File
... mostly empty space Because the alpha particles turned so much, the positive particles must have been heavy Small volume and big mass = big density. This small dense positive area is the nucleus ...
... mostly empty space Because the alpha particles turned so much, the positive particles must have been heavy Small volume and big mass = big density. This small dense positive area is the nucleus ...
atomic number - s3.amazonaws.com
... might expect them to repel each other just as the north ends of two magnets tend to push each other apart. • It is true that they normally would do just that. • However, when they are packed together in the nucleus with the neutrons, an even stronger binding force takes over. • That force is called ...
... might expect them to repel each other just as the north ends of two magnets tend to push each other apart. • It is true that they normally would do just that. • However, when they are packed together in the nucleus with the neutrons, an even stronger binding force takes over. • That force is called ...
The Atom - VCE Chemistry
... country of her birth, Poland. • Its atomic number is 84 and was placed in the same group as tellurium (Group IV, atomic number 52) because of their similar chemical properties. ...
... country of her birth, Poland. • Its atomic number is 84 and was placed in the same group as tellurium (Group IV, atomic number 52) because of their similar chemical properties. ...
Development of the Atomic Theory
... Element – A ____ substance that ________ be _________ into simpler substances by________ or ________ means. Atoms make up ________. Elements are made of only ______ kind of _______. Elements _______ to form _________. All matter is made of ________ or __________, so all matter is made of ato ...
... Element – A ____ substance that ________ be _________ into simpler substances by________ or ________ means. Atoms make up ________. Elements are made of only ______ kind of _______. Elements _______ to form _________. All matter is made of ________ or __________, so all matter is made of ato ...
Chapter 4
... Atomic Orbitals • The electron cloud represents all the orbitals in an atom. • An orbital is a region of space around the nucleus where an electron is likely to be found. • An electron cloud is a good approximation of how electrons behave in their orbitals. • The level in which an electron has the ...
... Atomic Orbitals • The electron cloud represents all the orbitals in an atom. • An orbital is a region of space around the nucleus where an electron is likely to be found. • An electron cloud is a good approximation of how electrons behave in their orbitals. • The level in which an electron has the ...
Chapter 04 Atomic Theory Notes
... Atomic Orbitals • The electron cloud represents all the orbitals in an atom. • An orbital is a region of space around the nucleus where an electron is likely to be found. • An electron cloud is a good approximation of how electrons behave in their orbitals. • The level in which an electron has the ...
... Atomic Orbitals • The electron cloud represents all the orbitals in an atom. • An orbital is a region of space around the nucleus where an electron is likely to be found. • An electron cloud is a good approximation of how electrons behave in their orbitals. • The level in which an electron has the ...
Electrons in atoms practice test File
... ____ 12. If three electrons are available to fill three empty 2p atomic orbitals, how will the electrons be distributed in the three orbitals? a. one electron in each orbital b. two electrons in one orbital, one in another, none in the third c. three in one orbital, none in the other two d. Three el ...
... ____ 12. If three electrons are available to fill three empty 2p atomic orbitals, how will the electrons be distributed in the three orbitals? a. one electron in each orbital b. two electrons in one orbital, one in another, none in the third c. three in one orbital, none in the other two d. Three el ...
The average atomic mass of an element is the sum of the
... of protons in the nucleus of one atom. For example, the element hydrogen (the lightest element) will always have one proton in its nucleus. The element helium will always have two ...
... of protons in the nucleus of one atom. For example, the element hydrogen (the lightest element) will always have one proton in its nucleus. The element helium will always have two ...
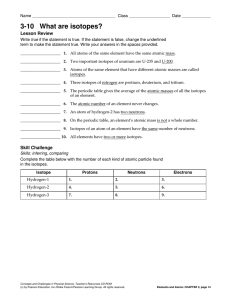
3-10 What are isotopes?
... reason for this? ____________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. According to the table, how are isotopes named? ______________________________________________ 6. What is true a ...
... reason for this? ____________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. According to the table, how are isotopes named? ______________________________________________ 6. What is true a ...
quantum number - WordPress.com
... numbers. Quantum numbers are basically used to describe certain aspects of the locations of electrons. For example, the quantum numbers n, l, and ml describe the position of the electron with respect to the nucleus, the shape of the orbital, and its special orientation, while the quantum number ms d ...
... numbers. Quantum numbers are basically used to describe certain aspects of the locations of electrons. For example, the quantum numbers n, l, and ml describe the position of the electron with respect to the nucleus, the shape of the orbital, and its special orientation, while the quantum number ms d ...
