FeCl2 and F ...
Atomic Structure Test – Study Guide
... What is the electrical charge and position in the atom for each of the subatomic particles? 1. Electron - negative charge; located in a “cloud” rotating around the nucleus 2. Proton – positive charge; located in the center or nucleus of the atom 3. Neutron - no charge; located in the center or nucle ...
... What is the electrical charge and position in the atom for each of the subatomic particles? 1. Electron - negative charge; located in a “cloud” rotating around the nucleus 2. Proton – positive charge; located in the center or nucleus of the atom 3. Neutron - no charge; located in the center or nucle ...
transcript for this video
... Rutherford experiment was an image linked to that, that has not been labelled or explained in enough detail, the idea that we then discover that there’s a core in the centre of the atom which is positively charged, and we found that by having alpha particles deflected from them. So, all-in-all, I re ...
... Rutherford experiment was an image linked to that, that has not been labelled or explained in enough detail, the idea that we then discover that there’s a core in the centre of the atom which is positively charged, and we found that by having alpha particles deflected from them. So, all-in-all, I re ...
4.1 History of Atomic Model - Collinsville Public Schools
... gold is called an atom of gold. An atom is the smallest particle of an element that acts like the element. ...
... gold is called an atom of gold. An atom is the smallest particle of an element that acts like the element. ...
CHEM 1211K Test I MULTIPLE CHOICE. (3 points each) 1
... B) Each element is composed of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms. C) Compounds are formed when atoms of different elements combine. D) Atoms of an element are not changed into different types of atoms by chemical reactions. E) All atoms of a given element are identical to each other and diffe ...
... B) Each element is composed of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms. C) Compounds are formed when atoms of different elements combine. D) Atoms of an element are not changed into different types of atoms by chemical reactions. E) All atoms of a given element are identical to each other and diffe ...
unit 3 - structure, history of the atom, density
... ATOM - the smallest particle of matter which will exhibit the properties of that element. When broken down smaller than an atom, the parts (protons, electrons, and neutrons) of different elements look exactly the same. You cannot tell a proton in a gold atom from a proton in oxygen gas. Atoms are ve ...
... ATOM - the smallest particle of matter which will exhibit the properties of that element. When broken down smaller than an atom, the parts (protons, electrons, and neutrons) of different elements look exactly the same. You cannot tell a proton in a gold atom from a proton in oxygen gas. Atoms are ve ...
Document
... 1. Identify the basic building block of matter. 2. Identify the THREE subatomic particles that make up an atom. 3. Describe the atomic number of an atom. 4. Describe the structure of an atom. ...
... 1. Identify the basic building block of matter. 2. Identify the THREE subatomic particles that make up an atom. 3. Describe the atomic number of an atom. 4. Describe the structure of an atom. ...
HCC4 Chapter 4 Objectives and Notes
... 4.1 Defining the Atom a. Early Models of the Atom 1. atom: The atom is so small. How small? It is so small that it is the smallest part of an element that maintains the properties of that element. It is an electrically neutral particle, therefore, it has no charge. 2. element: A substance that is c ...
... 4.1 Defining the Atom a. Early Models of the Atom 1. atom: The atom is so small. How small? It is so small that it is the smallest part of an element that maintains the properties of that element. It is an electrically neutral particle, therefore, it has no charge. 2. element: A substance that is c ...
Earth`s Chemistry PowerPoint
... where an electron is most likely to be found. • The mass of an atom depends mostly upon the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. ...
... where an electron is most likely to be found. • The mass of an atom depends mostly upon the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. ...
Atoms, Molecules, and Ions Chemistry Timeline #1
... particles in the atom to balance the negative charge of the electrons Electrons have so little mass that atoms must contain other particles that account for most of the mass ...
... particles in the atom to balance the negative charge of the electrons Electrons have so little mass that atoms must contain other particles that account for most of the mass ...
Ch#4 Atoms and Elements
... • Electrons are the parts of atoms that “intermingle” when atoms combine to form molecules. • It is the number of valence (furthest from nucleus) electrons that really determines chemical behavior. ...
... • Electrons are the parts of atoms that “intermingle” when atoms combine to form molecules. • It is the number of valence (furthest from nucleus) electrons that really determines chemical behavior. ...
NOTES Atomic Structure Number Mass.docx
... measure – atomic mass. Atomic mass is the relative average mass of an atom of the element. There are no mass units for atomic mass. They are simply a ratio. Carbon has an atomic mass of 12, so it is 12 times heavier than hydrogen, which is 1. Oxygen atoms have 16 times more mass than hydrogen. John ...
... measure – atomic mass. Atomic mass is the relative average mass of an atom of the element. There are no mass units for atomic mass. They are simply a ratio. Carbon has an atomic mass of 12, so it is 12 times heavier than hydrogen, which is 1. Oxygen atoms have 16 times more mass than hydrogen. John ...
Electrons
... • Describe the relationship between the wavelength and frequency of light. • Identify the source of atomic emission spectra. • Explain how the frequencies of emitted light are related to changes in electron energies. • Distinguish between quantum mechanics and classical ...
... • Describe the relationship between the wavelength and frequency of light. • Identify the source of atomic emission spectra. • Explain how the frequencies of emitted light are related to changes in electron energies. • Distinguish between quantum mechanics and classical ...
Chapter 2 - profpaz.com
... Atoms of the same element (same atomic number) can possess different number of neutrons (different mass numbers) and are called isotopes. Most elements have several isotopes, which are indicated by its chemical symbol, followed by a dash and the mass number of isotope. For example, the 3 isotopes of ...
... Atoms of the same element (same atomic number) can possess different number of neutrons (different mass numbers) and are called isotopes. Most elements have several isotopes, which are indicated by its chemical symbol, followed by a dash and the mass number of isotope. For example, the 3 isotopes of ...
Electrons in Energy Level
... of Dalton’s atomic theory. 1.All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. 2.Atoms of the same element are identical and different from atoms of other elements. ...
... of Dalton’s atomic theory. 1.All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. 2.Atoms of the same element are identical and different from atoms of other elements. ...
Chemical History for L3
... 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of other elements. 3. Atoms of different elements can chemically combine with one another in small whole-number ratios to form compounds. 4. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, join ...
... 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of other elements. 3. Atoms of different elements can chemically combine with one another in small whole-number ratios to form compounds. 4. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, join ...
Ch#4 Atoms and Elements
... • Atoms can form ions by gaining or losing electrons. Metals tend to lose one or more electrons to form positive ions called cations and are named by using the name of the parent atom. Nonmetals tend to gain electrons to form negative ions called anions and are named by using the root of the ato ...
... • Atoms can form ions by gaining or losing electrons. Metals tend to lose one or more electrons to form positive ions called cations and are named by using the name of the parent atom. Nonmetals tend to gain electrons to form negative ions called anions and are named by using the root of the ato ...
Atomic Structure PPT
... of 78 what is the –number of protons –number of neutrons –number of electrons –Complete symbol ...
... of 78 what is the –number of protons –number of neutrons –number of electrons –Complete symbol ...
14.1 Force inside atoms
... nucleus together? !There is another force that is even stronger than the electric force. !We call it the strong nuclear force. ...
... nucleus together? !There is another force that is even stronger than the electric force. !We call it the strong nuclear force. ...