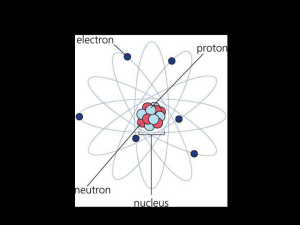
Electron config atomic structure
... of 78 what is the –number of protons –number of neutrons –number of electrons –Complete symbol ...
... of 78 what is the –number of protons –number of neutrons –number of electrons –Complete symbol ...
Name
... 1. Describe how particles move and draw a diagram for each state of matter: a. Solid b. Liquid ...
... 1. Describe how particles move and draw a diagram for each state of matter: a. Solid b. Liquid ...
atomic number
... nucleus of an atom is called the atomic number. For example, any atom with 6 protons in the nucleus is a Carbon atom. • Elements are arranged in the periodic table by their atomic number. • In a neutral atom, # electrons = #protons. • The symbol for an element is simply its 1, 2, or 3 letter abbrevi ...
... nucleus of an atom is called the atomic number. For example, any atom with 6 protons in the nucleus is a Carbon atom. • Elements are arranged in the periodic table by their atomic number. • In a neutral atom, # electrons = #protons. • The symbol for an element is simply its 1, 2, or 3 letter abbrevi ...
2.5 (Atom Review and Quiz 2.1)
... through, some were deflected a little, some were deflected a lot. ...
... through, some were deflected a little, some were deflected a lot. ...
The atomic number tells how many protons Protons make an atom
... Protons are all the same. If I try to put two together, they push away from each other. ...
... Protons are all the same. If I try to put two together, they push away from each other. ...
Unit 1 – Physical Science and Chemical Reactions
... quantity of energy Electrons cannot exist between orbits but can move to unfilled orbits The higher the energy level, the further from the nucleus the electron is The maximum numbers of electrons in the first three orbits are 2, 8, and 8 respectively (Octet Rule) An atom with the maximum num ...
... quantity of energy Electrons cannot exist between orbits but can move to unfilled orbits The higher the energy level, the further from the nucleus the electron is The maximum numbers of electrons in the first three orbits are 2, 8, and 8 respectively (Octet Rule) An atom with the maximum num ...
Ionic and Covalent Bonding
... • the electrons in the highest occupied energy level of an element’s atom ...
... • the electrons in the highest occupied energy level of an element’s atom ...
atom
... Identify each statement as describing a 1) proton, 2) neutron, or 3) electron. A. found outside the nucleus B. has a positive charge C. is neutral D. found in the nucleus ...
... Identify each statement as describing a 1) proton, 2) neutron, or 3) electron. A. found outside the nucleus B. has a positive charge C. is neutral D. found in the nucleus ...
atoms
... a) Combine protons and neutrons in one cluster using small pipe cleaner to form the nucleus. b) Make the correct number of energy levels (create circles with the pipe cleaners) and place the electrons on the pipe cleaners. 3) Draw your Lithium atom in data table 1. Don’t forget to label your drawing ...
... a) Combine protons and neutrons in one cluster using small pipe cleaner to form the nucleus. b) Make the correct number of energy levels (create circles with the pipe cleaners) and place the electrons on the pipe cleaners. 3) Draw your Lithium atom in data table 1. Don’t forget to label your drawing ...
1 km = 1 000 m 1 m = 100 cm 1 cm = 10 mm 1 m = 1 000 mm
... 1. Bohr proposed that while circling the nucleus of the atom, electrons could only occupy certain discrete orbits, that is to say energy levels. Bohr used Max Planck's equations describing quanta of radiation to determine what these discrete orbits would have to be. As long as electrons stay in thes ...
... 1. Bohr proposed that while circling the nucleus of the atom, electrons could only occupy certain discrete orbits, that is to say energy levels. Bohr used Max Planck's equations describing quanta of radiation to determine what these discrete orbits would have to be. As long as electrons stay in thes ...
K,7th Grade Test Review: Atoms and Chemical Reactions PART
... PART FOUR: Chemical Equations. For each equation, label the products and reactants. Then, count the number of atoms of each element on each side. Then fill in the blanks. ...
