MATTER IS MADE UP OF ATOMS
... 1) energy is given off in packets or bundles called quanta (singular, quantum) 2) What happens to energy as substances are heated? Planck tried to explain atomic spectra with equations. B. electrons in energy levels 1) valence electrons—the electrons in the highest energy level of at atom 2) for Gro ...
... 1) energy is given off in packets or bundles called quanta (singular, quantum) 2) What happens to energy as substances are heated? Planck tried to explain atomic spectra with equations. B. electrons in energy levels 1) valence electrons—the electrons in the highest energy level of at atom 2) for Gro ...
atomic number
... http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RIg1Vh7uPyw&list=TL9l iUotc3avVG69w_AB1a0zk9sCfDLWVc&safe=active ...
... http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RIg1Vh7uPyw&list=TL9l iUotc3avVG69w_AB1a0zk9sCfDLWVc&safe=active ...
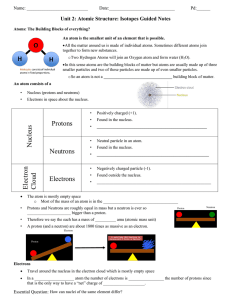
Nucleus Protons Neutrons Electron Cloud Electrons
... An atom is the smallest unit of an element that is possible. All the matter around us is made of individual atoms. Sometimes different atoms join together to form new substances. o Two Hydrogen Atoms will join an Oxygen atom and form water (H2O). In this sense atoms are the building blocks of ma ...
... An atom is the smallest unit of an element that is possible. All the matter around us is made of individual atoms. Sometimes different atoms join together to form new substances. o Two Hydrogen Atoms will join an Oxygen atom and form water (H2O). In this sense atoms are the building blocks of ma ...
What is hydrogen peroxide?
... substance, said to be capable of turning base metals , especially lead , into gold; it was also sometimes believed to be an elixir of life , useful for rejuvenation and possibly ...
... substance, said to be capable of turning base metals , especially lead , into gold; it was also sometimes believed to be an elixir of life , useful for rejuvenation and possibly ...
Atoms, Molecules, and Life Atoms
... cannot interact with other atoms and is called inert. • Atoms is reactive when its outer electron shell is only partially full and it can react with other atoms. ...
... cannot interact with other atoms and is called inert. • Atoms is reactive when its outer electron shell is only partially full and it can react with other atoms. ...
William Crooks (1832
... Rutherford (in 1914) described Moseley's discovery thus: "Recently Moseley has supplied very valuable evidence that this rule [atomic numbers changing by one from element to element] also holds for a number of the lighter elements. By examination of the wave-length of the characteristic X rays emit ...
... Rutherford (in 1914) described Moseley's discovery thus: "Recently Moseley has supplied very valuable evidence that this rule [atomic numbers changing by one from element to element] also holds for a number of the lighter elements. By examination of the wave-length of the characteristic X rays emit ...
Directed Reading B
... 10. In 1911, Rutherford revised the atomic theory. Which of the following is NOT part of that theory? a. Atoms are mostly empty space. b. The nucleus is a tiny, dense, positively charged region. c. Positively charged particles that pass close by the nucleus are pushed away by the positive charges in ...
... 10. In 1911, Rutherford revised the atomic theory. Which of the following is NOT part of that theory? a. Atoms are mostly empty space. b. The nucleus is a tiny, dense, positively charged region. c. Positively charged particles that pass close by the nucleus are pushed away by the positive charges in ...
Chapter 4 Modern Atomic Theory
... state or lower energy state, it emits a photon of radiation equal to difference in energy between atom’s initial state and its final state • Emits specific frequencies (energies) of light • i.e. hydrogen atom exists only in very specific energy states ...
... state or lower energy state, it emits a photon of radiation equal to difference in energy between atom’s initial state and its final state • Emits specific frequencies (energies) of light • i.e. hydrogen atom exists only in very specific energy states ...
Do Now - Montville.net
... - If an ion is positively charged, does it gain or lose electrons? - Negatively charged? - How many electrons does O3- have? ...
... - If an ion is positively charged, does it gain or lose electrons? - Negatively charged? - How many electrons does O3- have? ...
Unit Analysis Matter Classification
... 0.316522 nanometers. Each cube contains two tungsten atoms. Tungsten has a density of 19.300 g/cm3 . 1 mole of tungsten is 183.85 grams. Calculate the number of tungsten atoms in one mole of tungsten. Note: You do not need to know what a mole is to solve the problem! Only problem-solving skills! Use ...
