Downloaded on 2017-02
... activation energy for proton transfer from the incoming H2 O molecule to the carbon of the remaining ligands is calculated (see SI Fig. 2). For the first incoming H2 O molecule in the H2 O pulse, Ea = 0.52 eV is required for its dissociation as it adsorbs (Table 1 reaction 5). Transfer of the proton ...
... activation energy for proton transfer from the incoming H2 O molecule to the carbon of the remaining ligands is calculated (see SI Fig. 2). For the first incoming H2 O molecule in the H2 O pulse, Ea = 0.52 eV is required for its dissociation as it adsorbs (Table 1 reaction 5). Transfer of the proton ...
15anespp
... • leaded petrol must not pass through the catalyst as the lead deposits on the catalyst’s surface and “poisons” it, thus blocking sites for reactions to take place. ...
... • leaded petrol must not pass through the catalyst as the lead deposits on the catalyst’s surface and “poisons” it, thus blocking sites for reactions to take place. ...
chemistry-c7-what-you-should
... I can recall that the feedstocks of nitrogen and hydrogen for the Haber process are made from air, natural gas and steam I in the context of the Haber process: a. I understand that the reaction between hydrogen and nitrogen to form ammonia is a reversible reaction b. I understand how the yield of am ...
... I can recall that the feedstocks of nitrogen and hydrogen for the Haber process are made from air, natural gas and steam I in the context of the Haber process: a. I understand that the reaction between hydrogen and nitrogen to form ammonia is a reversible reaction b. I understand how the yield of am ...
www.xtremepapers.net
... electrolysis, its mass increased by 0.216 g. How many atoms of silver were deposited per cm2 on the surface of the medal? ...
... electrolysis, its mass increased by 0.216 g. How many atoms of silver were deposited per cm2 on the surface of the medal? ...
Net ionic equation
... 2) Atoms in elemental forms have an oxidation number of 0. 3) Hydrogen has an oxidation number of +1 when bonded with nonmetals (molecular compounds) and -1 when combined with metals (ionic compounds). ...
... 2) Atoms in elemental forms have an oxidation number of 0. 3) Hydrogen has an oxidation number of +1 when bonded with nonmetals (molecular compounds) and -1 when combined with metals (ionic compounds). ...
0.08206 L atm/K mol - Arizona State University
... Potential energy increases and kinetic energy increases. Potential energy increases and kinetic energy decreases. Potential energy decreases and kinetic energy increases. Potential energy decreases and kinetic energy decreases. There is no change at all. ...
... Potential energy increases and kinetic energy increases. Potential energy increases and kinetic energy decreases. Potential energy decreases and kinetic energy increases. Potential energy decreases and kinetic energy decreases. There is no change at all. ...
5 organic chemistry: functional groups
... The longest chain contains the OOH group, which means the compound is named as a derivative of octane. Because it is an alcohol, it would be tempting to name it as an octanol. But it contains a CPC double bond, which means it must be an octenol. We now have to indicate that the OOH group is on one e ...
... The longest chain contains the OOH group, which means the compound is named as a derivative of octane. Because it is an alcohol, it would be tempting to name it as an octanol. But it contains a CPC double bond, which means it must be an octenol. We now have to indicate that the OOH group is on one e ...
Guide to Chapter 17. Thermodynamics
... predict what change occurs in DGo if the temperature is increased or decreased, i.e., does DGo become more positive or more negative. Learning Objective 18: Given values of DHo and DSo for a reaction, predict how temperature affects a reactions spontaneity. Learning Objective 19: Given a ...
... predict what change occurs in DGo if the temperature is increased or decreased, i.e., does DGo become more positive or more negative. Learning Objective 18: Given values of DHo and DSo for a reaction, predict how temperature affects a reactions spontaneity. Learning Objective 19: Given a ...
Word - Chemistry and More
... f) Is this reaction endothermic or exothermic? 12. (Chapter 9) Barium hydroxide precipitates when it is formed in a double replacement reaction. a) Write a balanced molecular equation for the formation of barium hydroxide precipitate from barium nitrate and sodium hydroxide. b) Calculate the mass of ...
... f) Is this reaction endothermic or exothermic? 12. (Chapter 9) Barium hydroxide precipitates when it is formed in a double replacement reaction. a) Write a balanced molecular equation for the formation of barium hydroxide precipitate from barium nitrate and sodium hydroxide. b) Calculate the mass of ...
2000 us national chemistry olympiad
... This test is designed to be taken with an answer sheet on which the student records his or her responses. All answers are to be marked on that sheet, not written in the booklet. Each student should be provided with an answer sheet and scratch paper, both of which must be turned in with the test book ...