... PART FOUR: Chemical Equations. For each equation, label the products and reactants. Then, count the number of atoms of each element on each side. Then fill in the blanks. ...
Unit 1 – Atomic Structure
... A. Atomic Number (Z) 1. The number of protons in the nucleus of each atom of that element 2. Atoms are identified by their atomic number 3. Because atoms are neutral, # protons = # electrons 4. Periodic Table is in order of increasing atomic number B. Mass Number 1. The total number of protons and n ...
... A. Atomic Number (Z) 1. The number of protons in the nucleus of each atom of that element 2. Atoms are identified by their atomic number 3. Because atoms are neutral, # protons = # electrons 4. Periodic Table is in order of increasing atomic number B. Mass Number 1. The total number of protons and n ...
chapter 3 notes
... • Quantum Numbers are used to describe the location of an electron in an atom. • Four quantum numbers are needed for each electron and no electrons in an atom can have the same set on QN’s. • The principal QN is is identified by the letter n and gives the main energy level of the electron. • The pr ...
... • Quantum Numbers are used to describe the location of an electron in an atom. • Four quantum numbers are needed for each electron and no electrons in an atom can have the same set on QN’s. • The principal QN is is identified by the letter n and gives the main energy level of the electron. • The pr ...
SCIENCE 9
... ELEMENT- is a pure substance made up of one type of particle, or atom. Eache element has its own distinct properties and cannot be broken down into simpler substances by means of a chemical change. COMPOUNDS- are pure substances that are made up of two or more elements chemically combined together. ...
... ELEMENT- is a pure substance made up of one type of particle, or atom. Eache element has its own distinct properties and cannot be broken down into simpler substances by means of a chemical change. COMPOUNDS- are pure substances that are made up of two or more elements chemically combined together. ...
المرحلة الثانية / فيزياء المحاضرة الثامنة E
... C) Fill in the blanks with the most correct words from the list below: (basic substance. Chemical Philosophy, French nobleman, isotope, chemical properties, very small, equal number, subatomic components, join together, negative charge,) 1- During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, physicists d ...
... C) Fill in the blanks with the most correct words from the list below: (basic substance. Chemical Philosophy, French nobleman, isotope, chemical properties, very small, equal number, subatomic components, join together, negative charge,) 1- During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, physicists d ...
Lecture 1 Medical Chemistry
... Greek prefixes di-, tri-, tetra-, penta-, and hexa- to name them. Thus, the ligands in the cation [Co(NH3)4Cl2]+ are “tetraamminedichloro.” (Note that prefixes are ignored when alphabetizing ligands.) If the ligand itself contains a Greek prefix, we use the prefixes bis (2), tris (3), and tetrakis ( ...
... Greek prefixes di-, tri-, tetra-, penta-, and hexa- to name them. Thus, the ligands in the cation [Co(NH3)4Cl2]+ are “tetraamminedichloro.” (Note that prefixes are ignored when alphabetizing ligands.) If the ligand itself contains a Greek prefix, we use the prefixes bis (2), tris (3), and tetrakis ( ...
Honors Chemistry Exam Review Questions
... A adding together the numbers of electrons and protons. B subtracting the number of protons from the number of electrons. C subtracting the number of protons from the mass number D adding the mass number to the number of protons 27. An atom of an element with atomic number 48 and mass number 120 con ...
... A adding together the numbers of electrons and protons. B subtracting the number of protons from the number of electrons. C subtracting the number of protons from the mass number D adding the mass number to the number of protons 27. An atom of an element with atomic number 48 and mass number 120 con ...
atom
... Modern Atomic Theory • Not all aspects of Dalton’s atomic theory have proven to be correct. We now know that: • Atoms are divisible into even smaller particles. • A given element can have atoms with different masses. • Some important concepts remain unchanged. • All matter is composed of atoms. • At ...
... Modern Atomic Theory • Not all aspects of Dalton’s atomic theory have proven to be correct. We now know that: • Atoms are divisible into even smaller particles. • A given element can have atoms with different masses. • Some important concepts remain unchanged. • All matter is composed of atoms. • At ...