Chapter 4
... move with constant speed in fixed orbits around the nucleus (like planets around the sun) Each electron in an atom has a specific amount of energy. ENERGY LEVELS- the possible energies that electrons in an atom can have. ...
... move with constant speed in fixed orbits around the nucleus (like planets around the sun) Each electron in an atom has a specific amount of energy. ENERGY LEVELS- the possible energies that electrons in an atom can have. ...
a Charged
... Rutherford found that most of the alpha particles went straight through the gold foil. A few were deflected at varying angles and some were deflected backward towards the source. Rutherford suggested that the bulk of the mass and all of the positive charge was located in a tiny, dense central cor ...
... Rutherford found that most of the alpha particles went straight through the gold foil. A few were deflected at varying angles and some were deflected backward towards the source. Rutherford suggested that the bulk of the mass and all of the positive charge was located in a tiny, dense central cor ...
Parts Of An Atom
... Substances that contain only one kind of atom are called elements. Some familiar elements are oxygen, gold, silver, and helium. An atom is the smallest part of an element that can be broken down and still have the characteristics of that element. All atoms are basically the same. All atoms of the sa ...
... Substances that contain only one kind of atom are called elements. Some familiar elements are oxygen, gold, silver, and helium. An atom is the smallest part of an element that can be broken down and still have the characteristics of that element. All atoms are basically the same. All atoms of the sa ...
Catalyst
... The atomic number of the element: This number tells you the number of protons in the atom. And because, in a neutral atom, the number of protons and the number of electrons are equal, it also tells the number of ...
... The atomic number of the element: This number tells you the number of protons in the atom. And because, in a neutral atom, the number of protons and the number of electrons are equal, it also tells the number of ...
Atomic Terms/People
... Also, that atoms can combine in simple ratios to form compounds. His ideas explained the laws of conservation of mass and definite proportions. Antoine Lavoisier a French Chemist (1743-1794) Proposed the Law of Conservation of Mass: in ordinary chemical reactions, matter can be changed in many ...
... Also, that atoms can combine in simple ratios to form compounds. His ideas explained the laws of conservation of mass and definite proportions. Antoine Lavoisier a French Chemist (1743-1794) Proposed the Law of Conservation of Mass: in ordinary chemical reactions, matter can be changed in many ...
INTRODUCTION Basic Chemistry I
... nitrogen boils off harmlessly into the air rather than becoming an ingredient in the recipe. • Nitrogen is used to cool ice cream so that you don't have to wait around for a freezer or ice cream maker. ...
... nitrogen boils off harmlessly into the air rather than becoming an ingredient in the recipe. • Nitrogen is used to cool ice cream so that you don't have to wait around for a freezer or ice cream maker. ...
Modern Atomic Theory - Whitmore Lake Public Schools
... • During the 1800's, a French Chemist (Antoine Lavoisier) discovered that chemical "changes" occurring in a closed system - the mass after a chemical change equaled the mass before the chemical change. • He proposed that, in ordinary chemical reactions, matter can be changed in many ways, but it can ...
... • During the 1800's, a French Chemist (Antoine Lavoisier) discovered that chemical "changes" occurring in a closed system - the mass after a chemical change equaled the mass before the chemical change. • He proposed that, in ordinary chemical reactions, matter can be changed in many ways, but it can ...
What are the parts of an atom?
... What are the parts of an atom? As you have learned, an atom can be divided into smaller parts. That’s because atoms themselves are composed of particles even smaller then themselves. The parts are called protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons are found in the center of an atom, calle ...
... What are the parts of an atom? As you have learned, an atom can be divided into smaller parts. That’s because atoms themselves are composed of particles even smaller then themselves. The parts are called protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons are found in the center of an atom, calle ...
Chemistry Standard Course of Study -- Detailed - UNCG GK-12
... Activities and Labs listed below are suggested resources only. This list is not inclusive and only reflects labs and activities recommended by the Chemistry Curriculum Committee. Teachers should substitute other labs appropriate to the equipment available in their school. Effort should be made in ea ...
... Activities and Labs listed below are suggested resources only. This list is not inclusive and only reflects labs and activities recommended by the Chemistry Curriculum Committee. Teachers should substitute other labs appropriate to the equipment available in their school. Effort should be made in ea ...
Dalton Model Reading
... its volume). Avogadro's law allowed him to deduce the diatomic nature of numerous gases by studying the volumes at which they reacted. For instance: since two liters of hydrogen will react with just one liter of oxygen to produce two liters of water vapor (at constant pressure and temperature), it m ...
... its volume). Avogadro's law allowed him to deduce the diatomic nature of numerous gases by studying the volumes at which they reacted. For instance: since two liters of hydrogen will react with just one liter of oxygen to produce two liters of water vapor (at constant pressure and temperature), it m ...
Chemistry Fall Final Review 2012-2013 Alchemy Unit
... Hydrogen is an nonmetal. 2. Where are the alkali, alkaline earth, transition metals, halogens, and noble gases? Alkali metals = group 1, alkaline earth metals = group 2, transition metals = middle of periodic table, halogens = group 7, and noble gas = group 8 3. On the periodic table, what are the t ...
... Hydrogen is an nonmetal. 2. Where are the alkali, alkaline earth, transition metals, halogens, and noble gases? Alkali metals = group 1, alkaline earth metals = group 2, transition metals = middle of periodic table, halogens = group 7, and noble gas = group 8 3. On the periodic table, what are the t ...