... This test is designed to be taken with an answer sheet on which the student records his or her responses. All answers are to be marked on that sheet, not written in the booklet. Each student should be provided with an answer sheet and scratch paper, both of which must be turned in with the test book ...
Chemistry II Exams and Keys Corrected 2016 Season
... 11. Europium has two stable isotopes. A sample of elemental Eu is found to have 2.83034×1023 atoms of Eu-151. If elemental Europium is found to have a mass of 151.96 amu on earth, what is the natural abundance of Eu-153? A. 48.0 % B. 50.0 % C. 52.0 % D. 54.0% 12. The following figure depicts the two ...
... 11. Europium has two stable isotopes. A sample of elemental Eu is found to have 2.83034×1023 atoms of Eu-151. If elemental Europium is found to have a mass of 151.96 amu on earth, what is the natural abundance of Eu-153? A. 48.0 % B. 50.0 % C. 52.0 % D. 54.0% 12. The following figure depicts the two ...
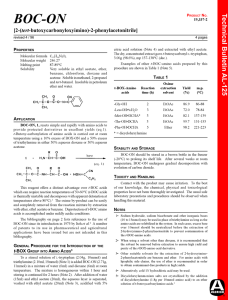
BOC-ON - Sigma
... is thermally unstable and decomposes with apparent detonation at temperatures above 80°C).1 The oxime by-product can be easily and completely removed from the reaction mixture by extraction with ether, ethyl acetate or benzene. Deprotection of t-BOC amino acids is accomplished under mildly acidic co ...
... is thermally unstable and decomposes with apparent detonation at temperatures above 80°C).1 The oxime by-product can be easily and completely removed from the reaction mixture by extraction with ether, ethyl acetate or benzene. Deprotection of t-BOC amino acids is accomplished under mildly acidic co ...
fulltext
... turn into a semi solid (an omelette6) whereas many other compounds or solutions thereof typically melt or lower in viscosity. This is a result of unfolding and subsequent aggregation of the protein chains. Looking at proteins in micro scale also yields fascinating findings. An enzyme is able to bind ...
... turn into a semi solid (an omelette6) whereas many other compounds or solutions thereof typically melt or lower in viscosity. This is a result of unfolding and subsequent aggregation of the protein chains. Looking at proteins in micro scale also yields fascinating findings. An enzyme is able to bind ...
hong kong diploma of secondary education examination
... The plunger is quickly pushed from position A to position B at time t while the temperature of the mixture is kept constant. Which of the following graphs represents how the concentration of NO2(g) in the mixture varies until a new state of equilibrium is established? ...
... The plunger is quickly pushed from position A to position B at time t while the temperature of the mixture is kept constant. Which of the following graphs represents how the concentration of NO2(g) in the mixture varies until a new state of equilibrium is established? ...
Section 2 Types of Chemical Reactions
... Write word and formula equations for the chemical reaction that occurs when solid sodium oxide is added to water at room temperature and forms sodium hydroxide (dissolved in the water). Include symbols for physical states in the formula equation. Then balance the formula equation to give a balanced ...
... Write word and formula equations for the chemical reaction that occurs when solid sodium oxide is added to water at room temperature and forms sodium hydroxide (dissolved in the water). Include symbols for physical states in the formula equation. Then balance the formula equation to give a balanced ...
Chapter 9 – Reaction Energetics
... determining how much energy must be supplied to break all of the interactions that had to be broken and subtracting the energy that is released when all of the new interactions form. Bond energies give us estimates of these energies, but tabulated bond energies are averages. For example, a C-Cl bond ...
... determining how much energy must be supplied to break all of the interactions that had to be broken and subtracting the energy that is released when all of the new interactions form. Bond energies give us estimates of these energies, but tabulated bond energies are averages. For example, a C-Cl bond ...
answers to part a of the national high school
... These answers are designed to help students who are preparing to take the Canadian National High School Chemistry Examination in 2007 or subsequent years. Note that information given here will generally not include material from answers given for previous years exams, so that students should go thr ...
... These answers are designed to help students who are preparing to take the Canadian National High School Chemistry Examination in 2007 or subsequent years. Note that information given here will generally not include material from answers given for previous years exams, so that students should go thr ...
Honors Chemistry Unit 4 Student Packet: Honors Chemistry Problem
... a. Determine the limiting reactant if 13.5 g of aluminum react with 0.72 moles of iodine. b. What is the maximum amount of aluminum iodide that could be formed from this reaction? c. What if the percent yield if only 188 g of aluminum iodide is formed? 10. In a reaction between zinc and hydrochloric ...
... a. Determine the limiting reactant if 13.5 g of aluminum react with 0.72 moles of iodine. b. What is the maximum amount of aluminum iodide that could be formed from this reaction? c. What if the percent yield if only 188 g of aluminum iodide is formed? 10. In a reaction between zinc and hydrochloric ...