... 0.316522 nanometers. Each cube contains two tungsten atoms. Tungsten has a density of 19.300 g/cm3 . 1 mole of tungsten is 183.85 grams. Calculate the number of tungsten atoms in one mole of tungsten. Note: You do not need to know what a mole is to solve the problem! Only problem-solving skills! Use ...
CH 5: The Atom
... • According to the law of definite composition, the mass ratio of carbon to oxygen in carbon dioxide is always the same. Carbon dioxide is composed of 1 carbon atom and 2 oxygen atoms. • Similarly, 2 atoms of hydrogen and 1 atom of oxygen combine to give water. • Dalton proposed that 2 hydrogen atom ...
... • According to the law of definite composition, the mass ratio of carbon to oxygen in carbon dioxide is always the same. Carbon dioxide is composed of 1 carbon atom and 2 oxygen atoms. • Similarly, 2 atoms of hydrogen and 1 atom of oxygen combine to give water. • Dalton proposed that 2 hydrogen atom ...
Atoms
... • It cannot be broken down any further without a chemical or nuclear reaction. – It will then become a different substance. • Uranium in a nuclear bomb ...
... • It cannot be broken down any further without a chemical or nuclear reaction. – It will then become a different substance. • Uranium in a nuclear bomb ...
the atom
... An element when composed of one type of atom, and canNOT be broken down chemically into simpler substances. Hydrogen and oxygen are examples of elements. A compound when composed of two or more types of elements combined in a definite ratio, and can be decomposed by a chemical change into two or mor ...
... An element when composed of one type of atom, and canNOT be broken down chemically into simpler substances. Hydrogen and oxygen are examples of elements. A compound when composed of two or more types of elements combined in a definite ratio, and can be decomposed by a chemical change into two or mor ...
Review Questions
... A. All scientists must agree with an idea for it to be considered a theory. B. Theories can be proven correct. C. Scientists usually create an entirely new theory when evidence is found that ...
... A. All scientists must agree with an idea for it to be considered a theory. B. Theories can be proven correct. C. Scientists usually create an entirely new theory when evidence is found that ...
Hein and Arena
... • Instead of being located in orbits, the electrons are located in orbitals. • An orbital is a region around the nucleus where there is a high probability of finding an electron. ...
... • Instead of being located in orbits, the electrons are located in orbitals. • An orbital is a region around the nucleus where there is a high probability of finding an electron. ...
Unit 3 - The Atom
... How can atoms of the same element be both similar and different at the same time? What do we call an atom that is not neutral? How can we calculate the average mass of isotopes? How has the model of the atom evolved over time? How can we describe the modern model of the atom? How can we describe whe ...
... How can atoms of the same element be both similar and different at the same time? What do we call an atom that is not neutral? How can we calculate the average mass of isotopes? How has the model of the atom evolved over time? How can we describe the modern model of the atom? How can we describe whe ...
CHEMISTRY IM 06 SYLLABUS 1
... Proton transfer equilibria and Lowry-Bronsted definition. Concept of conjugate pair; Ka and Kb. Ionic product of water, Kw; pH scale. Numerical calculations involving Ka and Kb will not be set but the ability to calculate pH from concentrations of hydroxonium or hydroxide ions will be expected. The ...
... Proton transfer equilibria and Lowry-Bronsted definition. Concept of conjugate pair; Ka and Kb. Ionic product of water, Kw; pH scale. Numerical calculations involving Ka and Kb will not be set but the ability to calculate pH from concentrations of hydroxonium or hydroxide ions will be expected. The ...
atom
... All atoms of a particular element have the same atomic number, and each element has a different atomic number from that of any other element. Mass number: total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom Number of neutrons = mass number – atomic number or N = A – Z All atoms of an elem ...
... All atoms of a particular element have the same atomic number, and each element has a different atomic number from that of any other element. Mass number: total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom Number of neutrons = mass number – atomic number or N = A – Z All atoms of an elem ...
Chapter 10
... It is correct to say that atoms that make up your body a. were formed in ancient stars. b. were previously a part of your neighbor’s bodies. c. are in motion at all times. d. All of these. ...
... It is correct to say that atoms that make up your body a. were formed in ancient stars. b. were previously a part of your neighbor’s bodies. c. are in motion at all times. d. All of these. ...
atoms
... Most of mass and all of positive charge of an atom are centered in a very small region called nucleus. The remainder of the atom is mostly empty space The magnitude of the positive charge is different for the different atoms and is approximately one-half the atomic weight of the element There a ...
... Most of mass and all of positive charge of an atom are centered in a very small region called nucleus. The remainder of the atom is mostly empty space The magnitude of the positive charge is different for the different atoms and is approximately one-half the atomic weight of the element There a ...