Atomic Theory Lecture Notes
... Five Principles-Dalton's Atomic Theory 1. All matter is made of indestructible atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are identical in their physical and chemical properties. 3. Atoms of different elements have different physical and chemical properties. 4. Atoms of different elements combine in simple ...
... Five Principles-Dalton's Atomic Theory 1. All matter is made of indestructible atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are identical in their physical and chemical properties. 3. Atoms of different elements have different physical and chemical properties. 4. Atoms of different elements combine in simple ...
Topic 7. 1 Atomic Structure
... Imagine a pea in the center of a football field with the track being the orbits. Protons and Neutrons have very similar mass. Protons and Neutrons are about 1800 times bigger than electrons. ****IB DATA*** See the data book for actual values. 7.1.2 Outline the evidence that supports a nuclear ...
... Imagine a pea in the center of a football field with the track being the orbits. Protons and Neutrons have very similar mass. Protons and Neutrons are about 1800 times bigger than electrons. ****IB DATA*** See the data book for actual values. 7.1.2 Outline the evidence that supports a nuclear ...
General Chemistry/Atomic Structure/History of Atomic Structure
... The Greek Theorists The earliest known proponent of anything resembling modern atomic theory was the ancient Greek thinker Democritus. He proposed the existence of indivisible atoms as a response to the arguments of Parmenides, and the paradoxes of Zeno. Parmenides argued against the possibility of ...
... The Greek Theorists The earliest known proponent of anything resembling modern atomic theory was the ancient Greek thinker Democritus. He proposed the existence of indivisible atoms as a response to the arguments of Parmenides, and the paradoxes of Zeno. Parmenides argued against the possibility of ...
Name Parts of an Atom Worksheet Date_______ Substances that
... Substances that contain only one kind of atom are called elements. Some familiar elements are oxygen, gold, silver, and helium. An atom is the smallest part of an element that can be broken down and still have the characteristics of that element. All atoms are basically the same. All atoms of the sa ...
... Substances that contain only one kind of atom are called elements. Some familiar elements are oxygen, gold, silver, and helium. An atom is the smallest part of an element that can be broken down and still have the characteristics of that element. All atoms are basically the same. All atoms of the sa ...
Ch. 2: Biochemistry
... Valence electrons: in the outermost shell, or valence shell Elements with full valence shell are chemically inert Chemical behavior of atom determined by distribution of electrons in electron shells, MOSTLY by valence electrons ...
... Valence electrons: in the outermost shell, or valence shell Elements with full valence shell are chemically inert Chemical behavior of atom determined by distribution of electrons in electron shells, MOSTLY by valence electrons ...
7th Science - Carterville CUSD #5
... 3. Who discovered the electron? 4. What else did discovering the electron tell this person about atoms? 5. Who discovered that atoms are mostly empty space with a small but dense positive center? 6. What is the modern (current) model of an atom? 7. Know scientists’ theories (big ideas) on atoms, the ...
... 3. Who discovered the electron? 4. What else did discovering the electron tell this person about atoms? 5. Who discovered that atoms are mostly empty space with a small but dense positive center? 6. What is the modern (current) model of an atom? 7. Know scientists’ theories (big ideas) on atoms, the ...
Atomic Structure and Elements
... – Electrons – (e-) – negative charge - In a neutral atom: Number of protons (+)= Number of electrons (-) ...
... – Electrons – (e-) – negative charge - In a neutral atom: Number of protons (+)= Number of electrons (-) ...
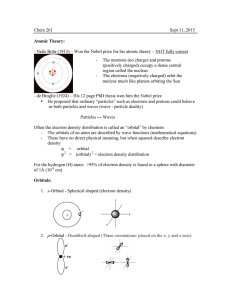
Chem 261 Sept 11, 2015 Atomic Theory:
... - Like charges repel each other; unlike charges attract each other - Atoms want to have an inert gas electron configuration (isoelectronic with inert gas, such as He, Ne, Ar. Helium is the inert gas that hydrogen can be isoelectronic with) Atoms H He Li ...
... - Like charges repel each other; unlike charges attract each other - Atoms want to have an inert gas electron configuration (isoelectronic with inert gas, such as He, Ne, Ar. Helium is the inert gas that hydrogen can be isoelectronic with) Atoms H He Li ...
Page | 1 MATS1101 Chemistry notes semester 2 2012 TOPIC 1
... Using this theory we can explain three fundamental laws of chemical behaviour: 1. Law of Conservation of Mass and Energy: Matter is neither created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. Energy is neither created or destroyed in a chemical reaction, but it may be transformed from one form to another. ...
... Using this theory we can explain three fundamental laws of chemical behaviour: 1. Law of Conservation of Mass and Energy: Matter is neither created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. Energy is neither created or destroyed in a chemical reaction, but it may be transformed from one form to another. ...
evolution of the atom essay
... (since it has about the same mass as a proton) and it can affect an atom’s properties. Isotopes are atoms with the same number of protons, but a different number of electrons. Different isotopes have different properties. For example, carbon-12 is stable and found everywhere in nature. Carbon-14, on ...
... (since it has about the same mass as a proton) and it can affect an atom’s properties. Isotopes are atoms with the same number of protons, but a different number of electrons. Different isotopes have different properties. For example, carbon-12 is stable and found everywhere in nature. Carbon-14, on ...