File
... (1) Rb (2) Ra (3) Re (4) Rn Which characteristics both generally decrease when the elements in Period 3 on the Periodic Table are considered in order from left to right? (1) nonmetallic properties and atomic radius (2) nonmetallic properties and ionization energy (3) metallic properties and atomic r ...
... (1) Rb (2) Ra (3) Re (4) Rn Which characteristics both generally decrease when the elements in Period 3 on the Periodic Table are considered in order from left to right? (1) nonmetallic properties and atomic radius (2) nonmetallic properties and ionization energy (3) metallic properties and atomic r ...
chapter5 - MrFoti.com
... the symbol of the element, the mass number and the atomic number. Mass number Atomic number ...
... the symbol of the element, the mass number and the atomic number. Mass number Atomic number ...
atomic number
... You know that neutrons are found in the nucleus of an atom. Under normal conditions, protons and neutrons stick together in the nucleus. During radioactive decay, they may be knocked out of there. Neutron numbers are able to change the mass of atoms, because they weigh about as much as a proton and ...
... You know that neutrons are found in the nucleus of an atom. Under normal conditions, protons and neutrons stick together in the nucleus. During radioactive decay, they may be knocked out of there. Neutron numbers are able to change the mass of atoms, because they weigh about as much as a proton and ...
Structure of an Atom
... protons and neutrons. These e particles are known as subatomic particles. Electrons: The negatively charged particles in an atom are called electrons. An electron has one unit negative charge. The mass of an electron is 1/1837 of the mass of hydrogen atom (lightest atom). Thus, electrons have a negl ...
... protons and neutrons. These e particles are known as subatomic particles. Electrons: The negatively charged particles in an atom are called electrons. An electron has one unit negative charge. The mass of an electron is 1/1837 of the mass of hydrogen atom (lightest atom). Thus, electrons have a negl ...
Name Period _____ Table _____ Vocabulary Log: ATOMS
... The particle of an atom with no charge. Most atoms have the same number of protons and neutrons, but some isotopes of an element have a different number of neutrons. (ALL atoms of an element will have the same number of protons.) ...
... The particle of an atom with no charge. Most atoms have the same number of protons and neutrons, but some isotopes of an element have a different number of neutrons. (ALL atoms of an element will have the same number of protons.) ...
Unit 5: Electrochemistry
... The substance that loses its electrons is oxidized and the one that gains electrons is reduced. From Ex. 1, Zn went from 0 to 2+ so it loses electrons and is oxidized. H goes from 1+ to 0 so it gains electrons and is reduced. ...
... The substance that loses its electrons is oxidized and the one that gains electrons is reduced. From Ex. 1, Zn went from 0 to 2+ so it loses electrons and is oxidized. H goes from 1+ to 0 so it gains electrons and is reduced. ...
atoms
... ago, scientists found that certain types of matter couldn’t be broken down into any other simpler substances They called these special pure substances: elements ...
... ago, scientists found that certain types of matter couldn’t be broken down into any other simpler substances They called these special pure substances: elements ...
Chapter 6: Electronic Structure of Atoms
... Explain how and why the energies of the orbitals are different in a many-electron atom from those in the hydrogen atom. Draw an energy-level diagram for the orbitals in a many-electron atom and describe how electrons populate the orbitals in the ground state of an atom, using the Pauli exclusion p ...
... Explain how and why the energies of the orbitals are different in a many-electron atom from those in the hydrogen atom. Draw an energy-level diagram for the orbitals in a many-electron atom and describe how electrons populate the orbitals in the ground state of an atom, using the Pauli exclusion p ...
internal geodynamics - Ninova
... • The idea of “element” as fundamental substance was first used by the Greek philosopher Empedocles (fl. ca. 450 BC) as rixwma (rixoma), meaning “stem, root, element.” He thought there were only four elements, namely air, water, earth, fire (the “anasır-ı erbaa” of the later Islamic philosophers an ...
... • The idea of “element” as fundamental substance was first used by the Greek philosopher Empedocles (fl. ca. 450 BC) as rixwma (rixoma), meaning “stem, root, element.” He thought there were only four elements, namely air, water, earth, fire (the “anasır-ı erbaa” of the later Islamic philosophers an ...
First Semester complete review with answers
... electron than to gain 7 electrons to get a full outer shell. When K gives up the electron, it has one more positive proton than negative electron. Potassium starts with 19 positive protons (+19) and 19 negative electron (-19). After it gives up the valence electron it still has 19 positive protons ( ...
... electron than to gain 7 electrons to get a full outer shell. When K gives up the electron, it has one more positive proton than negative electron. Potassium starts with 19 positive protons (+19) and 19 negative electron (-19). After it gives up the valence electron it still has 19 positive protons ( ...