Unit 8: Reactions - Mark Rosengarten
... An insoluble solid that is formed either in a double-replacement reaction or as excess solute added to a saturated solution. The substances that are formed by a chemical reaction, designated as the right side of a chemical equation. The substances that are reacted together, designated as the left si ...
... An insoluble solid that is formed either in a double-replacement reaction or as excess solute added to a saturated solution. The substances that are formed by a chemical reaction, designated as the right side of a chemical equation. The substances that are reacted together, designated as the left si ...
Reaction Stoichiometry
... Chlorobenzene, C6H5Cl, is used in the production of many important chemicals, such as aspirin, dyes, and disinfectants. One industrial method of preparing chlorobenzene is to react benzene, C6H6, with chlorine. C6H6(l) + Cl2(g) → C6H5Cl(l) + HCl(g) When 36.8 g benzene react with an excess of Cl2, th ...
... Chlorobenzene, C6H5Cl, is used in the production of many important chemicals, such as aspirin, dyes, and disinfectants. One industrial method of preparing chlorobenzene is to react benzene, C6H6, with chlorine. C6H6(l) + Cl2(g) → C6H5Cl(l) + HCl(g) When 36.8 g benzene react with an excess of Cl2, th ...
Chemistry
... Nomenclature of benzene derivatives. Aromatic nucleus and side chain. Structure of benzene: Molecular formula and Kekule’s structure. Stability and carbon-carbon bond lengths of benzene, resonance structure, MO picture. Aromaticity: Huckel rule, aromatic ions, Aromatic electrophilic substitution –Me ...
... Nomenclature of benzene derivatives. Aromatic nucleus and side chain. Structure of benzene: Molecular formula and Kekule’s structure. Stability and carbon-carbon bond lengths of benzene, resonance structure, MO picture. Aromaticity: Huckel rule, aromatic ions, Aromatic electrophilic substitution –Me ...
Unit 4 - Calculations and Chemical Reactions
... chemical reactions. One approach is to classify reactions into four types: combination, decomposition, single replacement and double replacement reactions. I) Combination Reactions In a combination reaction, two or more substances react to form a single product. The general form of this reaction is ...
... chemical reactions. One approach is to classify reactions into four types: combination, decomposition, single replacement and double replacement reactions. I) Combination Reactions In a combination reaction, two or more substances react to form a single product. The general form of this reaction is ...
Cheat Sheet for Chemical Equilibrium
... • Given: Initial Concentrations and asked whether a precipitate will form: Calculate Q (no ICE chart needed) and compare with Ksp: o Q>Ksp, precipitate will form o Q=Ksp, at equilibrium o Q
... • Given: Initial Concentrations and asked whether a precipitate will form: Calculate Q (no ICE chart needed) and compare with Ksp: o Q>Ksp, precipitate will form o Q=Ksp, at equilibrium o Q
Lewis acid catalysis
In Lewis acid catalysis of organic reactions, a metal-based Lewis acid acts as an electron pair acceptor to increase the reactivity of a substrate. Common Lewis acid catalysts are based on main group metals such as aluminum, boron, silicon, and tin, as well as many early (titanium, zirconium) and late (iron, copper, zinc) d-block metals. The metal atom forms an adduct with a lone-pair bearing electronegative atom in the substrate, such as oxygen (both sp2 or sp3), nitrogen, sulfur, and halogens. The complexation has partial charge-transfer character and makes the lone-pair donor effectively more electronegative, activating the substrate toward nucleophilic attack, heterolytic bond cleavage, or cycloaddition with 1,3-dienes and 1,3-dipoles.Many classical reactions involving carbon–carbon or carbon–heteroatom bond formation can be catalyzed by Lewis acids. Examples include the Friedel-Crafts reaction, the aldol reaction, and various pericyclic processes that proceed slowly at room temperature, such as the Diels-Alder reaction and the ene reaction. In addition to accelerating the reactions, Lewis acid catalysts are able to impose regioselectivity and stereoselectivity in many cases.Early developments in Lewis acid reagents focused on easily available compounds such as TiCl4, BF3, SnCl4, and AlCl3. The relative strengths of these (and other) Lewis acids may be estimated from NMR spectroscopy by the Childs method or the Gutmann-Beckett method. Over the years, versatile catalysts bearing ligands designed for specific applications have facilitated improvement in both reactivity and selectivity of Lewis acid-catalyzed reactions. More recently, Lewis acid catalysts with chiral ligands have become an important class of tools for asymmetric catalysis.Challenges in the development of Lewis acid catalysis include inefficient catalyst turnover (caused by catalyst affinity for the product) and the frequent requirement of two-point binding for stereoselectivity, which often necessitates the use of auxiliary groups.